Chemistry Entrance Material for Grade 11 to 12
... 38. Give examples of solid solutions. Effect of freezing or boiling salt water 39. Which of the following observation(s) is/are TRUE about boiling and freezing a sample of pure water and another one of salt solution? 1. When cooling, both samples freeze at the same temperature . 2. Heat some of each ...
... 38. Give examples of solid solutions. Effect of freezing or boiling salt water 39. Which of the following observation(s) is/are TRUE about boiling and freezing a sample of pure water and another one of salt solution? 1. When cooling, both samples freeze at the same temperature . 2. Heat some of each ...
S4 Standard Grade Revision Booklet
... The extraction of a metal from it’s ore is a reduction reaction (R.I.G.). The metal ion gains electrons to form metal atoms. Iron is extracted from iron ore in a BLAST FURNACE. The 3 raw materials are, iron ore, coke and limestone. Most of the iron produced is made into steel. Reasons for Re-Cycling ...
... The extraction of a metal from it’s ore is a reduction reaction (R.I.G.). The metal ion gains electrons to form metal atoms. Iron is extracted from iron ore in a BLAST FURNACE. The 3 raw materials are, iron ore, coke and limestone. Most of the iron produced is made into steel. Reasons for Re-Cycling ...
Answers to examination questions
... van der Waals’ forces whose size depends on the number of electrons present in the atom or molecule. A greater number of electrons in the ethane molecule results in a stronger temporary dipole which makes neighbouring molecules or atoms attract each other more strongly. This means more heat is requi ...
... van der Waals’ forces whose size depends on the number of electrons present in the atom or molecule. A greater number of electrons in the ethane molecule results in a stronger temporary dipole which makes neighbouring molecules or atoms attract each other more strongly. This means more heat is requi ...
2005 - NESACS
... 42. The hydrogen emission spectrum for galaxy NGC 3310 is shown below. Marked on the spectrum with a vertical line is the red hydrogen emission line, Hα, at 6562.8 Å (656.2 nm) that originates from the Balmer series (32) at the spot where it would be found in a hydrogen spectrum produced in a labor ...
... 42. The hydrogen emission spectrum for galaxy NGC 3310 is shown below. Marked on the spectrum with a vertical line is the red hydrogen emission line, Hα, at 6562.8 Å (656.2 nm) that originates from the Balmer series (32) at the spot where it would be found in a hydrogen spectrum produced in a labor ...
Class XII Chemistry IMPORTANT QUESTIONS and COMMON
... Doping: The process of adding impurities to a crystalline substance so as to change its properties is called doping. a) Doping in ionic solids : When NaCl is doped with SrCl2 , there are cationic vacancies created. b) Doping in co-valent solids: The impurities added may be electron rich or electron ...
... Doping: The process of adding impurities to a crystalline substance so as to change its properties is called doping. a) Doping in ionic solids : When NaCl is doped with SrCl2 , there are cationic vacancies created. b) Doping in co-valent solids: The impurities added may be electron rich or electron ...
Introduction to Computational Chemistry
... classical and quantum mechanics are now implemented in a form which can handle the many-body problems associated with the structure and behavior of complex molecular systems." John A. Pople (November 1997) (Nobel prize for chemistry 1998, together with Walter Kohn ) ...
... classical and quantum mechanics are now implemented in a form which can handle the many-body problems associated with the structure and behavior of complex molecular systems." John A. Pople (November 1997) (Nobel prize for chemistry 1998, together with Walter Kohn ) ...
Chapter 2 - Chemistry
... - not found in nature in pure form (highly reactive) - exception - hydrogen Group 7A (Halogens) -colorful, corrosive nonmetals - found in nature only in combination with other elements Karen Hattenhauer (Fall 2007) ...
... - not found in nature in pure form (highly reactive) - exception - hydrogen Group 7A (Halogens) -colorful, corrosive nonmetals - found in nature only in combination with other elements Karen Hattenhauer (Fall 2007) ...
Test - Regents
... They’re baaack . . . a splash from the past! Fizzies instant sparkling drink tablets, popular in the 1950s and 1960s, are now back on the market. What sets them apart from other powdered drinks is that they bubble and fizz when placed in water, forming an instant carbonated beverage. The fizz in Fiz ...
... They’re baaack . . . a splash from the past! Fizzies instant sparkling drink tablets, popular in the 1950s and 1960s, are now back on the market. What sets them apart from other powdered drinks is that they bubble and fizz when placed in water, forming an instant carbonated beverage. The fizz in Fiz ...
Setting the stage
... five atoms, 15 with six atoms, 9 with seven atoms, 10 with eight atoms, 9 with nine atoms, 15 with ten or more atoms and 17 deuterated molecules. 204 different molecules altogether who‘s ingredients include H, C, N, O, F, Na, Mg, Al, Si, P, S, Cl, K, Ti, Fe, I. ...
... five atoms, 15 with six atoms, 9 with seven atoms, 10 with eight atoms, 9 with nine atoms, 15 with ten or more atoms and 17 deuterated molecules. 204 different molecules altogether who‘s ingredients include H, C, N, O, F, Na, Mg, Al, Si, P, S, Cl, K, Ti, Fe, I. ...
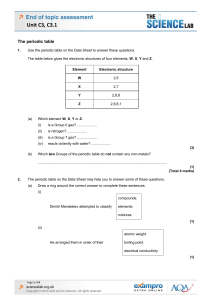
Unit C3, C3.1
... He then put elements with similar properties in the same column. However, he left gaps, and sometimes did not follow the order of increasing atomic weight – for example, he placed iodine (atomic weight 127) after tellurium (atomic weight 128). Within a few years there was sufficient evidence to prov ...
... He then put elements with similar properties in the same column. However, he left gaps, and sometimes did not follow the order of increasing atomic weight – for example, he placed iodine (atomic weight 127) after tellurium (atomic weight 128). Within a few years there was sufficient evidence to prov ...
Term 111, Final Exam (All correct choices are A): 1. What is the
... 12. Bonds with higher ionic character form between (note: Ei = ionization energy and Eea = electron affinity) A) an element with a large Ei and an element with a small negative Eea B) an element with a small Ei and an element with a small negative Eea C) elements with equal values of Ei and Eea D) a ...
... 12. Bonds with higher ionic character form between (note: Ei = ionization energy and Eea = electron affinity) A) an element with a large Ei and an element with a small negative Eea B) an element with a small Ei and an element with a small negative Eea C) elements with equal values of Ei and Eea D) a ...
Regents Review Questions
... A substance known as heavy water can be obtained from ordinary water and could be a significant source of energy in the future. Heavy water contains deuterium, H-2. Instead of the two hydrogen atoms in a typical water molecule, a heavy water molecule has two deuterium atoms. In 3.78 kilograms of ord ...
... A substance known as heavy water can be obtained from ordinary water and could be a significant source of energy in the future. Heavy water contains deuterium, H-2. Instead of the two hydrogen atoms in a typical water molecule, a heavy water molecule has two deuterium atoms. In 3.78 kilograms of ord ...
Descriptive Chemistry of Elements d-Block
... configuration of a d-block element can be represented as (n+1)s2 ndm or (n+1)s1 ndm where n = 3, 4, 5 or 6 and m = 1, 2, 3, …..or 10. When you look at the Periodic Table, you can see, that there are four series (or rows) in the d-block. They are the 3d, 4d, 5d and 6d-series and are in the 4th, 5th, ...
... configuration of a d-block element can be represented as (n+1)s2 ndm or (n+1)s1 ndm where n = 3, 4, 5 or 6 and m = 1, 2, 3, …..or 10. When you look at the Periodic Table, you can see, that there are four series (or rows) in the d-block. They are the 3d, 4d, 5d and 6d-series and are in the 4th, 5th, ...
Chemistry@YIA – additional information
... 0.429 g of crystalline sodium carbonate (Na2CO3.xH2O) required 15.0 cm3 of 0.2 mol/dm3 HCl for neutralisation. Calculate the Mr of Na2CO3.xH2O and x. Na2CO3.xH2O(s) + 2 HCl(aq) 2 NaCl(aq) + CO2(g) + (x+2) H2O(l) ...
... 0.429 g of crystalline sodium carbonate (Na2CO3.xH2O) required 15.0 cm3 of 0.2 mol/dm3 HCl for neutralisation. Calculate the Mr of Na2CO3.xH2O and x. Na2CO3.xH2O(s) + 2 HCl(aq) 2 NaCl(aq) + CO2(g) + (x+2) H2O(l) ...
Redox Reactions - Hillsborough County Public Schools
... H is always +1 (except when attached to more electronegative metals, Li, Na, Ca, and Al 7. Group 1A, 2A, and 3A always have an oxidation number equal to the group number (equal to the charge it would have if it were a ion with noble gas configuration.) 8. Sum of all oxidation numbers in a neutra ...
... H is always +1 (except when attached to more electronegative metals, Li, Na, Ca, and Al 7. Group 1A, 2A, and 3A always have an oxidation number equal to the group number (equal to the charge it would have if it were a ion with noble gas configuration.) 8. Sum of all oxidation numbers in a neutra ...
- Department of Chemistry, York University
... (NH2CH2COOH)H+ +CH3COOH(CH3CONHCH2COOH)H++H2O protonated N-acetyl-glycine (CH3CONHCH2COOH)H+ + NH2OH no (clusters) (NH2CH2CONHCH2COOH)H+ + H2O Fe+CH3CONHCH2COOH + NH2OH ? (too complicated) Fe+NH2CH2CONHCH2COOH + H2O diglycine, a dipeptide M+(Gly)n + CH3COOH + NH2OH M+(Gly)n+1 + H2O (M+ assemb ...
... (NH2CH2COOH)H+ +CH3COOH(CH3CONHCH2COOH)H++H2O protonated N-acetyl-glycine (CH3CONHCH2COOH)H+ + NH2OH no (clusters) (NH2CH2CONHCH2COOH)H+ + H2O Fe+CH3CONHCH2COOH + NH2OH ? (too complicated) Fe+NH2CH2CONHCH2COOH + H2O diglycine, a dipeptide M+(Gly)n + CH3COOH + NH2OH M+(Gly)n+1 + H2O (M+ assemb ...
112 ex iii lec outline f 04
... Structural Isomers: Different Sequences of Atoms a. Coordination Isomers differ in that the ligands that are directly bonded to the metal, would be instead outside of the complex ion and be the counter ions. ...
... Structural Isomers: Different Sequences of Atoms a. Coordination Isomers differ in that the ligands that are directly bonded to the metal, would be instead outside of the complex ion and be the counter ions. ...
The Copper Cycle
... the millions of chemical reactions occurring around us all the time; yet, most of these reactions can be classified into one of three main types of chemical reactions: precipitation reactions, acid-base neutralization reactions, and oxidation-reduction (also called “redox”) reactions. ...
... the millions of chemical reactions occurring around us all the time; yet, most of these reactions can be classified into one of three main types of chemical reactions: precipitation reactions, acid-base neutralization reactions, and oxidation-reduction (also called “redox”) reactions. ...
Chapter 18: The Representative Elements The Representative
... The Alkali Metals Electron configuration is ns1(n = period number). Lose their valence e- easily (great reducing agents). Most violently reactive of all the metals. React strongly with H2O(l); the vigor of the reaction increases down the group. The alkali metals are all too easily oxidized t ...
... The Alkali Metals Electron configuration is ns1(n = period number). Lose their valence e- easily (great reducing agents). Most violently reactive of all the metals. React strongly with H2O(l); the vigor of the reaction increases down the group. The alkali metals are all too easily oxidized t ...
Chapter 18: The Representative Elements
... All group 2 elements except for beryllium react with water and the vigor of the reaction increases going down the group. Chapter 18: The Representative Elements ...
... All group 2 elements except for beryllium react with water and the vigor of the reaction increases going down the group. Chapter 18: The Representative Elements ...
Summary - Clydebank High School
... 2. Ionic and polar substances tend to be ........................................ in polar solvents such as water. Non-polar substances tend to be .......................................... in polar solvents such as water 3. Water (H2O), ammonia (............) and hydrogen fluoride (...........) hav ...
... 2. Ionic and polar substances tend to be ........................................ in polar solvents such as water. Non-polar substances tend to be .......................................... in polar solvents such as water 3. Water (H2O), ammonia (............) and hydrogen fluoride (...........) hav ...
File
... Problem: How can you show that viscosity is a fluid’s resistance to flow? Background: There are several physical properties of fluids. Mass, volume, density, viscosity, color, and buoyancy are just a few. Density is the ratio of mass to volume and viscosity is the resistance to flow of a liquid. Vis ...
... Problem: How can you show that viscosity is a fluid’s resistance to flow? Background: There are several physical properties of fluids. Mass, volume, density, viscosity, color, and buoyancy are just a few. Density is the ratio of mass to volume and viscosity is the resistance to flow of a liquid. Vis ...
+ H 2 O(l)
... HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) NaCl (aq) + H2O (l) NH4Cl (aq) + NaOH (aq) NH3 (g) + H2O (l) + NaCl (aq) Blue color for the products represents the driving force which allows the chemical reaction to occur. ...
... HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) NaCl (aq) + H2O (l) NH4Cl (aq) + NaOH (aq) NH3 (g) + H2O (l) + NaCl (aq) Blue color for the products represents the driving force which allows the chemical reaction to occur. ...
Introduction to Computational Chemistry
... • Semiempirical methods rely on parametrization of some of the integrals that occur in the solution of the Schrödinger equation using experimental data. • Density functional methods are based on the specification of a certain functional form for the electron density in the molecule. B. Utility and A ...
... • Semiempirical methods rely on parametrization of some of the integrals that occur in the solution of the Schrödinger equation using experimental data. • Density functional methods are based on the specification of a certain functional form for the electron density in the molecule. B. Utility and A ...
Fall - Physical Chemistry Division
... structure in chemistry and physics. Many molecular processes involving energy transfer through excited states or transition metal catalysis, as well as exotic materials phenomena such as high temperature superconductivity, have an underlying physical origin in the behavior of strongly correlated ele ...
... structure in chemistry and physics. Many molecular processes involving energy transfer through excited states or transition metal catalysis, as well as exotic materials phenomena such as high temperature superconductivity, have an underlying physical origin in the behavior of strongly correlated ele ...