Nitrogen and its compounds - kcpe-kcse
... The drying agent used for ammonia is quick lime. Other drying agents such as concentrated sulphuric acid or phosphorus (V) oxide or fused calcium chloride cannot dry an alkaline gas like ammonia. Sulphuric acid and phosphorus (V) oxide are both acidic. They react with ammonia, forming their respecti ...
... The drying agent used for ammonia is quick lime. Other drying agents such as concentrated sulphuric acid or phosphorus (V) oxide or fused calcium chloride cannot dry an alkaline gas like ammonia. Sulphuric acid and phosphorus (V) oxide are both acidic. They react with ammonia, forming their respecti ...
Chapter 1 - Atoms: The Quantum World
... These values of the point electron density are huge. Expressing them on a scale more nearly comparable to the size of the atom (a0) gives the values electron electron ...
... These values of the point electron density are huge. Expressing them on a scale more nearly comparable to the size of the atom (a0) gives the values electron electron ...
Lecture Resource ()
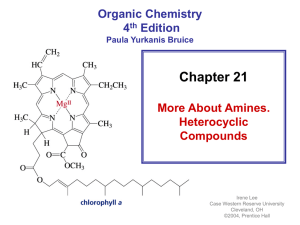
... • Some amines are heterocyclic compounds (or heterocycles) • Most drugs, vitamins, and many other natural products are heterocycles • A natural product is a compound synthesized by a plant or an animal ...
... • Some amines are heterocyclic compounds (or heterocycles) • Most drugs, vitamins, and many other natural products are heterocycles • A natural product is a compound synthesized by a plant or an animal ...
The Sabatier Principle Illustrated by Catalytic H2
... activities predicted by our model corresponds well with the observed activities. That is, the metals that bind OH too strongly are poor catalysts and thus lie on the left side of the volcano. These metals are inherently unstable in an oxidizing environment; indeed, these metals will form oxides afte ...
... activities predicted by our model corresponds well with the observed activities. That is, the metals that bind OH too strongly are poor catalysts and thus lie on the left side of the volcano. These metals are inherently unstable in an oxidizing environment; indeed, these metals will form oxides afte ...
energy and rates practice test answers
... combustion of magnesium the result would be a. x + y d. x – 2y b. x – y e. not enough information is given c. 2x – y ...
... combustion of magnesium the result would be a. x + y d. x – 2y b. x – y e. not enough information is given c. 2x – y ...
answer
... There are a number of reasons why platinum(II) forms square-planar rather than tetrahedral complexes. These include: (i) Pt(II) is a relatively big cation and so repulsion between the ligands are not too large. (ii) The Pt-ligands bonds are stronger as, with its 5d8 configuration, Pt(II) is able to ...
... There are a number of reasons why platinum(II) forms square-planar rather than tetrahedral complexes. These include: (i) Pt(II) is a relatively big cation and so repulsion between the ligands are not too large. (ii) The Pt-ligands bonds are stronger as, with its 5d8 configuration, Pt(II) is able to ...
Chapter 07 and 08 Chemical Bonding and Molecular
... • Made of 2 or more elements in a definite proportion by mass • Physically and chemically different from the elements that make up the compound • All elements (except Noble gases) react to gain a stable octet. (duet-for H through B) • Compounds form to gain a stable valence shell which is LOWER IN E ...
... • Made of 2 or more elements in a definite proportion by mass • Physically and chemically different from the elements that make up the compound • All elements (except Noble gases) react to gain a stable octet. (duet-for H through B) • Compounds form to gain a stable valence shell which is LOWER IN E ...
Solon City Schools
... • A piece of aluminum foil 5.11 in x 3.23 in x 0.0381 in is dissolved in excess HCl(aq). How many grams of H2(g) are produced? • How many grams of each reactant are needed to produce 15 grams of iron form the following reaction? Fe2O3(s) + Al(s) Fe(s) + Al2O3(s) ...
... • A piece of aluminum foil 5.11 in x 3.23 in x 0.0381 in is dissolved in excess HCl(aq). How many grams of H2(g) are produced? • How many grams of each reactant are needed to produce 15 grams of iron form the following reaction? Fe2O3(s) + Al(s) Fe(s) + Al2O3(s) ...
Chapter 20
... How do you identify the oxidizing agent and the reducing agent in a redox reaction? The species reduced is the oxidizing agent. The species oxidized is the reducing agent. ...
... How do you identify the oxidizing agent and the reducing agent in a redox reaction? The species reduced is the oxidizing agent. The species oxidized is the reducing agent. ...
Chapter 2
... • A piece of aluminum foil 5.11 in x 3.23 in x 0.0381 in is dissolved in excess HCl(aq). How many grams of H2(g) are produced? • How many grams of each reactant are needed to produce 15 grams of iron form the following reaction? Fe2O3(s) + Al(s) Fe(s) + Al2O3(s) ...
... • A piece of aluminum foil 5.11 in x 3.23 in x 0.0381 in is dissolved in excess HCl(aq). How many grams of H2(g) are produced? • How many grams of each reactant are needed to produce 15 grams of iron form the following reaction? Fe2O3(s) + Al(s) Fe(s) + Al2O3(s) ...
with answers
... (c) Give the electronic configurations of sodium (Na) and nitrogen (N), showing clearly how electrons are distributed between orbitals of the same energy. Na (Z=11): 1s²2s²2p63s N (Z=7): 1s²2s²2px2py2pz (d) Explain why compounds of the formulae Na2O and NH3 form from their respective constituent ele ...
... (c) Give the electronic configurations of sodium (Na) and nitrogen (N), showing clearly how electrons are distributed between orbitals of the same energy. Na (Z=11): 1s²2s²2p63s N (Z=7): 1s²2s²2px2py2pz (d) Explain why compounds of the formulae Na2O and NH3 form from their respective constituent ele ...
Matter and Measurement
... An atom is oxidized (loses electrons) if its oxidation number increases, and is reduced (gains electrons) if its oxidation number decreases An oxidizing agent causes the oxidation of another species by accepting an electron from it; in the process it is ...
... An atom is oxidized (loses electrons) if its oxidation number increases, and is reduced (gains electrons) if its oxidation number decreases An oxidizing agent causes the oxidation of another species by accepting an electron from it; in the process it is ...
sample - Bright Red Publishing
... entropy. Consider, for example, the reaction 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2NaCl(s). We know that the entropies of solids are very much smaller than the entropy of a gas and since this reaction results in a decrease in the number of moles of gaseous molecules (1 to 0), the entropy will decrease. Similarly, we w ...
... entropy. Consider, for example, the reaction 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2NaCl(s). We know that the entropies of solids are very much smaller than the entropy of a gas and since this reaction results in a decrease in the number of moles of gaseous molecules (1 to 0), the entropy will decrease. Similarly, we w ...
Chemical Reactions
... in the direction that removes heat from the system (In the above reaction you would decrease the amount of ...
... in the direction that removes heat from the system (In the above reaction you would decrease the amount of ...
chemical reaction?
... • A catalyst is a substance that changes the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up or changed very much. • Catalysts usually ____________ reaction rate by bringing together reactants • _____________ are an example of a catalyst found in living things ...
... • A catalyst is a substance that changes the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up or changed very much. • Catalysts usually ____________ reaction rate by bringing together reactants • _____________ are an example of a catalyst found in living things ...
powerpoint
... Do single replacement reactions always occur? NO! A metal will only replace a less reactive metal. The activity series is a way to predict whether or not certain reactions will occur. Any specific metal can replace any metal listed below it that is in a compound. It cannot replace any metal ...
... Do single replacement reactions always occur? NO! A metal will only replace a less reactive metal. The activity series is a way to predict whether or not certain reactions will occur. Any specific metal can replace any metal listed below it that is in a compound. It cannot replace any metal ...
Review Material
... The most common ionic charge of the fourth row transition elements, from scandium to zinc, is 2+ (e.g. Ti2+ & Fe2+). When such ions are formed, the transition metal atom loses its two 4s electrons (3d electrons are not lost). (In fact, whenever a positive ion is formed from an atom, electrons are al ...
... The most common ionic charge of the fourth row transition elements, from scandium to zinc, is 2+ (e.g. Ti2+ & Fe2+). When such ions are formed, the transition metal atom loses its two 4s electrons (3d electrons are not lost). (In fact, whenever a positive ion is formed from an atom, electrons are al ...
oxidation–reduction reaction
... • A reaction in which electrons are transferred from one atom to another is called an oxidation–reduction reaction. • Also called redox reactions ...
... • A reaction in which electrons are transferred from one atom to another is called an oxidation–reduction reaction. • Also called redox reactions ...
chemistry
... the rate of reaction by causing (1) a decrease in the activation energy (2) an increase in the activation energy (3) a decrease in the heat of reaction (4) an increase in the heat of reaction ...
... the rate of reaction by causing (1) a decrease in the activation energy (2) an increase in the activation energy (3) a decrease in the heat of reaction (4) an increase in the heat of reaction ...
File
... bonding in Metal Complexes • Basic Assumption in CFT: • Electrostatic interaction between ligand and metal d-orbitals align along the octahedral axis will be affected the most. More directly the ligand attacks the metal orbital, the higher the energy of the d-orbital. In an octahedral field the dege ...
... bonding in Metal Complexes • Basic Assumption in CFT: • Electrostatic interaction between ligand and metal d-orbitals align along the octahedral axis will be affected the most. More directly the ligand attacks the metal orbital, the higher the energy of the d-orbital. In an octahedral field the dege ...
Sample
... 41- How does the value of the equilibrium constant show that a reaction reaches equilibrium very quickly? a. The equilibrium constant Keq is large. b. The equilibrium constant Keq is small. c. The equilibrium constant Keq is zero. d. The value of the equilibrium constant does not show how quickly a ...
... 41- How does the value of the equilibrium constant show that a reaction reaches equilibrium very quickly? a. The equilibrium constant Keq is large. b. The equilibrium constant Keq is small. c. The equilibrium constant Keq is zero. d. The value of the equilibrium constant does not show how quickly a ...
Self-Test Worksheet for Thermodynamics Section (Quiz
... The heater costs $1 per min to run and it supplies 200,000 kJ of heat per minute (heat capacity of water is 4.18 J/g/°C, ∆Hfusion for water = 6.01 kJ/mol). (a) How much heat energy does the owner use? (b) How much does it cost the owner to do this? ...
... The heater costs $1 per min to run and it supplies 200,000 kJ of heat per minute (heat capacity of water is 4.18 J/g/°C, ∆Hfusion for water = 6.01 kJ/mol). (a) How much heat energy does the owner use? (b) How much does it cost the owner to do this? ...
Enthalpy diagram relating the change for a reaction to enthalpies of
... Factors That Affect Rates of Reactions 1. Physical state of the reactants: when reactants are in different phases for example when a solid reacts with a liquid the reaction is limited to the area of contact. Reactions involving solids will proceed faster if the surface area of the solid is increase ...
... Factors That Affect Rates of Reactions 1. Physical state of the reactants: when reactants are in different phases for example when a solid reacts with a liquid the reaction is limited to the area of contact. Reactions involving solids will proceed faster if the surface area of the solid is increase ...
Hydrogen Production by Splitting Water in an Electrolyzer
... II. THE COMPUTER SIMULATION TECHNIQUE Studies of reacting systems - whether small scale reactions in a laboratory or large scale processes, all focus on obtaining a basic description of the individual steps involved in the reaction, and the characteristic rate of each step. In most studies, this inf ...
... II. THE COMPUTER SIMULATION TECHNIQUE Studies of reacting systems - whether small scale reactions in a laboratory or large scale processes, all focus on obtaining a basic description of the individual steps involved in the reaction, and the characteristic rate of each step. In most studies, this inf ...
Photoredox catalysis
_Schematic.png?width=300)
Photoredox catalysis is a branch of catalysis that harnesses the energy of visible light to accelerate a chemical reaction via a single-electron transfer. This area is named as a combination of ""photo-"" referring to light and redox, a condensed expression for the chemical processes of reduction and oxidation. In particular, photoredox catalysis employs small quantities of a light-sensitive compound that, when excited by light, can mediate the transfer of electrons between chemical compounds that otherwise would not react. Photoredox catalysts are generally drawn from three classes of materials: transition-metal complexes, organic dyes and semiconductors. While each class of materials has advantages, soluble transition-metal complexes are used most often.Study of this branch of catalysis led to the development of new methods to accomplish known and new chemical transformations. One attraction to the area is that photoredox catalysts are often less toxic than other reagents often used to generate free radicals, such as organotin reagents. Furthermore, while photoredox catalysts generate potent redox agents while exposed to light, they are innocuous under ordinary conditions Thus transition-metal complex photoredox catalysts are in some ways more attractive than stoichiometric redox agents such as quinones. The properties of photoredox catalysts can be modified by changing ligands and the metal, reflecting the somewhat modular nature of the catalyst.While photoredox catalysis has most often been applied to generate known reactive intermediates in a novel way, the study of this mode of catalysis led to the discovery of new organic reactions, such as the first direct functionalization of the β-arylation of saturated aldehydes. Although the D3-symmetric transition-metal complexes used in many photoredox-catalyzed reactions are chiral, the use of enantioenriched photoredox catalysts led to low levels of enantioselectivity in a photoredox-catalyzed aryl-aryl coupling reaction, suggesting that the chiral nature of these catalysts is not yet a highly effective means of transmitting stereochemical information in photoredox reactions. However, while synthetically useful levels of enantioselectivity have not been achieved using chiral photoredox catalysts alone, optically-active products have been obtained through the synergistic combination of photoredox catalysis with chiral organocatalysts such as secondary amines and Brønsted acids.