Electrical properties of solids
... When atoms are brought as close together as those in a crystal, they interact with one another to such an extent that their outer electron shells constitute a single system of electrons common to the entire array of atoms that form the solid. The energy levels of the electrons are altered by the mut ...
... When atoms are brought as close together as those in a crystal, they interact with one another to such an extent that their outer electron shells constitute a single system of electrons common to the entire array of atoms that form the solid. The energy levels of the electrons are altered by the mut ...
Chapter notes Class: IX Chapter Name: Atoms and molecules Top
... 16. A negatively charged ion is called an ‘anion’ 17.A positively charged ion is called ‘cation’ 18. Ions may consist of a single charged atom or a group of atoms that have a net charge on them 19. Ionic compounds contain charged species called ions as their smallest unit 20.A group of atoms carryin ...
... 16. A negatively charged ion is called an ‘anion’ 17.A positively charged ion is called ‘cation’ 18. Ions may consist of a single charged atom or a group of atoms that have a net charge on them 19. Ionic compounds contain charged species called ions as their smallest unit 20.A group of atoms carryin ...
Stoichiometry - WordPress.com
... a) How much alumina (kg) is needed to produce 1000kg of pure aluminium? b) How much carbon dioxide (kg) would be produced? ...
... a) How much alumina (kg) is needed to produce 1000kg of pure aluminium? b) How much carbon dioxide (kg) would be produced? ...
Ch 8 Notes: Chemical Equations and Reactions
... If the compound is soluble that means that it will remain as ions in the solution, if it is insoluble then the compound precipitated out of the reaction (it became the precipitate or solid). 2. If at least one INSOLUBLE product is formed (which means a precipitate will form) the reaction will occur! ...
... If the compound is soluble that means that it will remain as ions in the solution, if it is insoluble then the compound precipitated out of the reaction (it became the precipitate or solid). 2. If at least one INSOLUBLE product is formed (which means a precipitate will form) the reaction will occur! ...
ch5_f08
... metals from most reactive to least reactive • Cu(s) + HCl(aq) → no reaction • Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) ...
... metals from most reactive to least reactive • Cu(s) + HCl(aq) → no reaction • Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) ...
Midterm Review Questions and Answers
... 18. What mass would a 34.6 cm3 block of tin have? __________________ ...
... 18. What mass would a 34.6 cm3 block of tin have? __________________ ...
Acids and Bases - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... The value of Kw is very small, meaning that very few ions are present. Most water remains "intact" as H2O, and few ions form. Why, then, do we even mention it? For a very important reason that we will examine in the next section. Calculating [H+] and [OH–] We can use Ka and Kb to calculate the conce ...
... The value of Kw is very small, meaning that very few ions are present. Most water remains "intact" as H2O, and few ions form. Why, then, do we even mention it? For a very important reason that we will examine in the next section. Calculating [H+] and [OH–] We can use Ka and Kb to calculate the conce ...
Chemical properties of amines:
... values slightly higher than amonia. Thus aliphatic amines are stronger bases than amonia. Like amonia, compounds with amino groups can also neutralize hydronium ions. This neutralization occurs very rapidly and essentially goes to completion at room temperature. Protonated amine cations can neutrali ...
... values slightly higher than amonia. Thus aliphatic amines are stronger bases than amonia. Like amonia, compounds with amino groups can also neutralize hydronium ions. This neutralization occurs very rapidly and essentially goes to completion at room temperature. Protonated amine cations can neutrali ...
Amino acids - CMA
... Amino acids The name “amino acid” is derived from the general structure of molecules belonging to that group. They all contain an amino group (NH2) and an carboxylic acid group (COOH). Often, they are drawn as such. In reality, however, (solid) amino acids at relatively neutral pH values exist as zw ...
... Amino acids The name “amino acid” is derived from the general structure of molecules belonging to that group. They all contain an amino group (NH2) and an carboxylic acid group (COOH). Often, they are drawn as such. In reality, however, (solid) amino acids at relatively neutral pH values exist as zw ...
Final Review
... c. Definite volume; shape of container; no intermolecular attractions d. Volume and shape of container; no intermolecular attractions e. Volume and shape of container; strong intermolecular attractions 102. Which transformation is evaporation? a. liquid ---> solid d. solid ---> gas b. liquid ---> ga ...
... c. Definite volume; shape of container; no intermolecular attractions d. Volume and shape of container; no intermolecular attractions e. Volume and shape of container; strong intermolecular attractions 102. Which transformation is evaporation? a. liquid ---> solid d. solid ---> gas b. liquid ---> ga ...
CH 2 development of atomic theory
... they are invisible but can be observed when they strike glass, which is coated with phosphorescent material; the particles in the ray have mass. Canal rays (anode rays) form when electrons are knocked out of neutral atoms. Anode rays consist of positive ions or cations. The properties of an anode ra ...
... they are invisible but can be observed when they strike glass, which is coated with phosphorescent material; the particles in the ray have mass. Canal rays (anode rays) form when electrons are knocked out of neutral atoms. Anode rays consist of positive ions or cations. The properties of an anode ra ...
Chem 30A Fa_06 FE Review
... The reaction between ammonia and carbon dioxide forms urea, CH4N2O(s), according to the following equation: 2NH3(g) + CO2(g) CH4N2O(s) + H2O(l) If 75.0 g of NH3 is reacted with 92.5 g of CO2, how many grams of urea are formed? If 115 g of urea is actually obtained, what is the percent yield? (Hint ...
... The reaction between ammonia and carbon dioxide forms urea, CH4N2O(s), according to the following equation: 2NH3(g) + CO2(g) CH4N2O(s) + H2O(l) If 75.0 g of NH3 is reacted with 92.5 g of CO2, how many grams of urea are formed? If 115 g of urea is actually obtained, what is the percent yield? (Hint ...
P BLOCK ELEMENT
... (a) Diamond : (i) It is the purest form of carbon. (ii) It is the hardest natural substance known In diamond, each carbon atom is in sp3 hybridized state and linked to four other carbon atoms tetrahedrally by covalent bonds. (b) Graphite : It has a two dimensional sheet structure. Each carbon atom i ...
... (a) Diamond : (i) It is the purest form of carbon. (ii) It is the hardest natural substance known In diamond, each carbon atom is in sp3 hybridized state and linked to four other carbon atoms tetrahedrally by covalent bonds. (b) Graphite : It has a two dimensional sheet structure. Each carbon atom i ...
Chemistry
... 27. __________________ – tentative explanation for an observation 28. __________________ – a set of controlled observations that test the hypothesis 29. _______________ – a quantity or condition that can have more than one value 30. Only ________________ variable can be tested at a time 31. _______ ...
... 27. __________________ – tentative explanation for an observation 28. __________________ – a set of controlled observations that test the hypothesis 29. _______________ – a quantity or condition that can have more than one value 30. Only ________________ variable can be tested at a time 31. _______ ...
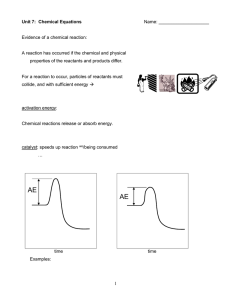
students - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... A reaction has occurred if the chemical and physical properties of the reactants and products differ. ...
... A reaction has occurred if the chemical and physical properties of the reactants and products differ. ...
Worksheet answers
... acids ionize in water to form H+ ions more precisely, the H from the acid molecule is donated to a water molecule to form hydronium ion, H3O+. A proton (H+) cannot exist on its own in water! bases dissociate in water to form OH ions bases, such as NH3, that do not contain OH ions, produce OH by p ...
... acids ionize in water to form H+ ions more precisely, the H from the acid molecule is donated to a water molecule to form hydronium ion, H3O+. A proton (H+) cannot exist on its own in water! bases dissociate in water to form OH ions bases, such as NH3, that do not contain OH ions, produce OH by p ...
Ch. 20- Electrochemistry
... 1. The energy released in a spontaneous redox reaction can be used to perform electrical work. This task is accomplished through a voltaic (or galvanic) cell, a device in which the transfer of electrons takes place through an external pathway rather than directly between reactants present in the sam ...
... 1. The energy released in a spontaneous redox reaction can be used to perform electrical work. This task is accomplished through a voltaic (or galvanic) cell, a device in which the transfer of electrons takes place through an external pathway rather than directly between reactants present in the sam ...
Module 4 Trivia Review
... Semi means half or partial. So semiconductors (metalloids) have electrical conductivity half way between those of a conductor and an insulator (non-metal). Since they are solid and ductile, these metalloids have been found to be indispensable to the technology industry. Metals would conduct too much ...
... Semi means half or partial. So semiconductors (metalloids) have electrical conductivity half way between those of a conductor and an insulator (non-metal). Since they are solid and ductile, these metalloids have been found to be indispensable to the technology industry. Metals would conduct too much ...
pulsed laser atom probe characterization of silicon carbide
... high strength applications. Sintered or hot pressed silicon carbide ceramics are generally polycrystalline forms of a-SiC which contain relatively small amounts of aluminum'11 or boron'2' intentionally added as densification aids. Silicon carbide, grown in whisker form, is also used as a high streng ...
... high strength applications. Sintered or hot pressed silicon carbide ceramics are generally polycrystalline forms of a-SiC which contain relatively small amounts of aluminum'11 or boron'2' intentionally added as densification aids. Silicon carbide, grown in whisker form, is also used as a high streng ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Chapter 2
... • A cation is a positively charged ion • An anion is a negatively charged ion • An ionic bond is an attraction between an anion and a cation ...
... • A cation is a positively charged ion • An anion is a negatively charged ion • An ionic bond is an attraction between an anion and a cation ...
Part 3 Answers Only for Questions, Exercises, and Problems in The
... 8. The particles in a solid occupy fixed positions relative to each other and cannot be poured, but different pieces of solids can move relative to each other. The slogan emphasizes that this brand of table salt has solid pieces small enough to move freely relative to one another, but not so small t ...
... 8. The particles in a solid occupy fixed positions relative to each other and cannot be poured, but different pieces of solids can move relative to each other. The slogan emphasizes that this brand of table salt has solid pieces small enough to move freely relative to one another, but not so small t ...
Page 1 of 25
... c. Definite volume; shape of container; no intermolecular attractions d. Volume and shape of container; no intermolecular attractions e. Volume and shape of container; strong intermolecular attractions 102. Which transformation is evaporation? a. liquid ---> solid d. solid ---> gas b. liquid ---> ga ...
... c. Definite volume; shape of container; no intermolecular attractions d. Volume and shape of container; no intermolecular attractions e. Volume and shape of container; strong intermolecular attractions 102. Which transformation is evaporation? a. liquid ---> solid d. solid ---> gas b. liquid ---> ga ...
Chemistry II Exams and Answer Keys 2015 Season
... 1. A sample of hydrogen is in a 2L flask and a sample of oxygen is in a different 2 L flask. Both samples are at the same temperature and pressure. You determine each of the following: ...
... 1. A sample of hydrogen is in a 2L flask and a sample of oxygen is in a different 2 L flask. Both samples are at the same temperature and pressure. You determine each of the following: ...
Chemistry Claims Unit 1: Alchemy: Matter, Atomic Structure, and
... A solid/liquid/gas is the easiest phase to change to. Unit 6: Showtime: Reversible Reactions and Chemical Equilibrium The best demonstrations include smoke/fire/color change. The best reactions are reversible. There are different models of equilibrium. A large equilibrium constant is bette ...
... A solid/liquid/gas is the easiest phase to change to. Unit 6: Showtime: Reversible Reactions and Chemical Equilibrium The best demonstrations include smoke/fire/color change. The best reactions are reversible. There are different models of equilibrium. A large equilibrium constant is bette ...