CHEMISTRY
... The nature of most atoms is that they are LONELY and sometimes AGGRESSIVE! Most atoms team up with or overtake other atoms in an attempt to get the “right” number of electrons. This is how molecules are formed. Only the NOBLE GASSES can exist on their own. ATOMS will switch partners when provoked. T ...
... The nature of most atoms is that they are LONELY and sometimes AGGRESSIVE! Most atoms team up with or overtake other atoms in an attempt to get the “right” number of electrons. This is how molecules are formed. Only the NOBLE GASSES can exist on their own. ATOMS will switch partners when provoked. T ...
Dr. Harris Chemistry 105 Practice Exam 1 Isotope Atomic Number
... a.) Using electron configurations, show the formation of BeO. See slides 7 and 10 of lecture 7. b.) Why does this reaction proceed? (3) So that each ion can reach a noble gas configuration. c.) Refer to the table of ionization energies in Ch 4 of your book, as well as the table of electron affinitie ...
... a.) Using electron configurations, show the formation of BeO. See slides 7 and 10 of lecture 7. b.) Why does this reaction proceed? (3) So that each ion can reach a noble gas configuration. c.) Refer to the table of ionization energies in Ch 4 of your book, as well as the table of electron affinitie ...
Answers for Review Questions Exam 3
... 9. Electrolysis is the use of an electric current to bring about a chemical change. Reduction and oxidation both occur at the same place as in a galvanic cell, but they have different polarities, - and + respectively. It differs from a galvanic cell in that it is in the opposite direction of a galva ...
... 9. Electrolysis is the use of an electric current to bring about a chemical change. Reduction and oxidation both occur at the same place as in a galvanic cell, but they have different polarities, - and + respectively. It differs from a galvanic cell in that it is in the opposite direction of a galva ...
Answers for Review Questions Exam 3
... 10. Electrolysis is used as a source of elements from their ions. Ex. Na from Molten NaCl, Cl2 from a NaCl solution. 11. 0.1663 A current is needed. 12. First 2.47 Volts should be 2.47 Amperes. That gives 4.100g of Fe deposited. 13. Corrosion is the loss of metals to a solution of some form. The pro ...
... 10. Electrolysis is used as a source of elements from their ions. Ex. Na from Molten NaCl, Cl2 from a NaCl solution. 11. 0.1663 A current is needed. 12. First 2.47 Volts should be 2.47 Amperes. That gives 4.100g of Fe deposited. 13. Corrosion is the loss of metals to a solution of some form. The pro ...
1) - Kurt Niedenzu
... 32) The increase in atomic radius of each successive element within a group is primarily due to an increase in the number of a) neutrons in the nucleus b) electrons in the outermost shell c) unpaired electrons d) occupied principal energy levels 33) Elements that have properties of both metals and n ...
... 32) The increase in atomic radius of each successive element within a group is primarily due to an increase in the number of a) neutrons in the nucleus b) electrons in the outermost shell c) unpaired electrons d) occupied principal energy levels 33) Elements that have properties of both metals and n ...
Chemical Bonding Quiz
... Study Guide: Chemical Bonding Quiz Students should be able to understand and apply the following Chemical Bonding concepts: ...
... Study Guide: Chemical Bonding Quiz Students should be able to understand and apply the following Chemical Bonding concepts: ...
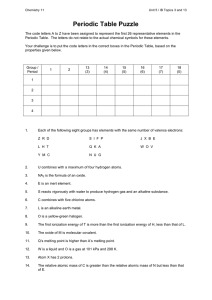
Periodic Table Puzzle
... The first ionization energy of T is more than the first ionization energy of H, less than that of L. ...
... The first ionization energy of T is more than the first ionization energy of H, less than that of L. ...
Chemical Bonds
... electrons) attract each other. These forces pull atoms together to form compounds An atom is chemically stable when it has a complete outer energy level ...
... electrons) attract each other. These forces pull atoms together to form compounds An atom is chemically stable when it has a complete outer energy level ...
Chem 400 Chem 150 REVIEW SHEET Amanda R
... o Elements in groups 1,2,13 and 14 form cations (positively charged ion) o Elements in groups 15, 16 and 17 form anions (negatively charged ions) o Most transition metals form cations of various charge Trends in Periodic Table – trends of elements to predict formation of bonds o Counting valence ele ...
... o Elements in groups 1,2,13 and 14 form cations (positively charged ion) o Elements in groups 15, 16 and 17 form anions (negatively charged ions) o Most transition metals form cations of various charge Trends in Periodic Table – trends of elements to predict formation of bonds o Counting valence ele ...
Biochemistry Introduction day 1
... Isotopes: Atoms of an element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Ex: Oxygen usually has 8 neutrons but 9 and 10 neutrons can be found in some oxygen atoms. Some isotopes are unstable in the nucleus which makes it more likely to decay and release energy. This i ...
... Isotopes: Atoms of an element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Ex: Oxygen usually has 8 neutrons but 9 and 10 neutrons can be found in some oxygen atoms. Some isotopes are unstable in the nucleus which makes it more likely to decay and release energy. This i ...
7_4-5.pdf
... excess electrons Therefore, the electrostatic potential difference is attributed to both the electric field and the Fermi energy (Ec-Ef) change, as shown in the following figure, where qV s = qV b + ∆( E c − E f ) = −E x ∆x + ...
... excess electrons Therefore, the electrostatic potential difference is attributed to both the electric field and the Fermi energy (Ec-Ef) change, as shown in the following figure, where qV s = qV b + ∆( E c − E f ) = −E x ∆x + ...
Draw atomic models showing the appropriate number of electrons
... 1. How strongly an atom is able to tug on bonding electrons ...
... 1. How strongly an atom is able to tug on bonding electrons ...
Chapter 8: Chemical Reactions and Physical Changes
... • Mass number: total protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus • Atomic mass: the average mass of a sample of atoms of that element found in nature • Periodic table: chart that arranges elements by atomic number into rows and columns according to similarities in their properties ...
... • Mass number: total protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus • Atomic mass: the average mass of a sample of atoms of that element found in nature • Periodic table: chart that arranges elements by atomic number into rows and columns according to similarities in their properties ...
Chapter 6 Quiz
... c. linear d. trigonal-planar ______ 8. Use VSEPR theory to predict the shape of the chlorate ion, ClO3–. a. trigonal-planar b. bent c. octahedral d. trigonal-pyramidal ______ 9. Use VSEPR theory to predict the shape of carbon dioxide, CO2. a. tetrahedral b. bent c. linear d. octahedral ______10. Whe ...
... c. linear d. trigonal-planar ______ 8. Use VSEPR theory to predict the shape of the chlorate ion, ClO3–. a. trigonal-planar b. bent c. octahedral d. trigonal-pyramidal ______ 9. Use VSEPR theory to predict the shape of carbon dioxide, CO2. a. tetrahedral b. bent c. linear d. octahedral ______10. Whe ...
Magnetic Susceptibility Synthesis of Mn(acac)3
... • Crystal field theory predicts that the five d orbitals split. – 3 orbitals of low energy, t2g – 2 orbitals of high energy, eg ...
... • Crystal field theory predicts that the five d orbitals split. – 3 orbitals of low energy, t2g – 2 orbitals of high energy, eg ...
Primary electrons make random elastic and inelastic collision either
... effect…. i.e. as to pass though the stronger electric filed, close to nuclei, it will suffer a “quantum jump” to a low energy state, which will make emission of X-ray photon, and it would be all possible energy up to E0… Secondary electron, (<50 eV, normally around 2-6 eV, larger than sample’s work ...
... effect…. i.e. as to pass though the stronger electric filed, close to nuclei, it will suffer a “quantum jump” to a low energy state, which will make emission of X-ray photon, and it would be all possible energy up to E0… Secondary electron, (<50 eV, normally around 2-6 eV, larger than sample’s work ...
File - Science With BLT
... ____ 20. Which is the best reason that the atomic radius generally increases with atomic number in each group of elements? a. The nuclear charge increases. c. The number of energy levels increases. b. The number of neutrons increases. d. A new octet forms. ____ 21. In Groups 13 through 18, valence e ...
... ____ 20. Which is the best reason that the atomic radius generally increases with atomic number in each group of elements? a. The nuclear charge increases. c. The number of energy levels increases. b. The number of neutrons increases. d. A new octet forms. ____ 21. In Groups 13 through 18, valence e ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... Anything that occupies space. Composed of one or more chemical elements. ...
... Anything that occupies space. Composed of one or more chemical elements. ...
1. Define each of the following terms: a.Alkaline earth metals
... to reverse all characteristics of a chemical change.) ...
... to reverse all characteristics of a chemical change.) ...
Materials Science for Chemical Engineers
... - When 2 atoms or more atoms are more stable as an aggregate, a chemical bond is formed. What is the criteria for an unstable atom?- an incompletely filled quantum shell How does the atom fill this cell?- by forming a chemical bond Types of Bonding (1) strong, primary or chemical bonds: Covalent Bon ...
... - When 2 atoms or more atoms are more stable as an aggregate, a chemical bond is formed. What is the criteria for an unstable atom?- an incompletely filled quantum shell How does the atom fill this cell?- by forming a chemical bond Types of Bonding (1) strong, primary or chemical bonds: Covalent Bon ...
2.1 The Nature of Matter - Sonoma Valley High School
... neutrons and different mass. All isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties b/c their electrons are the same. ...
... neutrons and different mass. All isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties b/c their electrons are the same. ...