Chapter 19 Magnetism
... the thermal motion immediately destroys any magnetic alignment. Lava flows “freeze” a record of the Earth’s magnetic field at the point where they cooled below the Curie temperature. In this way, historical values of the Earth’s field may be determined. ...
... the thermal motion immediately destroys any magnetic alignment. Lava flows “freeze” a record of the Earth’s magnetic field at the point where they cooled below the Curie temperature. In this way, historical values of the Earth’s field may be determined. ...
1B11 Foundations of Astronomy Star names and magnitudes
... •These “separate” plasma cells are partitioned by thin current sheets, which support the change in magnetic fields across the boundary. Recall: ...
... •These “separate” plasma cells are partitioned by thin current sheets, which support the change in magnetic fields across the boundary. Recall: ...
magnetism - Sakshi Education
... i) When a magnet with magnetic moment M is suspended in a uniform field of induction B at an angle θ with the field direction then the couple acting on the magnet, C = MB sinθ and vectorially C = M × B ii) When θ = 90° C is maximum. If | C max |= MB. If θ = 90° and B = 1 Cmax = M iii) When θ = 0° C ...
... i) When a magnet with magnetic moment M is suspended in a uniform field of induction B at an angle θ with the field direction then the couple acting on the magnet, C = MB sinθ and vectorially C = M × B ii) When θ = 90° C is maximum. If | C max |= MB. If θ = 90° and B = 1 Cmax = M iii) When θ = 0° C ...
electromagnetism guide
... Television, cable, or satellite rights are also available, but must be negotiated with the Visual Learning Company. Closed circuit rights are available, and are defined as the use of the program beyond a single classroom but within a single campus. Institutions wishing to utilize the program in mult ...
... Television, cable, or satellite rights are also available, but must be negotiated with the Visual Learning Company. Closed circuit rights are available, and are defined as the use of the program beyond a single classroom but within a single campus. Institutions wishing to utilize the program in mult ...
Development of Land Adjacent to or within the
... transmission lines are defined as overhead or underground powerlines that carry 110kV (kilovolts) or greater. EMFs occur everywhere. The human body produces EMFs as nerve impulses, which are transferred through the body. However, they are very weak. The Earth has an EMF (its magnetic field) which is ...
... transmission lines are defined as overhead or underground powerlines that carry 110kV (kilovolts) or greater. EMFs occur everywhere. The human body produces EMFs as nerve impulses, which are transferred through the body. However, they are very weak. The Earth has an EMF (its magnetic field) which is ...
chapter-23
... There are 3 ways to change the magnetic flux through the coil: 1. Change the strength of the magnetic field at the plane of the coil. 2. Change the angle (orientation) of the coil, with respect to the magnetic field. 3. Change the area of the coil. ...
... There are 3 ways to change the magnetic flux through the coil: 1. Change the strength of the magnetic field at the plane of the coil. 2. Change the angle (orientation) of the coil, with respect to the magnetic field. 3. Change the area of the coil. ...
MAPWORK CALCULATIONS 10 APRIL 2014
... What is north? True North: (also known as Geographic North or Map North - marked as N on a topographic map - is the geographic North Pole where all longitude lines meet. All maps are laid out with true north directly at the top. Unfortunately for the wilderness traveller, true north is not at the sa ...
... What is north? True North: (also known as Geographic North or Map North - marked as N on a topographic map - is the geographic North Pole where all longitude lines meet. All maps are laid out with true north directly at the top. Unfortunately for the wilderness traveller, true north is not at the sa ...
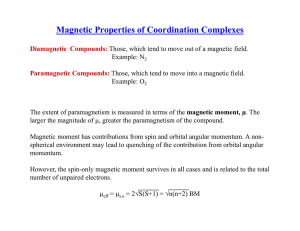
Magnetic Properties of Coordination Complexes √ √ μ
... Total unpaired electrons = 1, S = 1/2 Oxygenated form is low-spin The magnetic moment of Fe3+ and the superoxide radical involves in antiferromagnetic coupling and the oxygenated complex is not paramagnetic ...
... Total unpaired electrons = 1, S = 1/2 Oxygenated form is low-spin The magnetic moment of Fe3+ and the superoxide radical involves in antiferromagnetic coupling and the oxygenated complex is not paramagnetic ...
Alternating current
... in the United States both found that moving a loop of wire through a magnetic field caused an electric current to flow in the wire. • They also found that moving a magnet through a loop of wire produces a current. • The magnet and wire loop must be moving relative to each other for an electric curre ...
... in the United States both found that moving a loop of wire through a magnetic field caused an electric current to flow in the wire. • They also found that moving a magnet through a loop of wire produces a current. • The magnet and wire loop must be moving relative to each other for an electric curre ...
Superconducting magnet
A superconducting magnet is an electromagnet made from coils of superconducting wire. They must be cooled to cryogenic temperatures during operation. In its superconducting state the wire can conduct much larger electric currents than ordinary wire, creating intense magnetic fields. Superconducting magnets can produce greater magnetic fields than all but the strongest electromagnets and can be cheaper to operate because no energy is dissipated as heat in the windings. They are used in MRI machines in hospitals, and in scientific equipment such as NMR spectrometers, mass spectrometers and particle accelerators.