Answers - University of Waterloo
... 5. Carefully detach the last page. It is the datasheet. 6. Now answer the exam questions. Questions are not in order of difficulty. Indicate your choice on the STUDENT RESPONSE sheet by marking one letter beside the question number. • Mark only one answer for each question. • Questions are all of th ...
... 5. Carefully detach the last page. It is the datasheet. 6. Now answer the exam questions. Questions are not in order of difficulty. Indicate your choice on the STUDENT RESPONSE sheet by marking one letter beside the question number. • Mark only one answer for each question. • Questions are all of th ...
Chapter 4: Reactions in Aqueous Solution
... B) Solvent – dissolving medium. This component is always in greatest amount. C) Most chemical reactions are carried out in the liquid state or in solution. This is due to the requirement that reactant molecules or ions be highly mobile so they can interact with each other. 2) Although solutions can ...
... B) Solvent – dissolving medium. This component is always in greatest amount. C) Most chemical reactions are carried out in the liquid state or in solution. This is due to the requirement that reactant molecules or ions be highly mobile so they can interact with each other. 2) Although solutions can ...
`A` LEVEL H2 CHEMISTRY ORGANIC REACTIONS SUMMARY By
... (a) explain that some chemical reactions are accompanied by energy changes, principally in the form of heat energy; the energy changes can be exothermic (∆H negative) or endothermic (∆H positive) (b) explain and use the terms: (i) enthalpy change of reaction and standard conditions, with particular ...
... (a) explain that some chemical reactions are accompanied by energy changes, principally in the form of heat energy; the energy changes can be exothermic (∆H negative) or endothermic (∆H positive) (b) explain and use the terms: (i) enthalpy change of reaction and standard conditions, with particular ...
Full text, pdf
... life. To better understand these constraints, it might be useful to formulate those traits of the evolutionary process that might be instrumental for the reconstruction of the primordial events. 1) According to Darwin, biological evolution is driven by the selection of the fittest. Living organisms ...
... life. To better understand these constraints, it might be useful to formulate those traits of the evolutionary process that might be instrumental for the reconstruction of the primordial events. 1) According to Darwin, biological evolution is driven by the selection of the fittest. Living organisms ...
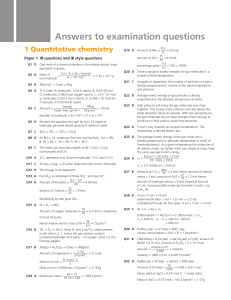
Answers to examination questions
... directly proportional to volume at the same temperature and pressure. Q22 D Average kinetic energy of gas particles is directly proportional to the absolute temperature in kelvin. Q23 D High pressure will bring the gas molecules very close together. This causes more collisions and also allow ...
... directly proportional to volume at the same temperature and pressure. Q22 D Average kinetic energy of gas particles is directly proportional to the absolute temperature in kelvin. Q23 D High pressure will bring the gas molecules very close together. This causes more collisions and also allow ...
Chemical Energy
... The energy released in a chemical reaction raises the internal energy, E, and does work under constant pressure at the expense of energy stored in compounds. Thus, ...
... The energy released in a chemical reaction raises the internal energy, E, and does work under constant pressure at the expense of energy stored in compounds. Thus, ...
Chapter 23 The Chemistry of Amines
... product A can form an ethyl ether, its —OH group is not affected in the first reaction. Consequently, compound A is p-acetamidophenol and compound B is its ethyl ether. This is reasonable because, so long as the hydroxy group is not ionized, the amino group is the most basic group in the molecule, a ...
... product A can form an ethyl ether, its —OH group is not affected in the first reaction. Consequently, compound A is p-acetamidophenol and compound B is its ethyl ether. This is reasonable because, so long as the hydroxy group is not ionized, the amino group is the most basic group in the molecule, a ...
CO Oxidation on Palladium. 2. A Combined
... Representative isosteric plots are shown in Figure 4 for CO coverages of 0.005, 0.12, 0.24, and 0.31 monolayer. Applying the Clausius-Clapeyron equation, d(ln P)/d(l/T) = -E/R, desorption activation energies can be determined for various CO coverages. The isosteric heat of adsorption of CO on Pd( 11 ...
... Representative isosteric plots are shown in Figure 4 for CO coverages of 0.005, 0.12, 0.24, and 0.31 monolayer. Applying the Clausius-Clapeyron equation, d(ln P)/d(l/T) = -E/R, desorption activation energies can be determined for various CO coverages. The isosteric heat of adsorption of CO on Pd( 11 ...
1.02 x 10 = 3 mol lit 3.4 x 10
... (ii) When hydrogen sulphide is passed through acidified zinc sulphate solution, white ppt of zinc sulphide is not formed. Ans: The solubility product of zinc sulphide is high and is not exceeded by ionic product in acid solution and so remains in solution. In acid solution dissociation of H2S is sup ...
... (ii) When hydrogen sulphide is passed through acidified zinc sulphate solution, white ppt of zinc sulphide is not formed. Ans: The solubility product of zinc sulphide is high and is not exceeded by ionic product in acid solution and so remains in solution. In acid solution dissociation of H2S is sup ...
DFT Studies of the Zinc Complexes of DNA Bases
... complex is the bridging complex in which Zn forms a fivemembered ring, interacting with both N and N . The zinc cation association energy of this complex is −213.79 kcal/ mol as shown in Table 2. The bicoordination of zinc cation yields the more stable adenine-Zn complex. As shown in Table 1, associ ...
... complex is the bridging complex in which Zn forms a fivemembered ring, interacting with both N and N . The zinc cation association energy of this complex is −213.79 kcal/ mol as shown in Table 2. The bicoordination of zinc cation yields the more stable adenine-Zn complex. As shown in Table 1, associ ...
Energetics - chemistryatdulwich
... size of ion: the smaller the ion , the larger the electrostatic attraction and the more energy is needed to sublime the ions. charge of the ion: the larger the charge, the greater the electrostatic attraction. The smaller the ionic radius and the greater the charge of the ion the greater the charg ...
... size of ion: the smaller the ion , the larger the electrostatic attraction and the more energy is needed to sublime the ions. charge of the ion: the larger the charge, the greater the electrostatic attraction. The smaller the ionic radius and the greater the charge of the ion the greater the charg ...
Formation Mechanism of Non-Metallic Inclusions in
... considered; they included Fe, Cr, Ni, Si, Mn, Al, S and O. It was observed that this approach is more accurate, as all interactions among the system elements are considered. Especially important is the effect of O on Al activity: since the interaction coefficient is negative and significant in absol ...
... considered; they included Fe, Cr, Ni, Si, Mn, Al, S and O. It was observed that this approach is more accurate, as all interactions among the system elements are considered. Especially important is the effect of O on Al activity: since the interaction coefficient is negative and significant in absol ...
Equilibrium chemistry
Equilibrium chemistry is a concerned with systems in chemical equilibrium. The unifying principle is that the free energy of a system at equilibrium is the minimum possible, so that the slope of the free energy with respect to the reaction coordinate is zero. This principle, applied to mixtures at equilibrium provides a definition of an equilibrium constant. Applications include acid-base, host-guest, metal-complex, solubility, partition, chromatography and redox equilibria.