HS-PS1-2. Construct and revise an explanation for the outcome of a
... reactions, graphs showing the relative energies of reactants and products, and representations showing energy is conserved.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include calculating the total bond energy changes during a chemical reaction from the bond energies of reactants and products.] ...
... reactions, graphs showing the relative energies of reactants and products, and representations showing energy is conserved.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include calculating the total bond energy changes during a chemical reaction from the bond energies of reactants and products.] ...
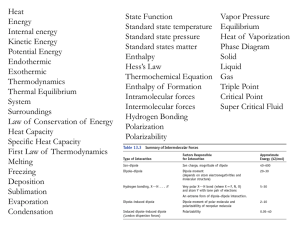
Glossary
... Equipartition theorem − consequence of the kinetic molecular theory that molecules have average kinetic energy proportional to the number of different types of molecular motion. Equivalent − one mol of charge (protons, electrons, ions). Exclusion principle− no two electrons can have the same set of ...
... Equipartition theorem − consequence of the kinetic molecular theory that molecules have average kinetic energy proportional to the number of different types of molecular motion. Equivalent − one mol of charge (protons, electrons, ions). Exclusion principle− no two electrons can have the same set of ...
chemical reaction
... 3. All metal halide (halogen) compounds are soluble, except those of Ag+, Hg+ & Pb+2 4. All sulfates are soluble except: Ba+2, Sr+2, Ca+2, Pb+2,Ag+, ...
... 3. All metal halide (halogen) compounds are soluble, except those of Ag+, Hg+ & Pb+2 4. All sulfates are soluble except: Ba+2, Sr+2, Ca+2, Pb+2,Ag+, ...
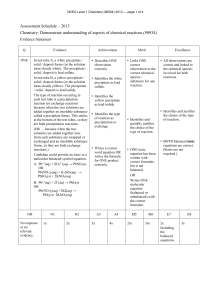
Scientific Principles: Chemical Properties
... • When you look at the chemical formula, you see that it takes one atom of sodium to combine with one item of chlorine • Stoichiometry aids us in determining the amounts of substances needed to fulfill the requirements of the reaction • Stoichiometry tells us that if you have 100 atoms of sodium and ...
... • When you look at the chemical formula, you see that it takes one atom of sodium to combine with one item of chlorine • Stoichiometry aids us in determining the amounts of substances needed to fulfill the requirements of the reaction • Stoichiometry tells us that if you have 100 atoms of sodium and ...
Make Your Own Summary 1. single displacement reaction 2
... neither a single reactant nor a single product, so it can be neither a synthesis reaction nor a decomposition reaction. The reactants are a compound and an element, which prevents the reaction from being a double displacement reaction. The products are two compounds, which prevent the reaction from ...
... neither a single reactant nor a single product, so it can be neither a synthesis reaction nor a decomposition reaction. The reactants are a compound and an element, which prevents the reaction from being a double displacement reaction. The products are two compounds, which prevent the reaction from ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.