A hormone is a chemical substance. It helps different parts of an
... 1. A hormone is a chemical substance. It helps different parts of an organism to function in a coordinated way. 2. The endocrine system works with the nervous system to maintain homeostasis (balance) in the body. The glands and organs regulate and control body functions such a growth and development ...
... 1. A hormone is a chemical substance. It helps different parts of an organism to function in a coordinated way. 2. The endocrine system works with the nervous system to maintain homeostasis (balance) in the body. The glands and organs regulate and control body functions such a growth and development ...
Thyroid gland
... 4. Dilation of bronchioles 5. Changes in blood flow patterns leading to decreased digestive system activity and reduced urine output 6. Increased metabolic rate ...
... 4. Dilation of bronchioles 5. Changes in blood flow patterns leading to decreased digestive system activity and reduced urine output 6. Increased metabolic rate ...
Name
... The heart’s pacemaker is located in the __SA___________ node of the __right_____ atrium. Impulses arising in this structure spread through the two atria, causing the _P_ wave of the EKG. The wave of excitation then arrives at the __AV____ node and spreads from there into the Bundle of His, which bra ...
... The heart’s pacemaker is located in the __SA___________ node of the __right_____ atrium. Impulses arising in this structure spread through the two atria, causing the _P_ wave of the EKG. The wave of excitation then arrives at the __AV____ node and spreads from there into the Bundle of His, which bra ...
Lesson 8.2 Major Endocrine Organs
... fright) has a critical effect. It causes the release of the hormone adrenalin (epinephrine) from the interior of the adrenal glands. The adrenal glands are located on top of the kidneys. The noradrenalin and the adrenalin initiate and sustain what is known as the ‘Fight or Flight” response. They pre ...
... fright) has a critical effect. It causes the release of the hormone adrenalin (epinephrine) from the interior of the adrenal glands. The adrenal glands are located on top of the kidneys. The noradrenalin and the adrenalin initiate and sustain what is known as the ‘Fight or Flight” response. They pre ...
Endocrine
... Negative Feedback Mechanism Involved in Control of Blood Calcium The presence of calcium ions is critical to the functioning of all cells. In mammals, the two hormones parathyroid hormone and calcitonin regulate and stabilize the blood calcium level at about 10 mg/100 mL. When blood calcium levels f ...
... Negative Feedback Mechanism Involved in Control of Blood Calcium The presence of calcium ions is critical to the functioning of all cells. In mammals, the two hormones parathyroid hormone and calcitonin regulate and stabilize the blood calcium level at about 10 mg/100 mL. When blood calcium levels f ...
Regulatory systems
... hormone (ADH). ADH is produced in hypothalamus of the brain and stored in and released from the pituitary gland, which lies just below the hypothalamus. Osmoreceptor cells in the hypothalamus monitor the osmolarity of the blood. • When blood osmolarity rises above a set point of 300 mosm/L, more ADH ...
... hormone (ADH). ADH is produced in hypothalamus of the brain and stored in and released from the pituitary gland, which lies just below the hypothalamus. Osmoreceptor cells in the hypothalamus monitor the osmolarity of the blood. • When blood osmolarity rises above a set point of 300 mosm/L, more ADH ...
List of Hormones to Know ANSWERS
... Regulates sleep/wake cycles (circadian rhythm) stimulates immunological activity of lymphoid tissue promotes reabsorption of Na+ ions – water follows which increases blood volume and blood pressure heart beats faster and stronger blood shunted away from skin and viscera to the skeletal muscles, brai ...
... Regulates sleep/wake cycles (circadian rhythm) stimulates immunological activity of lymphoid tissue promotes reabsorption of Na+ ions – water follows which increases blood volume and blood pressure heart beats faster and stronger blood shunted away from skin and viscera to the skeletal muscles, brai ...
The regulation of blood glucose
... sugar levels. The most well known is adrenaline • Produced in adrenal glands (above kidneys) •It raises blood glucose by: Activating an enzyme that causes breakdown of glycogen to glucose in the liver Inactivating an enzyme that synthesises glycogen from glucose ...
... sugar levels. The most well known is adrenaline • Produced in adrenal glands (above kidneys) •It raises blood glucose by: Activating an enzyme that causes breakdown of glycogen to glucose in the liver Inactivating an enzyme that synthesises glycogen from glucose ...
The Endocrine System
... – T4 (thyroxine): major form that consists of two tyrosine molecules with four bound iodine atoms – T3 (triiodothyronine): form that has two tyrosines with three bound iodine atoms • Must be converted to T4 at tissue level ...
... – T4 (thyroxine): major form that consists of two tyrosine molecules with four bound iodine atoms – T3 (triiodothyronine): form that has two tyrosines with three bound iodine atoms • Must be converted to T4 at tissue level ...
Lecture topics - Austin Community College
... 1. location – median inferior brain 2. basic structure – individual nuclei 3. hormones and their functions a. regulatory hormones control (increase or decrease) the secretion of anterior pituitary hormones b. antidiuretic hormone (ADH) secreted in response to increased blood osmotic pressure act ...
... 1. location – median inferior brain 2. basic structure – individual nuclei 3. hormones and their functions a. regulatory hormones control (increase or decrease) the secretion of anterior pituitary hormones b. antidiuretic hormone (ADH) secreted in response to increased blood osmotic pressure act ...
Ch 15 ANS - Lake–Sumter State College
... of activity that represents the balance of the two systems ...
... of activity that represents the balance of the two systems ...
Glossary
... flow in the body. Constriction of arterioles therefore increases the blood pressure, just like tightening the nozzle increase the pressure in a garden hose. Asphyxiation Loss of consciousness from lack of breathing, such as in suffocation. Aspiration Inhalation of a foreign body into the airway. Aut ...
... flow in the body. Constriction of arterioles therefore increases the blood pressure, just like tightening the nozzle increase the pressure in a garden hose. Asphyxiation Loss of consciousness from lack of breathing, such as in suffocation. Aspiration Inhalation of a foreign body into the airway. Aut ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... HORMONES AND THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Chapter 45 The glands of the endocrine system secrete hormones that send a stimulus to another cell. The response that is elicited by the target cell helps bring the organism back to homeostasis ...
... HORMONES AND THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Chapter 45 The glands of the endocrine system secrete hormones that send a stimulus to another cell. The response that is elicited by the target cell helps bring the organism back to homeostasis ...
The Endocrine System
... • The thyroid gland – TSH which stimulates thyroid to produce T3 and T4 (metabolic rates) • Stimulate all body cells • More glucose is utilized to form ATP • Necessary for normal growth and nervous system function – Thyroid requires iodine to produce these hormones • A deficiency of iodine causes a ...
... • The thyroid gland – TSH which stimulates thyroid to produce T3 and T4 (metabolic rates) • Stimulate all body cells • More glucose is utilized to form ATP • Necessary for normal growth and nervous system function – Thyroid requires iodine to produce these hormones • A deficiency of iodine causes a ...
The Endocrine System (Chap 11)
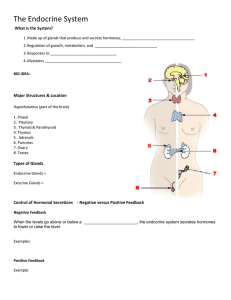
... What is the System? 1. Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones, ___________________________________ 2. Regulation of growth, metabolism, and ______________________________ 3. Responses to ________________________________ ...
... What is the System? 1. Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones, ___________________________________ 2. Regulation of growth, metabolism, and ______________________________ 3. Responses to ________________________________ ...
23 Comp Review 2
... The sound your heart makes when it is beating is the sound of the blood hitting the valves after they are closed. The heart normally beats at a rate of 60-80 beats per minute. A faster (tachycardia) or slower (bradycardia) heart rate is an indication of a problem. ...
... The sound your heart makes when it is beating is the sound of the blood hitting the valves after they are closed. The heart normally beats at a rate of 60-80 beats per minute. A faster (tachycardia) or slower (bradycardia) heart rate is an indication of a problem. ...
The Endocrine System and Homeostasis
... Stimulates the distal and collecting tubules of the kidneys to increase the absorption of sodium into the bloodstream. This increases the solute concentration of the blood, which then draws in more water from the nephrons, raising blood pressure. Addison’s disease can result, if the adrenal cortex i ...
... Stimulates the distal and collecting tubules of the kidneys to increase the absorption of sodium into the bloodstream. This increases the solute concentration of the blood, which then draws in more water from the nephrons, raising blood pressure. Addison’s disease can result, if the adrenal cortex i ...
Stress Psychophysiology Introduction The Brain
... Actions of the Adrenal Gland (outside part) • Influenced by ACTH, the adrenal cortex (outer portion of the adrenal gland) will release two types of hormones, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. • The primary glucocorticoid is cortisol, which is responsible for providing the body with increased e ...
... Actions of the Adrenal Gland (outside part) • Influenced by ACTH, the adrenal cortex (outer portion of the adrenal gland) will release two types of hormones, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. • The primary glucocorticoid is cortisol, which is responsible for providing the body with increased e ...
Stress and the Body`s Response
... Myocardial ischemia- coronary arteries normally dilate in response to stress ...
... Myocardial ischemia- coronary arteries normally dilate in response to stress ...
HORMONE HALL OF FAME – Rev. 11/12/12 based on V9
... Gluconeogenesis from lactic acid and noncarboydrates Helps keep blood glucose up to its normal level between meals by 1) causing cells to make glucose from lipids and proteins and 2) causing cells to burn more FAs and less glucose. Excessive levels are anti-inflammatory, depress the normal functioni ...
... Gluconeogenesis from lactic acid and noncarboydrates Helps keep blood glucose up to its normal level between meals by 1) causing cells to make glucose from lipids and proteins and 2) causing cells to burn more FAs and less glucose. Excessive levels are anti-inflammatory, depress the normal functioni ...
Unit 4 Review Key pg. 570
... been interfered with by hormones produced during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes usually does not occur until later in pregnancy, when the placenta is producing more of the hormones that interfere with the mother’s insulin. 79. (a) These observations demonstrate the all-or-nothing response principle ...
... been interfered with by hormones produced during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes usually does not occur until later in pregnancy, when the placenta is producing more of the hormones that interfere with the mother’s insulin. 79. (a) These observations demonstrate the all-or-nothing response principle ...
1) - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... 21) Most often, the kidney is confused with the __________ when viewed superficially. A) gallbladder B) urinary bladder C) liver D) spleen E) pancreas 22) A glomerulus A) is a capillary knot contained within the renal corpuscle. B) occurs in the loop of Henle. C) filters urine just prior to its exit ...
... 21) Most often, the kidney is confused with the __________ when viewed superficially. A) gallbladder B) urinary bladder C) liver D) spleen E) pancreas 22) A glomerulus A) is a capillary knot contained within the renal corpuscle. B) occurs in the loop of Henle. C) filters urine just prior to its exit ...
Ch 17 PowerPoint - Damien Rutkoski
... hormone into the bloodstream to regulate the body the body’s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells ...
... hormone into the bloodstream to regulate the body the body’s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells ...
Cardiac physiology

Cardiac physiology or heart function is the study of healthy, unimpaired function of the heart: involving blood flow; myocardium structure; the electrical conduction system of the heart; the cardiac cycle and cardiac output and how these interact and depend on one another.