MAGNETIC FORCE ON A MOVING CHARGE – 1302Lab5Prob8
... Review the magnetic field map from the Helmholtz Coils. Does it matter what direction the currents flows in the two Helmholtz coils? Should it be in the same direction or opposite directions? Ensure to send currents in the coils accordingly. Set up your Hall probe as explained in the Equipment and S ...
... Review the magnetic field map from the Helmholtz Coils. Does it matter what direction the currents flows in the two Helmholtz coils? Should it be in the same direction or opposite directions? Ensure to send currents in the coils accordingly. Set up your Hall probe as explained in the Equipment and S ...
HighFour General Sciences Round 6 Category A: Grades 4 – 5
... by both a direction and a magnitude (or strength); as such it is a vector field. B Magnetism is one aspect of the combined electromagnetic force. It refers to physical phenomena arising from the ...
... by both a direction and a magnitude (or strength); as such it is a vector field. B Magnetism is one aspect of the combined electromagnetic force. It refers to physical phenomena arising from the ...
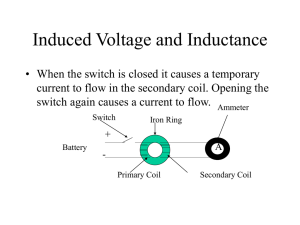
Induced Voltage and Inductance
... Lenz’s Law • Lenz’s law states that the direction of the induced emf is such that if an induced current were able to flow, it oppose the change that causes it. • In the above diagram as the bar moves to the right the flux is increased into the page. To offset this the induced current must flow coun ...
... Lenz’s Law • Lenz’s law states that the direction of the induced emf is such that if an induced current were able to flow, it oppose the change that causes it. • In the above diagram as the bar moves to the right the flux is increased into the page. To offset this the induced current must flow coun ...
path to electron - FSU High Energy Physics
... Ignores the model previously proposed for the ether, but keeps the mathematical treatment; Asserts that equations valid without any assumptions about nature of medium equations “Maxwell’s equations” describe interplay between electric and magnetic fields and their relation to charges and currents M. ...
... Ignores the model previously proposed for the ether, but keeps the mathematical treatment; Asserts that equations valid without any assumptions about nature of medium equations “Maxwell’s equations” describe interplay between electric and magnetic fields and their relation to charges and currents M. ...
The Magnetic Field
... terms of the magnetic force FB that the field exerts on a charged particle moving with a velocity v. • Experiments on charged particles moving in a magnetic field give the following results: – The magnitude FB of the magnetic force exerted on the particle is proportional to the magnitude of the char ...
... terms of the magnetic force FB that the field exerts on a charged particle moving with a velocity v. • Experiments on charged particles moving in a magnetic field give the following results: – The magnitude FB of the magnetic force exerted on the particle is proportional to the magnitude of the char ...
PowerPoint
... cannot change a charged particle’s potential energy or electric potential. But electric fields can do work. This equation shows that a changing magnetic flux induces an electric field, which can change a charged particle’s potential energy. This induced electric field is responsible for induced emf. ...
... cannot change a charged particle’s potential energy or electric potential. But electric fields can do work. This equation shows that a changing magnetic flux induces an electric field, which can change a charged particle’s potential energy. This induced electric field is responsible for induced emf. ...
Electromagnetic Frequencies and Direct Current Transmission
... detect the static magnetic field of the earth. Would the proposed Project be likely to affect animals that might spend more time near the DC line than do people? A. Studies of cattle have not provided any clear evidence that they detect variations in the earth’s geomagnetic field. Multiple studies ...
... detect the static magnetic field of the earth. Would the proposed Project be likely to affect animals that might spend more time near the DC line than do people? A. Studies of cattle have not provided any clear evidence that they detect variations in the earth’s geomagnetic field. Multiple studies ...
current fuction usage for current lines construction in 2d models
... along the inhomogeneities' strike direction. In this case both the medium and the electric field depend on two space coordinates only. Modeling becomes much easier than considering point current electrodes, where the electrical field always is three-dimensional. Meanwhile the actual results of such ...
... along the inhomogeneities' strike direction. In this case both the medium and the electric field depend on two space coordinates only. Modeling becomes much easier than considering point current electrodes, where the electrical field always is three-dimensional. Meanwhile the actual results of such ...
Presentation - Dagotto Group
... a simple Weiss mean field theory that studies the collective distribution of magnetic moments as a single continuous field This is an approximation of the Zener model for the local (p-d) exchange coupling between the impurity magnetic moment, S 5/2 d levels of Mn and the itinerant carrier spin polar ...
... a simple Weiss mean field theory that studies the collective distribution of magnetic moments as a single continuous field This is an approximation of the Zener model for the local (p-d) exchange coupling between the impurity magnetic moment, S 5/2 d levels of Mn and the itinerant carrier spin polar ...
Superconducting magnet
A superconducting magnet is an electromagnet made from coils of superconducting wire. They must be cooled to cryogenic temperatures during operation. In its superconducting state the wire can conduct much larger electric currents than ordinary wire, creating intense magnetic fields. Superconducting magnets can produce greater magnetic fields than all but the strongest electromagnets and can be cheaper to operate because no energy is dissipated as heat in the windings. They are used in MRI machines in hospitals, and in scientific equipment such as NMR spectrometers, mass spectrometers and particle accelerators.