Endocrinology_2
... Hormones: thyroxine and triiodothyronine. Have similar actions but T3 is five times more potent. They help regulate the metabolism of carbs, lipids, and proteins and increase the rate at which cells release energy from carbs, the rate of protein synthesis, and stimulate breakdown and mobilization ...
... Hormones: thyroxine and triiodothyronine. Have similar actions but T3 is five times more potent. They help regulate the metabolism of carbs, lipids, and proteins and increase the rate at which cells release energy from carbs, the rate of protein synthesis, and stimulate breakdown and mobilization ...
Ch 11 The Endocrine System
... THYROID HORMONES ● Thyroxin (T4) & Tri-iodothyronine (T3) both increase the rate at which cells release energy from carbohydrates ● Calcitonin – regulates the blood concentration of calcium • BMR – basal metabolic rate : how many calories the body must consume to maintain life ...
... THYROID HORMONES ● Thyroxin (T4) & Tri-iodothyronine (T3) both increase the rate at which cells release energy from carbohydrates ● Calcitonin – regulates the blood concentration of calcium • BMR – basal metabolic rate : how many calories the body must consume to maintain life ...
Endocrine System
... THYROID HORMONES • Thyroxin (T4) & Tri-iodothyronine (T3) both increase the rate at which cells release energy from carbohydrates • Calcitonin – regulates the blood concentration of calcium • BMR – basal metabolic rate : how many calories the body must consume to maintain life ...
... THYROID HORMONES • Thyroxin (T4) & Tri-iodothyronine (T3) both increase the rate at which cells release energy from carbohydrates • Calcitonin – regulates the blood concentration of calcium • BMR – basal metabolic rate : how many calories the body must consume to maintain life ...
Endocrine System - WCED: Curriculum Development
... Posterior lobe releases: •ADH (Anti-diuretic hormone) ...
... Posterior lobe releases: •ADH (Anti-diuretic hormone) ...
Physiology is an Integrated Science
... learning goals for each hormone – know: it’s effects , functions what stim its release where is it made its target organs ...
... learning goals for each hormone – know: it’s effects , functions what stim its release where is it made its target organs ...
The Endocrine System
... Thyroid helps with calcium • The thyroid gland also helps with calcium regulation • It secretes calcitonin, which decreases level of blood calcium by encouraging the kidney to excrete calcium and inhibiting osteoclasts • PTH and calcitonin are opposites ...
... Thyroid helps with calcium • The thyroid gland also helps with calcium regulation • It secretes calcitonin, which decreases level of blood calcium by encouraging the kidney to excrete calcium and inhibiting osteoclasts • PTH and calcitonin are opposites ...
11. Principal Glands
... • It has both an exocrine and endocrine function • Its specialized cells produce digestive enzymes which are released to the small intestine through the pancreatic duct (exocrine function). • It also contains clusters of cells called Islets of Langerhans which produce two hormones – insulin and gluc ...
... • It has both an exocrine and endocrine function • Its specialized cells produce digestive enzymes which are released to the small intestine through the pancreatic duct (exocrine function). • It also contains clusters of cells called Islets of Langerhans which produce two hormones – insulin and gluc ...
15.3
... tissues and bone begin to grow by increasing the number of cells (hyperplasia) and increasing the size of ...
... tissues and bone begin to grow by increasing the number of cells (hyperplasia) and increasing the size of ...
Endocrine Glands - Dr. Annette M. Parrott
... (PTH) – Stimulates osteoclasts to free Ca2+ from bone – Stimulates Ca2+ uptake from intestine & kindey ...
... (PTH) – Stimulates osteoclasts to free Ca2+ from bone – Stimulates Ca2+ uptake from intestine & kindey ...
the autonomic nervous system (ANS)
... Q/the adrenal medulla can be classified as part of sympathetic nervous system. Why? because its innervation comes through the sympathetic nerves preganglionic segments that arise from the intermediolateral horns of the spinal cord to the adrenal medulla, and the cells of the adrenal medulla are cons ...
... Q/the adrenal medulla can be classified as part of sympathetic nervous system. Why? because its innervation comes through the sympathetic nerves preganglionic segments that arise from the intermediolateral horns of the spinal cord to the adrenal medulla, and the cells of the adrenal medulla are cons ...
Chapter 1 A Perspective on Human Genetics
... Diabetes Mellitus • Most common of all endocrine disorders • Prominent feature is elevated blood glucose levels – Urine acquires sweetness from excess blood glucose that spills into urine • Two major types – Type I diabetes • Characterized by lack of insulin secretion ...
... Diabetes Mellitus • Most common of all endocrine disorders • Prominent feature is elevated blood glucose levels – Urine acquires sweetness from excess blood glucose that spills into urine • Two major types – Type I diabetes • Characterized by lack of insulin secretion ...
File - Patricia Schwandt Courses
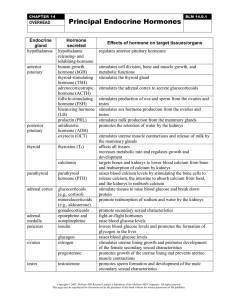
... stimulates milk production from the mammary glands promotes the retention of water by the kidneys stimulates uterine muscle contractions and release of milk by the mammary glands affects all tissues increases metabolic rate and regulates growth and development targets bones and kidneys to lower bloo ...
... stimulates milk production from the mammary glands promotes the retention of water by the kidneys stimulates uterine muscle contractions and release of milk by the mammary glands affects all tissues increases metabolic rate and regulates growth and development targets bones and kidneys to lower bloo ...
File
... decreased in fasting animals and increased when fasting animals are re-fed. These changes may explain the decrease in blood pressure and metabolic rate produced by fasting and the opposite changes produced by feeding. Sympathetic and parasympathetic tone: Normally, the sympathetic and parasympatheti ...
... decreased in fasting animals and increased when fasting animals are re-fed. These changes may explain the decrease in blood pressure and metabolic rate produced by fasting and the opposite changes produced by feeding. Sympathetic and parasympathetic tone: Normally, the sympathetic and parasympatheti ...
Lab 9: Endocrine System
... • Hormones – Insulin- increases uptake of glucose by cells – Glucagon- increases release of glucose by cells and increases liver glucose production • Released in response to… – Insulin: high blood glucose levels – Glucagon: low blood glucose levels ...
... • Hormones – Insulin- increases uptake of glucose by cells – Glucagon- increases release of glucose by cells and increases liver glucose production • Released in response to… – Insulin: high blood glucose levels – Glucagon: low blood glucose levels ...
19_endocrine
... Effect of thyroid hormones – increase energy utilization, oxygen consumption, growth, development Thyroid hormone release is controlled by TSH from the anterior pituitary ...
... Effect of thyroid hormones – increase energy utilization, oxygen consumption, growth, development Thyroid hormone release is controlled by TSH from the anterior pituitary ...
Hormones: definition - a chemical signal released into body fluids
... definition - a chemical signal released into body fluids. Generally this regulates or causes a specific action. Usually, only specific cells known as target cells will respond, but some hormones can affect many different systems: A simple example: Adrenal gland -> epinephrine -> ...
... definition - a chemical signal released into body fluids. Generally this regulates or causes a specific action. Usually, only specific cells known as target cells will respond, but some hormones can affect many different systems: A simple example: Adrenal gland -> epinephrine -> ...
enodcrine newer - ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
... 95% of hormonal activity is due to cortisol Functions = help regulate metabolism a) increase rate of protein catabolism & lipolysis b) conversion of amino & fatty acids to glucose c) provide resistance to stress by making ...
... 95% of hormonal activity is due to cortisol Functions = help regulate metabolism a) increase rate of protein catabolism & lipolysis b) conversion of amino & fatty acids to glucose c) provide resistance to stress by making ...
File
... &pain ( Ibuprofin and aspirin inhibit) • Blood: regulate aggregation of platelets involved in blood clotting • Help protect the lining of the stomach ...
... &pain ( Ibuprofin and aspirin inhibit) • Blood: regulate aggregation of platelets involved in blood clotting • Help protect the lining of the stomach ...
Hormonal
... Same as nervous system: communication and control Slower acting than nervous system Effects are longer lasting Hormones Chemicals that influence or control the activity of a specific tissue or organ Secreted by endocrine glands directly into blood or lymph Exocrine glands secrete into body cavities ...
... Same as nervous system: communication and control Slower acting than nervous system Effects are longer lasting Hormones Chemicals that influence or control the activity of a specific tissue or organ Secreted by endocrine glands directly into blood or lymph Exocrine glands secrete into body cavities ...
NAME:
... ___ 6. A physiologist removed the pancreas from several dogs in an experiment to investigate its function. He placed five normal dogs in one kennel and five dogs lacking a pancreas in another kennel. The physiologist observed that ants were attracted in large numbers to the kennel of the dogs lackin ...
... ___ 6. A physiologist removed the pancreas from several dogs in an experiment to investigate its function. He placed five normal dogs in one kennel and five dogs lacking a pancreas in another kennel. The physiologist observed that ants were attracted in large numbers to the kennel of the dogs lackin ...
Hormones: definition - a chemical signal released into body fluids
... definition - a chemical signal released into body fluids. Generally this regulates or causes a specific action. Usually, only specific cells known as target cells will respond, but some hormones can affect many different systems: A simple example: Adrenal gland -> epinephrine -> ...
... definition - a chemical signal released into body fluids. Generally this regulates or causes a specific action. Usually, only specific cells known as target cells will respond, but some hormones can affect many different systems: A simple example: Adrenal gland -> epinephrine -> ...
4.1.3 Hormones - WordPress.com
... Heart Rate is the number of heart beats per minute or the number of cardiac cycles per minute Stroke Volume is the volume of blood pumped through the heart in one cardiac cycle. The units are cm3 or dm3 Cardiac Output is the volume of blood pumped through the heart in one minute. It is calculated by ...
... Heart Rate is the number of heart beats per minute or the number of cardiac cycles per minute Stroke Volume is the volume of blood pumped through the heart in one cardiac cycle. The units are cm3 or dm3 Cardiac Output is the volume of blood pumped through the heart in one minute. It is calculated by ...
The Endocrine System
... caused by diabetes. People with diabetes can develop nerve damage throughout the body. Symptoms include pain, tingling, or numbness-loss of feeling-in the hands, arms, feet, and legs. This can result in wounds that are slow to heal. ...
... caused by diabetes. People with diabetes can develop nerve damage throughout the body. Symptoms include pain, tingling, or numbness-loss of feeling-in the hands, arms, feet, and legs. This can result in wounds that are slow to heal. ...
Cardiac physiology

Cardiac physiology or heart function is the study of healthy, unimpaired function of the heart: involving blood flow; myocardium structure; the electrical conduction system of the heart; the cardiac cycle and cardiac output and how these interact and depend on one another.