Stoichiometry Mole Concept Balancing Chemical Equations
... To make the crystal lattice collapse (melt) requires high temperatures Gaseous ion pairs exist when the compound vaporises – this requires very high temperatures ...
... To make the crystal lattice collapse (melt) requires high temperatures Gaseous ion pairs exist when the compound vaporises – this requires very high temperatures ...
Study Guide Answers
... 21. A mixture is created when two pure substances are combined so that each of the pure substances retains its own properties. 22. Where is the majority of the mass of an atom located? In the nucleus. 23. If an atom loses electron’s, will it have a positive or negative charge? Explain. Positive char ...
... 21. A mixture is created when two pure substances are combined so that each of the pure substances retains its own properties. 22. Where is the majority of the mass of an atom located? In the nucleus. 23. If an atom loses electron’s, will it have a positive or negative charge? Explain. Positive char ...
Chapter 5 The Drude Theory of Metals
... * A “ gas of conduction electrons of mass m, which move against a background of heavy immobile ions Electron density ...
... * A “ gas of conduction electrons of mass m, which move against a background of heavy immobile ions Electron density ...
Review Questions
... 5. Find the percent composition of Oxygen in Na2S2O3 __________________________ ...
... 5. Find the percent composition of Oxygen in Na2S2O3 __________________________ ...
Trends in the periodic table - Brigham Young University
... M + H2O MOH (M = Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs) ...
... M + H2O MOH (M = Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs) ...
Review-Semester Final (Part I)
... 20. List two ways that elements in the same group are similar to one another: ...
... 20. List two ways that elements in the same group are similar to one another: ...
File
... • The chemical formula gives the exact numbers of atoms in each molecule • Diatomic molecules consist of only two atoms of either the same or different elements ...
... • The chemical formula gives the exact numbers of atoms in each molecule • Diatomic molecules consist of only two atoms of either the same or different elements ...
First Semester Honors Chemistry Exam Review (2011
... 68. In drawing a Lewis structure, each nonmetal atom except hydrogen should be surrounded by how many electrons? 69. What do you need to know to draw a Lewis structure? 70. Multiple covalent bonds may occur in atoms that contain carbon, nitrogen, or… 71. Explain the valence electrons in metals. 72. ...
... 68. In drawing a Lewis structure, each nonmetal atom except hydrogen should be surrounded by how many electrons? 69. What do you need to know to draw a Lewis structure? 70. Multiple covalent bonds may occur in atoms that contain carbon, nitrogen, or… 71. Explain the valence electrons in metals. 72. ...
chemistry i
... decreases. The equation E = hν means that as frequency increases, energy increases. Using this information and the reference tables, which color of visible light has the least energy? A. Red b. Yellow c. Green d. Violet 38. If an electron drops from n=6 to n=2, what type of electromagnetic radiation ...
... decreases. The equation E = hν means that as frequency increases, energy increases. Using this information and the reference tables, which color of visible light has the least energy? A. Red b. Yellow c. Green d. Violet 38. If an electron drops from n=6 to n=2, what type of electromagnetic radiation ...
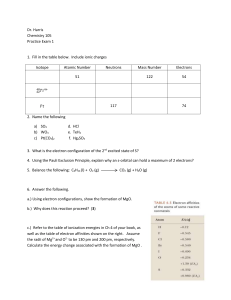
Dr. Harris Chemistry 105 Practice Exam 1 Isotope Atomic Number
... c.) Refer to the table of ionization energies in Ch 4 of your book, as well as the table of electron affinities shown on the right. Assume the radii of Mg2+ and O2- to be 130 pm and 200 pm, respectively. Calculate the energy change associated with the formation of MgO . ...
... c.) Refer to the table of ionization energies in Ch 4 of your book, as well as the table of electron affinities shown on the right. Assume the radii of Mg2+ and O2- to be 130 pm and 200 pm, respectively. Calculate the energy change associated with the formation of MgO . ...
Chemical Bonding
... of only one type of atom. • Isotopes are elements with different numbers of neutrons. • Because isotopes have the same number electrons, all isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties. ...
... of only one type of atom. • Isotopes are elements with different numbers of neutrons. • Because isotopes have the same number electrons, all isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties. ...
Learning Standards vocab chemical basis and molecules of life 09
... Given the number of protons, identify the element using a Periodic Table. Explain the arrangement of the elements on the Periodic Table, including the significant relationships among elements in a given column or row. Explain how ions and ionic bonds are formed (e.g., sodium atoms lose an elec ...
... Given the number of protons, identify the element using a Periodic Table. Explain the arrangement of the elements on the Periodic Table, including the significant relationships among elements in a given column or row. Explain how ions and ionic bonds are formed (e.g., sodium atoms lose an elec ...
smart_materials_1 - Aldercar High School
... Regular structure, layers slide CONDUCT: YES (very well) Free electrons between ions ...
... Regular structure, layers slide CONDUCT: YES (very well) Free electrons between ions ...
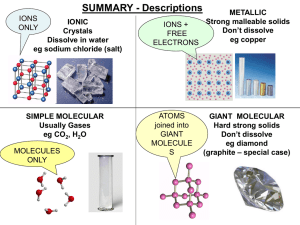
2 Types of Chemical Bonds
... 1. Ionic Bond – gain or lose valence electrons • This is a chemical bond formed by the attraction between positive (+) and negative (-) ions. What types of elements form Ionic Bonds? Metal elements: • Lose valence electrons to form (+) ions • Easier to lose than gain to get 8 Non Metal elements: • G ...
... 1. Ionic Bond – gain or lose valence electrons • This is a chemical bond formed by the attraction between positive (+) and negative (-) ions. What types of elements form Ionic Bonds? Metal elements: • Lose valence electrons to form (+) ions • Easier to lose than gain to get 8 Non Metal elements: • G ...
Study Guide Matter: Building Blocks of the Universe
... * Know that transition metals can conduct heat and electricity may be brightly colored Matter: Building Blocks of the Universe Chapter 4 & 5 Study Guide ...
... * Know that transition metals can conduct heat and electricity may be brightly colored Matter: Building Blocks of the Universe Chapter 4 & 5 Study Guide ...
Chemistry for Bio 11
... • All Living things are made of matter • The interactions of matter are described by chemical principles • Biolgists are interested in: – Biochemical reactions ...
... • All Living things are made of matter • The interactions of matter are described by chemical principles • Biolgists are interested in: – Biochemical reactions ...
CHEMISTRY
... and neutrons Isotope: different number of neutrons Changes weight Ex: C12 vs C14 ...
... and neutrons Isotope: different number of neutrons Changes weight Ex: C12 vs C14 ...
chapter02_part1_lecture - bloodhounds Incorporated
... 2.2 Elements and Compounds • Molecules form when two or more atoms bond together (example: O2) • Compounds form when two or more different elements bond together (H2O) • When a chemical reaction occurs, energy may be given off or absorbed. ...
... 2.2 Elements and Compounds • Molecules form when two or more atoms bond together (example: O2) • Compounds form when two or more different elements bond together (H2O) • When a chemical reaction occurs, energy may be given off or absorbed. ...
Chapter 2 part 1
... 2.2 Elements and Compounds • Molecules form when two or more atoms bond together (example: O2) • Compounds form when two or more different elements bond together (H2O) • When a chemical reaction occurs, energy may be given off or absorbed. ...
... 2.2 Elements and Compounds • Molecules form when two or more atoms bond together (example: O2) • Compounds form when two or more different elements bond together (H2O) • When a chemical reaction occurs, energy may be given off or absorbed. ...
Unit 6 Worksheet Package
... charged ions, or _____________, and negatively charged ions called _____________. The attraction between these two types of ions forms an _____________ bond. Nearly all ionic compounds are _____________ solids at room temperature. In these solids the total _____________ charge is balanced by the tot ...
... charged ions, or _____________, and negatively charged ions called _____________. The attraction between these two types of ions forms an _____________ bond. Nearly all ionic compounds are _____________ solids at room temperature. In these solids the total _____________ charge is balanced by the tot ...
Remember Question words
... shell = a particular region where electrons can orbit the nucleus of an atom valence electron = an electron in the outermost shell of an atom charges (positive = proton; neutral = neutron; negative = ...
... shell = a particular region where electrons can orbit the nucleus of an atom valence electron = an electron in the outermost shell of an atom charges (positive = proton; neutral = neutron; negative = ...
Introduction_to_Geochemistry_Pre-Lecture_Quiz
... detach the loosest electron from atoms of that element. (e) All alkali metals have similar chemical properties. (f) Alkali earths have one electron in the outer shell. (g) Electronegativity is the amount of negative charge on an atom. (h) Ca has a valency of 2. (i) True ionic bonds are unknown and a ...
... detach the loosest electron from atoms of that element. (e) All alkali metals have similar chemical properties. (f) Alkali earths have one electron in the outer shell. (g) Electronegativity is the amount of negative charge on an atom. (h) Ca has a valency of 2. (i) True ionic bonds are unknown and a ...
Nickel 28 Ni 58.693
... particles are loosely packed liquids do not have a definite shape & take the shape of their container particles are spaced far apart gases do not have a definite shape they fill their container (particles spread out) ...
... particles are loosely packed liquids do not have a definite shape & take the shape of their container particles are spaced far apart gases do not have a definite shape they fill their container (particles spread out) ...