Ch. 7 & 8 Notes (Chemical Reactions) teacher
... Review: Reactants are on the ______ left side of the arrow, and the right yields products are on the __________ side. The arrow means “________”, or “reacts to produce” when read aloud. ...
... Review: Reactants are on the ______ left side of the arrow, and the right yields products are on the __________ side. The arrow means “________”, or “reacts to produce” when read aloud. ...
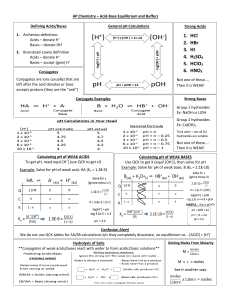
Full answers
... There are only dispersion forces between the molecules in CH4 and I2. The I atom is a large, many-electron atom so its electron cloud is more easily polarised than the C or H in CH4 and therefore I2 has stronger dispersion forces and the higher melting point. NaCl is an ionic compound with strong co ...
... There are only dispersion forces between the molecules in CH4 and I2. The I atom is a large, many-electron atom so its electron cloud is more easily polarised than the C or H in CH4 and therefore I2 has stronger dispersion forces and the higher melting point. NaCl is an ionic compound with strong co ...
Examples of Colligative properties are
... Introduction Colligative properties ==> Properties of solutions which depend on the number of solute particles but not on their nature. Examples of Colligative properties are: ...
... Introduction Colligative properties ==> Properties of solutions which depend on the number of solute particles but not on their nature. Examples of Colligative properties are: ...
Name……………………………………............................. Index number
... (b)Use dots ( ) and crosses (x) to show bonding in the compound formed in (a) above. (1mark) ...
... (b)Use dots ( ) and crosses (x) to show bonding in the compound formed in (a) above. (1mark) ...
Study Guide KEY Exam III F 2012
... b) Use the initial rate data to write the specific rate law consistent with the data. Make sure you solve to obtain a numerical value for k. c) Write a chemical rxn. for the reactant side of the rate limiting step in the rxn. mechanism. d) What is the initial rate of the rxn. with 0.090 M Fe3+ and 0 ...
... b) Use the initial rate data to write the specific rate law consistent with the data. Make sure you solve to obtain a numerical value for k. c) Write a chemical rxn. for the reactant side of the rate limiting step in the rxn. mechanism. d) What is the initial rate of the rxn. with 0.090 M Fe3+ and 0 ...
Final Exam Review Day 1
... Kinetic Molecular Theory assumes gases are made up of _________ ___________ moving in _____________ ___________, colliding into each other with ______________ collisions. As temperature increases, the particle movement also _____________________. Gases do not behave ideally when gases stop moving (o ...
... Kinetic Molecular Theory assumes gases are made up of _________ ___________ moving in _____________ ___________, colliding into each other with ______________ collisions. As temperature increases, the particle movement also _____________________. Gases do not behave ideally when gases stop moving (o ...
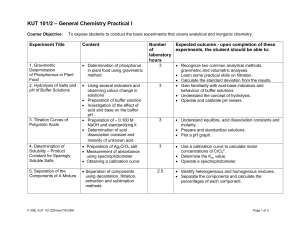
KUT 101/2 – General Chemistry Practical I
... • Differentiate the primary and secondary standards. • Differentiate the equivalence and end-points. • Choose suitable indicators for acid-base titration. • Determine the amount of acid in an unknown. • Know a quantitative technique of volumetric analysis. • Understand the definition of BOD (Biochem ...
... • Differentiate the primary and secondary standards. • Differentiate the equivalence and end-points. • Choose suitable indicators for acid-base titration. • Determine the amount of acid in an unknown. • Know a quantitative technique of volumetric analysis. • Understand the definition of BOD (Biochem ...
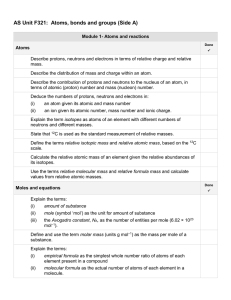
Document
... 13.11.2014 => Calculation of composition of reaction under equilibrium conditions, Phase equilibrium in a one-component system 20.11.2014 => Standard free energy, equilibrium constant, calculation of composition of reaction under equilibrium conditions, Phase equilibrium in a one-component system 27 ...
... 13.11.2014 => Calculation of composition of reaction under equilibrium conditions, Phase equilibrium in a one-component system 20.11.2014 => Standard free energy, equilibrium constant, calculation of composition of reaction under equilibrium conditions, Phase equilibrium in a one-component system 27 ...
Chemistry
... you will have to develop good study habits. Science courses, and chemistry in particular, make different demands on your learning skills than do other types of courses. We offer the following tips for success in your study of chemistry: Don’t fall behind! As the course moves along, new topics will b ...
... you will have to develop good study habits. Science courses, and chemistry in particular, make different demands on your learning skills than do other types of courses. We offer the following tips for success in your study of chemistry: Don’t fall behind! As the course moves along, new topics will b ...
UNIT 7 – CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... 1. A ________________________ is simply a chemical change. It is the process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances. 2. The original substances are known as ____________________ while the resulting substances are called ____________________. 3. Evidence of ...
... 1. A ________________________ is simply a chemical change. It is the process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances. 2. The original substances are known as ____________________ while the resulting substances are called ____________________. 3. Evidence of ...
Equilibrium chemistry
Equilibrium chemistry is a concerned with systems in chemical equilibrium. The unifying principle is that the free energy of a system at equilibrium is the minimum possible, so that the slope of the free energy with respect to the reaction coordinate is zero. This principle, applied to mixtures at equilibrium provides a definition of an equilibrium constant. Applications include acid-base, host-guest, metal-complex, solubility, partition, chromatography and redox equilibria.