Chapter8 - Louisiana Tech University
... Two laws of thermodynamics, the science involved with energy flow in physical and chemical change, are of particular importance to us. The first law, the law of conservation of energy, and the second law, entropy or disorder, can provide us with basic information regarding the spontaneity of chemica ...
... Two laws of thermodynamics, the science involved with energy flow in physical and chemical change, are of particular importance to us. The first law, the law of conservation of energy, and the second law, entropy or disorder, can provide us with basic information regarding the spontaneity of chemica ...
CHEM WKST: EQUILIBRIUM / LE CHATELIER`S PRINCIPLE
... g) A catalyst is added. no shift 8) For the reaction: N2(g) + 6HCl(g) ⇄ 2NH3(g) + 3Cl2(g); ΔH = +461 kJ Indicate what happens to [HCl] if the following changes occur. a) More N2 is added. [HCl] ↓ b) Some NH3 is removed. [HCl] ↓ c) The temperature is increased. [HCl] ↓ d) The pressure is lowered. [HC ...
... g) A catalyst is added. no shift 8) For the reaction: N2(g) + 6HCl(g) ⇄ 2NH3(g) + 3Cl2(g); ΔH = +461 kJ Indicate what happens to [HCl] if the following changes occur. a) More N2 is added. [HCl] ↓ b) Some NH3 is removed. [HCl] ↓ c) The temperature is increased. [HCl] ↓ d) The pressure is lowered. [HC ...
Week - Mat-Su School District
... iii. Oxidation-reduction (redox) 1. Oxidation numbers 2. The electrons role 3. Electrochemistry, electrolytic & galvanic cells, Faradays laws, standard half-cell potentials, Nernst equation ...
... iii. Oxidation-reduction (redox) 1. Oxidation numbers 2. The electrons role 3. Electrochemistry, electrolytic & galvanic cells, Faradays laws, standard half-cell potentials, Nernst equation ...
PPT - Unit 5
... -(C2H2(g) + 5/2O2(g) → 2CO2(g) + H2O(l) ΔH = -1300. kJ) 2( C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ) 2(ΔH = -394 kJ) H2(g) + 1/2O2(g) → H2O(l) ΔH = -286 kJ Calculate ΔH for the following reaction: 2C(s) + H2(g) → C2H2(g) 2C(s) + 2O2(g) → 2CO2(g) ΔH = -788 kJ 2CO2(g) + H2O(l) → C2H2(g) + 5/2O2(g) ΔH = +1300 kJ H2(g) + ...
... -(C2H2(g) + 5/2O2(g) → 2CO2(g) + H2O(l) ΔH = -1300. kJ) 2( C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ) 2(ΔH = -394 kJ) H2(g) + 1/2O2(g) → H2O(l) ΔH = -286 kJ Calculate ΔH for the following reaction: 2C(s) + H2(g) → C2H2(g) 2C(s) + 2O2(g) → 2CO2(g) ΔH = -788 kJ 2CO2(g) + H2O(l) → C2H2(g) + 5/2O2(g) ΔH = +1300 kJ H2(g) + ...
do not - wwphs
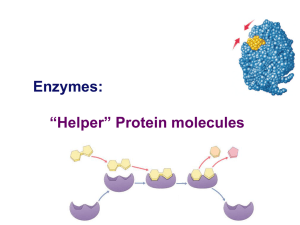
... How do enzymes work? 1) Enzymes act upon a substance called a substrate 2) The enzyme has an indent in it called the active site where the substrate can fit into, kind of like a lock and a key ...
... How do enzymes work? 1) Enzymes act upon a substance called a substrate 2) The enzyme has an indent in it called the active site where the substrate can fit into, kind of like a lock and a key ...
Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi © 2016 Ebneshahidi
... - Hypotonic : solution with a lower osmotic pressure cells in hyportonic solution gain H2O and swell. - Isotonic : same tonicity - cell in isotonic solutions neither gain, nor lose H2O. ...
... - Hypotonic : solution with a lower osmotic pressure cells in hyportonic solution gain H2O and swell. - Isotonic : same tonicity - cell in isotonic solutions neither gain, nor lose H2O. ...
! !! ! n nn N P =
... Which of the following is the Zeroth law of thermodynamics? A. Energy can never be created or destroyed but it can be changed from one form to another. B. Two bodies in thermal contact are at thermal equilibrium with each other if the two bodies are at the same absolute temperature. C. Any process c ...
... Which of the following is the Zeroth law of thermodynamics? A. Energy can never be created or destroyed but it can be changed from one form to another. B. Two bodies in thermal contact are at thermal equilibrium with each other if the two bodies are at the same absolute temperature. C. Any process c ...
Practice Test 2
... acidity. In one analysis of a commercial vinegar brand, a 15.0 mL sample was titrated with 0.4500 M NaOH. It required 30.50 mL of this NaOH solution to neutralize the acid in the vinegar sample. What is the molar concentration of acetic acid in vinegar? A) B) C) D) ...
... acidity. In one analysis of a commercial vinegar brand, a 15.0 mL sample was titrated with 0.4500 M NaOH. It required 30.50 mL of this NaOH solution to neutralize the acid in the vinegar sample. What is the molar concentration of acetic acid in vinegar? A) B) C) D) ...
Equilibrium (Sheet 1)
... Section III La Chatelier's principle states that if a stress such as a change in concentration, pressure or temperature is applied to a system in equilibrium, the equilibrium will shift in a way that tends to undo the effect of the stress. For example: H2O + CO H2 + CO2 + heat. If no stress is intro ...
... Section III La Chatelier's principle states that if a stress such as a change in concentration, pressure or temperature is applied to a system in equilibrium, the equilibrium will shift in a way that tends to undo the effect of the stress. For example: H2O + CO H2 + CO2 + heat. If no stress is intro ...
2. Covalent network
... Ideal Gas Law: PV=nRT Constants from previous 3 laws (k,b,a) are combined to make a universal constant R. R=.0821 (L*atm)/(mol*k) It can be used to solve for pressure, number of moles, volume, or temberature when all other variables are held constant. At STP (0C and 1atm), the molar volume of an id ...
... Ideal Gas Law: PV=nRT Constants from previous 3 laws (k,b,a) are combined to make a universal constant R. R=.0821 (L*atm)/(mol*k) It can be used to solve for pressure, number of moles, volume, or temberature when all other variables are held constant. At STP (0C and 1atm), the molar volume of an id ...
Effect of Potassium on Sol-Gel Cerium and Lanthanum Oxide
... Therefore, the catalysts used in the catalytic combustion of soot must be capable of presenting catalyst activity at low temperatures [10]. An important number of catalytic formulations have been developed in this field, including oxides [11]-[14], perovskites [9] [15]-[17], spinels [18] and metals ...
... Therefore, the catalysts used in the catalytic combustion of soot must be capable of presenting catalyst activity at low temperatures [10]. An important number of catalytic formulations have been developed in this field, including oxides [11]-[14], perovskites [9] [15]-[17], spinels [18] and metals ...
Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... Enzymes aren’t used up Enzymes are not changed by the reaction used only temporarily – like a taxi re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions ...
... Enzymes aren’t used up Enzymes are not changed by the reaction used only temporarily – like a taxi re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions ...
chemical reaction
... • Most chemical reactions speed up when temperature increases. • Molecules collide more frequently at higher temperatures that at lower temperatures. ...
... • Most chemical reactions speed up when temperature increases. • Molecules collide more frequently at higher temperatures that at lower temperatures. ...
Example - cloudfront.net
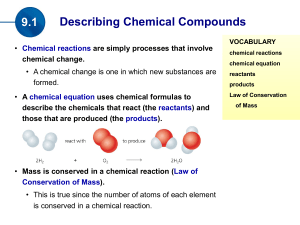
... The law of conservation of _________ must be satisfied. Chemical Reactions Chemical equations give information in two major areas: 1. ______________ and ______________ of the reaction. 2. __________________ of a balanced chemical equation tell us the ___________ of the substances involved. Example o ...
... The law of conservation of _________ must be satisfied. Chemical Reactions Chemical equations give information in two major areas: 1. ______________ and ______________ of the reaction. 2. __________________ of a balanced chemical equation tell us the ___________ of the substances involved. Example o ...
(the products). Mass is conserved in a chemical reaction
... which states that molecules must collide in order to react. • Collisions must also be effective, which means that they must have sufficient energy for a reaction to occur. ...
... which states that molecules must collide in order to react. • Collisions must also be effective, which means that they must have sufficient energy for a reaction to occur. ...
Conservation of Energy in chemical reactions, Hess`s Law
... What kind of change is occurring this time, and what elements are involved? What is the critical difference? What would H be in the second reaction? _____ Why does this make sense? ...
... What kind of change is occurring this time, and what elements are involved? What is the critical difference? What would H be in the second reaction? _____ Why does this make sense? ...
Surface chemistry Surface chemistry deals with phenomena that
... The reactants must get adsorbed reasonably strongly on to the catalyst to become active. However, they must not get adsorbed so strongly that they are immobilised and other reactants are left with no space on the catalyst’s surface for adsorption. (b) Selectivity The selectivity of a catalyst is its ...
... The reactants must get adsorbed reasonably strongly on to the catalyst to become active. However, they must not get adsorbed so strongly that they are immobilised and other reactants are left with no space on the catalyst’s surface for adsorption. (b) Selectivity The selectivity of a catalyst is its ...
Catalysis

Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required.