High School Physical Science Glossary
... subshell- orbitals of various shapes and energies within an energy level; which are s,p,d,f synthesis reactions- chemical reaction in which a single compound is created from two or more reactants (A + B AB) temperature- measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles within a substance test ...
... subshell- orbitals of various shapes and energies within an energy level; which are s,p,d,f synthesis reactions- chemical reaction in which a single compound is created from two or more reactants (A + B AB) temperature- measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles within a substance test ...
Supercatalysis by superexchange
... element HDA might be a constant for a given D−A pair and thus impossible to change. On closer examination, however, it becomes clear that the magnitude of HDA can actually be modified by the insertion of an intermediate state from the nearby environment, known as a bridge state.28−32 Provided the orb ...
... element HDA might be a constant for a given D−A pair and thus impossible to change. On closer examination, however, it becomes clear that the magnitude of HDA can actually be modified by the insertion of an intermediate state from the nearby environment, known as a bridge state.28−32 Provided the orb ...
High School Curriculum Standards: Chemistry
... with them in the 1860s, led to the proposal that small, negatively charged particles—electrons—are part of the internal structure of atoms. In the early 1900s, to explain the results of the "gold foil experiment," a small, dense nucleus was proposed to be at the center of the atom with electrons mov ...
... with them in the 1860s, led to the proposal that small, negatively charged particles—electrons—are part of the internal structure of atoms. In the early 1900s, to explain the results of the "gold foil experiment," a small, dense nucleus was proposed to be at the center of the atom with electrons mov ...
Thermodynamics Enthalpy Entropy and Free Energy Student
... § Enthalpy is not dependent on the reaction pathway. If you can find a combination of chemical equations that add up to the desired overall equation, you can sum up the ΔHrxn’s for the individual reactions to get the overall ΔHrxn. § Remember this: § First decide how to rearrange equations so rea ...
... § Enthalpy is not dependent on the reaction pathway. If you can find a combination of chemical equations that add up to the desired overall equation, you can sum up the ΔHrxn’s for the individual reactions to get the overall ΔHrxn. § Remember this: § First decide how to rearrange equations so rea ...
Chapter 14 Enzyme Characteristics
... Note that the slope of the progress curve changes with time. Most studies in enzyme kinetics try to deal with the initial rate of a reaction, that is the slope of the curve where t = 0. Many things can influence the catalytic ability of an enzyme, including the accumulation of products as well as de ...
... Note that the slope of the progress curve changes with time. Most studies in enzyme kinetics try to deal with the initial rate of a reaction, that is the slope of the curve where t = 0. Many things can influence the catalytic ability of an enzyme, including the accumulation of products as well as de ...
Dalton`s Atomic Theory
... c. The atoms of different elements differ in fundamental ways (e.g., different masses, different chemical behavior). d. Compounds form when atoms of different elements join together in simple whole number ratios. Thus, a given compound always contains the same relative number and types of atoms. e. ...
... c. The atoms of different elements differ in fundamental ways (e.g., different masses, different chemical behavior). d. Compounds form when atoms of different elements join together in simple whole number ratios. Thus, a given compound always contains the same relative number and types of atoms. e. ...
Chapter 7 - Chemical Reactions
... CHAPTER 17 OBJECTIVES Calculate the molarity of a solution that contains 50.0 g of NaCl per 0.6 L of solution. How many moles of solute are present in 3.5 L of a 0.50 M LiNO3 solution? How many grams of solute are there? What is the percent (m/v) of a water solution that contains 80 g of NaOH, and t ...
... CHAPTER 17 OBJECTIVES Calculate the molarity of a solution that contains 50.0 g of NaCl per 0.6 L of solution. How many moles of solute are present in 3.5 L of a 0.50 M LiNO3 solution? How many grams of solute are there? What is the percent (m/v) of a water solution that contains 80 g of NaOH, and t ...
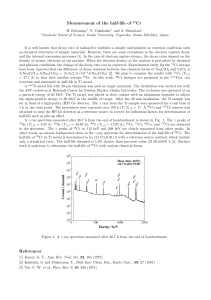
Measurement of the half-life of
... the AVF cyclotron at Research Center for Nuclear Physics, Osaka University. The cyclotron was operated at an α-particle energy of 40 MeV. The Ti target was placed in close contact with an aluminium degrader to adjust the alpha-particle energy to 30 MeV in the middle of target. After the 30 min irrad ...
... the AVF cyclotron at Research Center for Nuclear Physics, Osaka University. The cyclotron was operated at an α-particle energy of 40 MeV. The Ti target was placed in close contact with an aluminium degrader to adjust the alpha-particle energy to 30 MeV in the middle of target. After the 30 min irrad ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.