2010 Chemistry Written examination 2
... • show all working in your answers to numerical questions. No marks will be given for an incorrect answer unless it is accompanied by details of the working. • make sure chemical equations are balanced and that the formulas for individual substances include an indication of state; for example, H2(g) ...
... • show all working in your answers to numerical questions. No marks will be given for an incorrect answer unless it is accompanied by details of the working. • make sure chemical equations are balanced and that the formulas for individual substances include an indication of state; for example, H2(g) ...
Spring 2013 Semester Exam Study Guide (Bonding, Nomenclature
... ____ 40. The concept that electrostatic repulsion between electron pairs surrounding an atom causes these pairs to be separated as far as possible is the foundation of a. VSEPR theory. c. the electron-sea model. b. the hybridization model. d. Lewis theory. ____ 41. The strong forces of attraction be ...
... ____ 40. The concept that electrostatic repulsion between electron pairs surrounding an atom causes these pairs to be separated as far as possible is the foundation of a. VSEPR theory. c. the electron-sea model. b. the hybridization model. d. Lewis theory. ____ 41. The strong forces of attraction be ...
Chemistry 11th
... (ii) The oxides of alkali and alkaline earth metal dissolve in water to form their respective hydroxides. These oxides are strong bases. However, the oxides of alkali metals are more basic than those of alkaline earth metals. This is because the ionization enthalpy of alkali metals is lower. The e ...
... (ii) The oxides of alkali and alkaline earth metal dissolve in water to form their respective hydroxides. These oxides are strong bases. However, the oxides of alkali metals are more basic than those of alkaline earth metals. This is because the ionization enthalpy of alkali metals is lower. The e ...
Honors Chemistry Curr
... Chemistry is the study of matter and the changes it undergoes. This is a comprehensive and intensive course in experimental and conceptual chemistry. The work includes history and methods of science and ranges over the nature of atoms, molecules and reactions. Among the major topics are structure, n ...
... Chemistry is the study of matter and the changes it undergoes. This is a comprehensive and intensive course in experimental and conceptual chemistry. The work includes history and methods of science and ranges over the nature of atoms, molecules and reactions. Among the major topics are structure, n ...
Lecture 3: Reaction Tables and Limiting Reactants start with PRS
... equation to obtain a different, but also balanced chemical equation for the reaction of hydrogen and oxygen molecules to form water. We will use this equation to explore our problem with 100 H2 ...
... equation to obtain a different, but also balanced chemical equation for the reaction of hydrogen and oxygen molecules to form water. We will use this equation to explore our problem with 100 H2 ...
Honors Chemistry
... Chemistry is the study of matter and the changes it undergoes. This is a comprehensive and intensive course in experimental and conceptual chemistry. The work includes history and methods of science and ranges over the nature of atoms, molecules and reactions. Among the major topics are structure, n ...
... Chemistry is the study of matter and the changes it undergoes. This is a comprehensive and intensive course in experimental and conceptual chemistry. The work includes history and methods of science and ranges over the nature of atoms, molecules and reactions. Among the major topics are structure, n ...
chemistry
... 20 A molecule of an unsaturated hydrocarbon must have (1) at least one single carbon-carbon bond (2) at least one multiple carbon-carbon bond (3) two or more single carbon-carbon bonds (4) two or more multiple carbon-carbon bonds ...
... 20 A molecule of an unsaturated hydrocarbon must have (1) at least one single carbon-carbon bond (2) at least one multiple carbon-carbon bond (3) two or more single carbon-carbon bonds (4) two or more multiple carbon-carbon bonds ...
Chapter 7: Chemical Formulas and Chemical Compounds
... In HF, the bond is polar with a partial negative charge on the fluorine and a partial positive charge on the hydrogen. If HF were an ionic compound in which an electron was fully transferred to the fluorine ion, H would have a 1+ charge and F would have a 1- charge. Thus the oxidation numbers of H a ...
... In HF, the bond is polar with a partial negative charge on the fluorine and a partial positive charge on the hydrogen. If HF were an ionic compound in which an electron was fully transferred to the fluorine ion, H would have a 1+ charge and F would have a 1- charge. Thus the oxidation numbers of H a ...
0.08206 L atm/K mol - Arizona State University
... Potential energy increases and kinetic energy increases. Potential energy increases and kinetic energy decreases. Potential energy decreases and kinetic energy increases. Potential energy decreases and kinetic energy decreases. There is no change at all. ...
... Potential energy increases and kinetic energy increases. Potential energy increases and kinetic energy decreases. Potential energy decreases and kinetic energy increases. Potential energy decreases and kinetic energy decreases. There is no change at all. ...
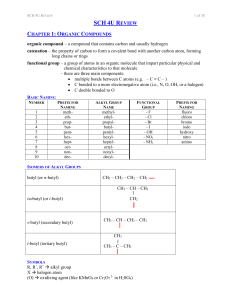
SCH 4U REVIEW Notes
... monomers; two types: addition and condensation monomer – a molecule or compound usually containing carbon and of relatively low molecular weight and simple structure which is capable of conversion to polymers by combination with itself or other similar molecules or compounds dimer – a molecule made ...
... monomers; two types: addition and condensation monomer – a molecule or compound usually containing carbon and of relatively low molecular weight and simple structure which is capable of conversion to polymers by combination with itself or other similar molecules or compounds dimer – a molecule made ...
Chemistry
... sketch and construct cells not composed of metals and solutions of their ions including cells with inert electrodes and electrolytes containing species with different oxidation states ...
... sketch and construct cells not composed of metals and solutions of their ions including cells with inert electrodes and electrolytes containing species with different oxidation states ...
Fast hydrogen elimination from the †Ru„PH3…3„CO…„H…2‡ and
... reported time-resolved data.24 In both cases we will obtain two-dimensional potential energy surfaces by fitting analytical functions to electronic calculations and will analyze the nuclear dynamics on them through the use of rigorous quantum mechanical procedures. In order to explain the experiment ...
... reported time-resolved data.24 In both cases we will obtain two-dimensional potential energy surfaces by fitting analytical functions to electronic calculations and will analyze the nuclear dynamics on them through the use of rigorous quantum mechanical procedures. In order to explain the experiment ...
Chemistry 11 Review
... Given the following balanced equation, answer the questions below it. 3 Cu(s) + 8HNO3(l) 3 Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2NO(g) + 4 H2O(l) a) ...
... Given the following balanced equation, answer the questions below it. 3 Cu(s) + 8HNO3(l) 3 Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2NO(g) + 4 H2O(l) a) ...
Leaving Cert Physics Long Questions 13. The
... Read this passage and answer the questions below. Einstein explained the photoelectric effect by using Planck’s quantum theory (E=hf). The German physicist Heinrich Hertz in 1887 was the first to discover that when light shines on certain metals, they emit electrons. Metals have the property that so ...
... Read this passage and answer the questions below. Einstein explained the photoelectric effect by using Planck’s quantum theory (E=hf). The German physicist Heinrich Hertz in 1887 was the first to discover that when light shines on certain metals, they emit electrons. Metals have the property that so ...
Subject Materials for Chemistry
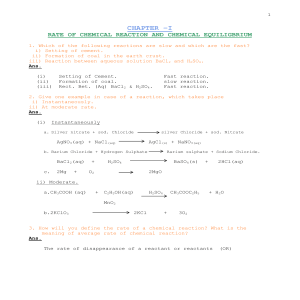
... The rate of a reaction depends upon the following factors a) Concentration of the reactants. b) Effect of Temperature. c) Effect of Catalyst. d) Effect of Light/radiation. e) Surface area of the reactants. a) Concentration of the reactants: The rate of a reaction generally increases with increase in ...
... The rate of a reaction depends upon the following factors a) Concentration of the reactants. b) Effect of Temperature. c) Effect of Catalyst. d) Effect of Light/radiation. e) Surface area of the reactants. a) Concentration of the reactants: The rate of a reaction generally increases with increase in ...
Describe properties of particles and thermochemical - Mr
... The explanations for the trends are essentially the same as the explanations for atomic size. e.g. although both the nuclear charge and the number of filled energy levels increases down a group, the shielding from the inner shells of electrons more than compensates for the increased nuclear charge, ...
... The explanations for the trends are essentially the same as the explanations for atomic size. e.g. although both the nuclear charge and the number of filled energy levels increases down a group, the shielding from the inner shells of electrons more than compensates for the increased nuclear charge, ...
South Pasadena • AP Chemistry Name
... 6 Energy and Chemical Reactions HESS’S LAW CALCULATIONS The enthalpy of the reactants, Hreactants and the enthalpy of the products, Hproducts depend on the bonding of the reactants and products… nothing else. So, the Hreaction only depends on the initial and final state of the reaction, not how y ...
... 6 Energy and Chemical Reactions HESS’S LAW CALCULATIONS The enthalpy of the reactants, Hreactants and the enthalpy of the products, Hproducts depend on the bonding of the reactants and products… nothing else. So, the Hreaction only depends on the initial and final state of the reaction, not how y ...
ch16powerpoint
... Substitute initial rates, changes and [B] is orders, and concentrations Find k at held constant and into general rate law: varied T m n vice versa rate = k [A] [B] ...
... Substitute initial rates, changes and [B] is orders, and concentrations Find k at held constant and into general rate law: varied T m n vice versa rate = k [A] [B] ...
5H2O → CuSO4 + 5H2O(g)
... Draw these compounds in two separate aqueous environments. What are the possible products when they are combined? ...
... Draw these compounds in two separate aqueous environments. What are the possible products when they are combined? ...
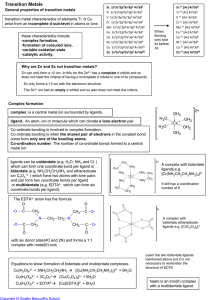
Transition Metals
... It could also be done by use of a spectrometer measuring the intensity of the purple colour. This method has the advantage that it does not disrupt the reaction mixture, using up the reactants and it leads to a much quicker determination of concentration ...
... It could also be done by use of a spectrometer measuring the intensity of the purple colour. This method has the advantage that it does not disrupt the reaction mixture, using up the reactants and it leads to a much quicker determination of concentration ...
Chemistry II Aqueous Reactions and Solution Chemistry Chapter 4
... are substances that ionize in aqueous solutions to form hydrogen ions, increasing the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution. Because hydrogen ions are just a proton, acids are known as proton ...
... are substances that ionize in aqueous solutions to form hydrogen ions, increasing the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution. Because hydrogen ions are just a proton, acids are known as proton ...
Fall 2012
... 67. (11 pts) When 35.00 mL of 0.100 M HBr is added to 0. 275 g of strontium hydroxide in a calorimeter, 195.3 J of energy are released. What is the ΔH for this reaction? The balanced reaction is: Sr(OH)2 + 2 HBr ! SrBr2 + 2 H2O 68. (11 pts) One type of weather balloon has a volume limit of 2.00 x 10 ...
... 67. (11 pts) When 35.00 mL of 0.100 M HBr is added to 0. 275 g of strontium hydroxide in a calorimeter, 195.3 J of energy are released. What is the ΔH for this reaction? The balanced reaction is: Sr(OH)2 + 2 HBr ! SrBr2 + 2 H2O 68. (11 pts) One type of weather balloon has a volume limit of 2.00 x 10 ...
Introduction
... ◦ Acid-base neutralization: acid and base react to form water and a salt (ionic compound) ◦ Oxidation-Reduction: electrons are transferred between atoms in reaction Combination Decomposition Single-replacement (metal or hydrogen) ...
... ◦ Acid-base neutralization: acid and base react to form water and a salt (ionic compound) ◦ Oxidation-Reduction: electrons are transferred between atoms in reaction Combination Decomposition Single-replacement (metal or hydrogen) ...
Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization of Norbornene by Cp
... class of carbene compounds with the general formula RuCl2(PR3)2(dCHR′), where R ) Ph or c-Hx and R′ ) Me, Et, Ph, or p-C6H4Cl, which are capable of polymerizingcyclobutenesandfunctionalizedcycloalkenes.45-47,49,50 By attaching water-soluble phosphines such as P(c-Hx)2(CH2CH2NMe3)+ instead of PPh3 or ...
... class of carbene compounds with the general formula RuCl2(PR3)2(dCHR′), where R ) Ph or c-Hx and R′ ) Me, Et, Ph, or p-C6H4Cl, which are capable of polymerizingcyclobutenesandfunctionalizedcycloalkenes.45-47,49,50 By attaching water-soluble phosphines such as P(c-Hx)2(CH2CH2NMe3)+ instead of PPh3 or ...
Photoredox catalysis
_Schematic.png?width=300)
Photoredox catalysis is a branch of catalysis that harnesses the energy of visible light to accelerate a chemical reaction via a single-electron transfer. This area is named as a combination of ""photo-"" referring to light and redox, a condensed expression for the chemical processes of reduction and oxidation. In particular, photoredox catalysis employs small quantities of a light-sensitive compound that, when excited by light, can mediate the transfer of electrons between chemical compounds that otherwise would not react. Photoredox catalysts are generally drawn from three classes of materials: transition-metal complexes, organic dyes and semiconductors. While each class of materials has advantages, soluble transition-metal complexes are used most often.Study of this branch of catalysis led to the development of new methods to accomplish known and new chemical transformations. One attraction to the area is that photoredox catalysts are often less toxic than other reagents often used to generate free radicals, such as organotin reagents. Furthermore, while photoredox catalysts generate potent redox agents while exposed to light, they are innocuous under ordinary conditions Thus transition-metal complex photoredox catalysts are in some ways more attractive than stoichiometric redox agents such as quinones. The properties of photoredox catalysts can be modified by changing ligands and the metal, reflecting the somewhat modular nature of the catalyst.While photoredox catalysis has most often been applied to generate known reactive intermediates in a novel way, the study of this mode of catalysis led to the discovery of new organic reactions, such as the first direct functionalization of the β-arylation of saturated aldehydes. Although the D3-symmetric transition-metal complexes used in many photoredox-catalyzed reactions are chiral, the use of enantioenriched photoredox catalysts led to low levels of enantioselectivity in a photoredox-catalyzed aryl-aryl coupling reaction, suggesting that the chiral nature of these catalysts is not yet a highly effective means of transmitting stereochemical information in photoredox reactions. However, while synthetically useful levels of enantioselectivity have not been achieved using chiral photoredox catalysts alone, optically-active products have been obtained through the synergistic combination of photoredox catalysis with chiral organocatalysts such as secondary amines and Brønsted acids.