PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION BSc Counselling Psychology
... 78. The ______________ tends to be more analytical; processes information bit by bit. a. Right hemisphere c. Occipital lobe b. Left hemisphere d. Temporal lobe 79. The _______________ tends to be more holistic; processes information with respect to global patterns. a. Right hemisphere c. Occipital l ...
... 78. The ______________ tends to be more analytical; processes information bit by bit. a. Right hemisphere c. Occipital lobe b. Left hemisphere d. Temporal lobe 79. The _______________ tends to be more holistic; processes information with respect to global patterns. a. Right hemisphere c. Occipital l ...
Understanding genetic, neurophysiological, and experiential
... well in A-trials. On B-trials, parietally lesioned and unlesioned controls performed well at all delays, but DLPFC-lesioned animals searched incorrectly at the Alocation following 2- and 10-s delays. The disinhibited pattern of behavior exhibited by the DLPFC-lesioned animals parallels performance o ...
... well in A-trials. On B-trials, parietally lesioned and unlesioned controls performed well at all delays, but DLPFC-lesioned animals searched incorrectly at the Alocation following 2- and 10-s delays. The disinhibited pattern of behavior exhibited by the DLPFC-lesioned animals parallels performance o ...
information society technologies
... mapped directly to actuator controls. Reasoning at this level selects and regulates the transformations. At intermediate levels, compositions of actions or behaviours bring the system and the world to desired state. Reasoning may be used to select and apply a predetermined plan of action. Reasoning ...
... mapped directly to actuator controls. Reasoning at this level selects and regulates the transformations. At intermediate levels, compositions of actions or behaviours bring the system and the world to desired state. Reasoning may be used to select and apply a predetermined plan of action. Reasoning ...
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
... i. Receptor - Site of stimulus ii. Sensory neuron - Transmits an afferent impulse to CNS iii. Integration center - Region within the CNS iv. Motor neuron - Conducts efferent impulses from integration center to an effector v. Effector - Muscle fiber or gland that responds to the efferent impulse 4. T ...
... i. Receptor - Site of stimulus ii. Sensory neuron - Transmits an afferent impulse to CNS iii. Integration center - Region within the CNS iv. Motor neuron - Conducts efferent impulses from integration center to an effector v. Effector - Muscle fiber or gland that responds to the efferent impulse 4. T ...
Artificial intelligence - University of London International Programmes
... with which the agent can interact (reinforcement learning). 5. Vision, where an agent must interpret or otherwise process raw visual images. 6. Natural language, where an agent must process input in a natural language (e.g. English), or generate it. The technology resulting from progress in these ar ...
... with which the agent can interact (reinforcement learning). 5. Vision, where an agent must interpret or otherwise process raw visual images. 6. Natural language, where an agent must process input in a natural language (e.g. English), or generate it. The technology resulting from progress in these ar ...
document
... • With Eliza or Alice like rules, we can eventually solve the Turing Test – it just takes writing enough rules • Does the system understand what it is responding to? – No, neither Eliza nor Alice understand the text, its just that Alice has better, more in depth and wider ranging rules ...
... • With Eliza or Alice like rules, we can eventually solve the Turing Test – it just takes writing enough rules • Does the system understand what it is responding to? – No, neither Eliza nor Alice understand the text, its just that Alice has better, more in depth and wider ranging rules ...
Somatosensory system
... -ruffini’s endings(II) : extremes of joint range and respond more to passive than to active movement - paciniform corpuscles(II) : respond to movement - free nerve endings(Aδ and C) : stimulated by inflammation - ligament receptors(Ib) : similar to Golgi tendon organs and ...
... -ruffini’s endings(II) : extremes of joint range and respond more to passive than to active movement - paciniform corpuscles(II) : respond to movement - free nerve endings(Aδ and C) : stimulated by inflammation - ligament receptors(Ib) : similar to Golgi tendon organs and ...
brain
... synaptic connections underlie memory and learning • Two processes dominate embryonic development of the nervous system – Neurons compete for growth-supporting factors in order to survive, they have many synapses – Only half the synapses that form during embryo development survive into adulthood (bec ...
... synaptic connections underlie memory and learning • Two processes dominate embryonic development of the nervous system – Neurons compete for growth-supporting factors in order to survive, they have many synapses – Only half the synapses that form during embryo development survive into adulthood (bec ...
Homeostasis Test%28CNS%29-Tawsif Hossain
... case of the reflex arc. In the reflex arc a stimulus causes the body to react fast to prevent damage. For eg: if the sensory system detected a large rise in temperature of the skin surface. A nerve impulse would be sent through the sensory neurons to the interneurons and finally the motor neurons. I ...
... case of the reflex arc. In the reflex arc a stimulus causes the body to react fast to prevent damage. For eg: if the sensory system detected a large rise in temperature of the skin surface. A nerve impulse would be sent through the sensory neurons to the interneurons and finally the motor neurons. I ...
Unit 3
... Turn and Talk: Discussion • 1. Knowing what we do about collision sports, do you think you’ll see less people playing them? • 2. Why is it that parents allow children to play collision sports at such a young age? • 3. If you were a parent and know what you know about the brain, would you allow your ...
... Turn and Talk: Discussion • 1. Knowing what we do about collision sports, do you think you’ll see less people playing them? • 2. Why is it that parents allow children to play collision sports at such a young age? • 3. If you were a parent and know what you know about the brain, would you allow your ...
Intelligent Databases
... Knowledge graphs belong to the category of semantic networks. One essential difference between knowledge graphs and semantic networks is the explicit choice of only a few types of relations. For example, it uses relations such as, ...
... Knowledge graphs belong to the category of semantic networks. One essential difference between knowledge graphs and semantic networks is the explicit choice of only a few types of relations. For example, it uses relations such as, ...
Artificial intelligence (AI)
... recognition, Natural language processing and more. This system is working throughout the world as an artificial brain. Intelligence involves mechanisms, and AI research has discovered how to make computers carry out some of them and not others. If doing a task requires only mechanisms that are well ...
... recognition, Natural language processing and more. This system is working throughout the world as an artificial brain. Intelligence involves mechanisms, and AI research has discovered how to make computers carry out some of them and not others. If doing a task requires only mechanisms that are well ...
Superintelligence
... quality of information found. • To answer a question, Watson: • searches millions of documents to find thousands of possible answers • Collects evidence and uses a scoring algorithm to rate the quality of this evidence • Ranks all possible answers based on the score of its supporting evidence • To l ...
... quality of information found. • To answer a question, Watson: • searches millions of documents to find thousands of possible answers • Collects evidence and uses a scoring algorithm to rate the quality of this evidence • Ranks all possible answers based on the score of its supporting evidence • To l ...
Chapter 16
... 51. Distinguish between the two kinds of equilibrium. Otolithic Organs: Saccule and Utricle 52. Describe the cellular and extracellular constituents of the maculae, and the relative spacial position of these otoliths organs with the saccule and utricle. 53. Discuss how the otoliths work with the cil ...
... 51. Distinguish between the two kinds of equilibrium. Otolithic Organs: Saccule and Utricle 52. Describe the cellular and extracellular constituents of the maculae, and the relative spacial position of these otoliths organs with the saccule and utricle. 53. Discuss how the otoliths work with the cil ...
Pursuing commitments
... variety of brain circuits to focus machinery on the location of interest. In principle, it ought to be possible to study the mechanism of attention/commitment by stimulating the FEF and recording from neurons involved in visual processing. Experiments using this approach will be presented at the nex ...
... variety of brain circuits to focus machinery on the location of interest. In principle, it ought to be possible to study the mechanism of attention/commitment by stimulating the FEF and recording from neurons involved in visual processing. Experiments using this approach will be presented at the nex ...
pdf version
... “Finding Legally Relevant Passages in Case Opinions.” J. J. Daniels and E. L. Rissland. Sixth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Law. July 1997. To appear. “What you saw is what you want: Using Cases to seed Information Retrieval.” J. J. Daniels and E. L. Rissland. Second Intern ...
... “Finding Legally Relevant Passages in Case Opinions.” J. J. Daniels and E. L. Rissland. Sixth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Law. July 1997. To appear. “What you saw is what you want: Using Cases to seed Information Retrieval.” J. J. Daniels and E. L. Rissland. Second Intern ...
Ch 7 The Nervous System Notes
... 3 functions: 1. sensory receptors to monitor changes occurring inside & outside body stimuli- changes sensory input- gathered information 2. processes and interprets the sensory input integration- nervous system makes decisions about what should be done 3. effects a response by activating muscles or ...
... 3 functions: 1. sensory receptors to monitor changes occurring inside & outside body stimuli- changes sensory input- gathered information 2. processes and interprets the sensory input integration- nervous system makes decisions about what should be done 3. effects a response by activating muscles or ...
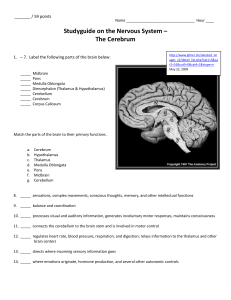
Major Parts of the Brain:
... 10. _____ processes visual and auditory information, generates involuntary motor responses, maintains consciousness 11. _____ connects the cerebellum to the brain stem and is involved in motor control 12. _____ regulates heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, and digestion; relays information to t ...
... 10. _____ processes visual and auditory information, generates involuntary motor responses, maintains consciousness 11. _____ connects the cerebellum to the brain stem and is involved in motor control 12. _____ regulates heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, and digestion; relays information to t ...
Artificial General Intelligence and Classical Neural Network
... so, for a given problem, it may be easier to find solutions in one framework than in the other frameworks. Therefore, the frameworks are not always equivalent in practical applications. On the implementational level, the central issues include efficiency and naturalness. These three levels have stro ...
... so, for a given problem, it may be easier to find solutions in one framework than in the other frameworks. Therefore, the frameworks are not always equivalent in practical applications. On the implementational level, the central issues include efficiency and naturalness. These three levels have stro ...
Medical applications of Multi-Agent Systems
... - Age, weight & size: maximum difference - Waiting time ...
... - Age, weight & size: maximum difference - Waiting time ...
Knowledge management systems - Oman College of Management
... provides a range of strategies for indexing, organizing and storing the resources that are linked to the KMS. ...
... provides a range of strategies for indexing, organizing and storing the resources that are linked to the KMS. ...
Structured Knowledge Representation and Schema Systems
... A slot is a named place-holder for a pointer. The slots point to other frames that represent entities that are described (or interpreted) by the frame. Ultimately, some slots point to raw perceptions. When a slot points to an entity it is said to play a "role" in the frame. Frames typically come wit ...
... A slot is a named place-holder for a pointer. The slots point to other frames that represent entities that are described (or interpreted) by the frame. Ultimately, some slots point to raw perceptions. When a slot points to an entity it is said to play a "role" in the frame. Frames typically come wit ...
Class
... When this lobe of the brain is electrically stimulated people report physical sensations, as if they had been touched, for example, on the arm. a. occipital b. parietal c. frontal d. temporal ...
... When this lobe of the brain is electrically stimulated people report physical sensations, as if they had been touched, for example, on the arm. a. occipital b. parietal c. frontal d. temporal ...
Mindfulness - Maine Psychological Association
... providing measures of attention, memory, executive functions and further miscellaneous measures of cognition were included. Fifteen were controlled or randomized controlled studies and 8 were case-control studies. Overall, reviewed studies suggested that early phases of mindfulness training, which a ...
... providing measures of attention, memory, executive functions and further miscellaneous measures of cognition were included. Fifteen were controlled or randomized controlled studies and 8 were case-control studies. Overall, reviewed studies suggested that early phases of mindfulness training, which a ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM I
... body is called the axon which carries information away from the cell body. • Axons are highly variable in length and may divide into several branches or collaterals through which information can be distributed to a number of different destinations ...
... body is called the axon which carries information away from the cell body. • Axons are highly variable in length and may divide into several branches or collaterals through which information can be distributed to a number of different destinations ...