Notebook - Science
... principal quantum number n: describes energy of the electron; always a positive integer; large numbers seldom encountered; each atom has many orbitals associated with each value of n; these orbitals together are sometimes called electron shells azimuthal quantum number ℓ: describes orbital angular m ...
... principal quantum number n: describes energy of the electron; always a positive integer; large numbers seldom encountered; each atom has many orbitals associated with each value of n; these orbitals together are sometimes called electron shells azimuthal quantum number ℓ: describes orbital angular m ...
Electronic Structure - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... The shape of d-orbitals (l = 2) are more complicated. Each shell, from the third shell onwards, contains five of these d-orbitals, ( ml = -2 -1 0 +1 +2 ). ...
... The shape of d-orbitals (l = 2) are more complicated. Each shell, from the third shell onwards, contains five of these d-orbitals, ( ml = -2 -1 0 +1 +2 ). ...
Chapter 2
... electrons of nitrogen are distributed into three unshared orbitals and one shared orbital. • When atoms interact to complete their valence shells, it is the __________ electrons that are involved. ...
... electrons of nitrogen are distributed into three unshared orbitals and one shared orbital. • When atoms interact to complete their valence shells, it is the __________ electrons that are involved. ...
CMC Chapter 5
... • Bohr’s atomic model attributes hydrogen’s emission spectrum to electrons dropping from higher-energy to lower-energy orbits. ∆E = E higher-energy orbit - E lower-energy orbit = E photon = hν • The de Broglie equation relates a particle’s wavelength to its mass, its velocity, and Planck’s constant. ...
... • Bohr’s atomic model attributes hydrogen’s emission spectrum to electrons dropping from higher-energy to lower-energy orbits. ∆E = E higher-energy orbit - E lower-energy orbit = E photon = hν • The de Broglie equation relates a particle’s wavelength to its mass, its velocity, and Planck’s constant. ...
Chapter 5 Homework
... 19. Which one of the following statements is not consistent with the Bohr theory? (a) An electron moves in a circular orbit around the nucleus. (b) The energy of an electron is quantized. (c) An electron may move to a lower energy orbital by emitting radiation of a frequency proportional to the ener ...
... 19. Which one of the following statements is not consistent with the Bohr theory? (a) An electron moves in a circular orbit around the nucleus. (b) The energy of an electron is quantized. (c) An electron may move to a lower energy orbital by emitting radiation of a frequency proportional to the ener ...
Ch8lsn22Chem105
... HUND’S RULE - When placing electrons in a set of orbitals having the same energy, we place them singly as long as possible. aufbau principle is the building up process that results in ground-state electron configurations Kull Spring07 Lesson 22 Ch 7/8 ...
... HUND’S RULE - When placing electrons in a set of orbitals having the same energy, we place them singly as long as possible. aufbau principle is the building up process that results in ground-state electron configurations Kull Spring07 Lesson 22 Ch 7/8 ...
In the Classroom
... kinetic energy occurs because orbital contraction has reduced the volume occupied by the electrons, thereby reducing the level of delocalization. It has been shown that at the equilibrium bond distance the net transfer of electron density into the internuclear region is only 16% [5]. According to th ...
... kinetic energy occurs because orbital contraction has reduced the volume occupied by the electrons, thereby reducing the level of delocalization. It has been shown that at the equilibrium bond distance the net transfer of electron density into the internuclear region is only 16% [5]. According to th ...
Unit 4 - School District of Durand
... ml is described numerically using 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 and so on. o The + sign indicates a positive direction, the – sign indicates a negative direction. o ml for the s orbital= 0 o ml for the p orbitals= 0, 1 (-1, 0, 1) o ml for the d orbitals= 0, 1, 2 (-2, -1, 0, 1, 2) o ml for the f orbitals= 0 ...
... ml is described numerically using 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 and so on. o The + sign indicates a positive direction, the – sign indicates a negative direction. o ml for the s orbital= 0 o ml for the p orbitals= 0, 1 (-1, 0, 1) o ml for the d orbitals= 0, 1, 2 (-2, -1, 0, 1, 2) o ml for the f orbitals= 0 ...
Reconfigurable Quantum-Dot Molecules Created by Atom
... to each other, quantum tunneling can lead to the coherent superposition and entanglement of dot-confined states [4–9], a key ingredient for quantum information processing [10,11]. Coupled quantum dots—often referred to as “quantum-dot molecules”—have been created in semiconductor heterostructures us ...
... to each other, quantum tunneling can lead to the coherent superposition and entanglement of dot-confined states [4–9], a key ingredient for quantum information processing [10,11]. Coupled quantum dots—often referred to as “quantum-dot molecules”—have been created in semiconductor heterostructures us ...
Chem fundamentals 1a
... Comments on chemical notation: Single lines = single bonds = 2 electrons Double lines = double bonds = 4 electrons Nonbonding electrons (depends on the element) are not shown but are counted to balance electrons. O has 4 nonbonding electrons; N has 2. Organic chemical structures often are ...
... Comments on chemical notation: Single lines = single bonds = 2 electrons Double lines = double bonds = 4 electrons Nonbonding electrons (depends on the element) are not shown but are counted to balance electrons. O has 4 nonbonding electrons; N has 2. Organic chemical structures often are ...
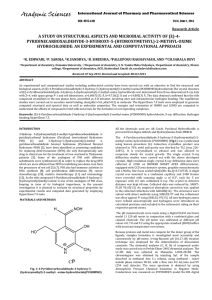
Electronic structures of „In,Ga…As/GaAs quantum dot molecules
... molecular orbitals8,9 g and u originating from s orbitals and u and g originating from p orbitals. The bonding and antibonding splittings ⌬ = ⑀共u兲 − ⑀共g兲 and ⌬ = ⑀共g兲 − ⑀共u兲 increase with the decrease of interdot distance, because the coupling between the top and bottom dots gets stronger. ...
... molecular orbitals8,9 g and u originating from s orbitals and u and g originating from p orbitals. The bonding and antibonding splittings ⌬ = ⑀共u兲 − ⑀共g兲 and ⌬ = ⑀共g兲 − ⑀共u兲 increase with the decrease of interdot distance, because the coupling between the top and bottom dots gets stronger. ...
Document
... Mechanics of Waves on a Surface E.g.2. Waves in two dimensions: Modes of a drumhead Standing waves can also be generated on a surface or thin membrane. A drumhead has a fixed perimeter, and oscillations on this surface lead to more complicated patterns of displacement and nodes First, consider the ...
... Mechanics of Waves on a Surface E.g.2. Waves in two dimensions: Modes of a drumhead Standing waves can also be generated on a surface or thin membrane. A drumhead has a fixed perimeter, and oscillations on this surface lead to more complicated patterns of displacement and nodes First, consider the ...
Introduction to elementary quantum mechanics
... theory is the description of the state of a physical system. In classical mechanics the state of a system built of many material points is uniquely determined by positions and momenta of all the elements of the system in any instant of time. The values of positions and momenta are found by solving e ...
... theory is the description of the state of a physical system. In classical mechanics the state of a system built of many material points is uniquely determined by positions and momenta of all the elements of the system in any instant of time. The values of positions and momenta are found by solving e ...
Review II
... A. Write the correct skeletal structure for the molecule B. Calculate the total number of valence electrons C. Distribute electrons among atoms giving each an octet (duet) D. If any atoms the lack an octet, form double or triple bonds as necessary E. Exception to the octet rule 1. Duet rule for hydr ...
... A. Write the correct skeletal structure for the molecule B. Calculate the total number of valence electrons C. Distribute electrons among atoms giving each an octet (duet) D. If any atoms the lack an octet, form double or triple bonds as necessary E. Exception to the octet rule 1. Duet rule for hydr ...
Quantum Chemistry
... Mechanics of Waves on a Surface E.g.2. Waves in two dimensions: Modes of a drumhead Standing waves can also be generated on a surface or thin membrane. A drumhead has a fixed perimeter, and oscillations on this surface lead to more complicated patterns of displacement and nodes First, consider the ...
... Mechanics of Waves on a Surface E.g.2. Waves in two dimensions: Modes of a drumhead Standing waves can also be generated on a surface or thin membrane. A drumhead has a fixed perimeter, and oscillations on this surface lead to more complicated patterns of displacement and nodes First, consider the ...
Molecular orbital

In chemistry, a molecular orbital (or MO) is a mathematical function describing the wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The term orbital was introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 as an abbreviation for one-electron orbital wave function. At an elementary level, it is used to describe the region of space in which the function has a significant amplitude. Molecular orbitals are usually constructed by combining atomic orbitals or hybrid orbitals from each atom of the molecule, or other molecular orbitals from groups of atoms. They can be quantitatively calculated using the Hartree–Fock or self-consistent field (SCF) methods.