Calculating a Ka Value from a Known pH - Chemwiki
... Ka, the acid ionization constant, is the equilibrium constant for chemical reactions involving weak acids in aqueous solution. The numerical value of Ka is used to predict the extent of acid dissociation. A large Ka value indicates a stronger acid (more of the acid dissociates) and small Ka val ...
... Ka, the acid ionization constant, is the equilibrium constant for chemical reactions involving weak acids in aqueous solution. The numerical value of Ka is used to predict the extent of acid dissociation. A large Ka value indicates a stronger acid (more of the acid dissociates) and small Ka val ...
1. Naturally occurring boron consists of two isotopes, boron–10 and
... increased by a factor of 363/323. C) The average kinetic energy of the sample increased by a factor of 9/5. D) The average kinetic energy increased by a factor of 81/25. E) More information is needed to know whether the ...
... increased by a factor of 363/323. C) The average kinetic energy of the sample increased by a factor of 9/5. D) The average kinetic energy increased by a factor of 81/25. E) More information is needed to know whether the ...
S - Valdosta State University
... Probability and the locations of gas molecules. The two molecules are colored red and blue. a) Before the stopcock is opened, both molecules are in the left-hand flask. b) After the stopcock is opened, there are 4 possible arrangements of the two molecules. The greater number of possible arrangement ...
... Probability and the locations of gas molecules. The two molecules are colored red and blue. a) Before the stopcock is opened, both molecules are in the left-hand flask. b) After the stopcock is opened, there are 4 possible arrangements of the two molecules. The greater number of possible arrangement ...
Enthalpy
... The molecules in a solid are vibrating in place. Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy that the molecules. As the temperature rises, more kinetic energy is added and the molecules vibrate more. At one particular temperature, the molecules begin to tumble past each other. This breaki ...
... The molecules in a solid are vibrating in place. Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy that the molecules. As the temperature rises, more kinetic energy is added and the molecules vibrate more. At one particular temperature, the molecules begin to tumble past each other. This breaki ...
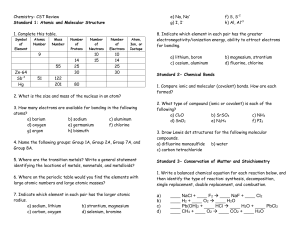
Chemistry- CST Review
... people in the back of the room eventually be able to smell it? Why? Explain completely. ...
... people in the back of the room eventually be able to smell it? Why? Explain completely. ...
Test review
... b. mixing 5 mL ethanol with 25 mL water c. compressing 1 mol Ne at constant temperature from 1.5 L to 0.5 L d. raising the temperature of 100 g Cu from 275 K to 295 K e. grinding a large crystal of KCl to powder 10. Hydrogen for use in ammonia production is produced by the reaction CH4(g) + H2O(g) ↔ ...
... b. mixing 5 mL ethanol with 25 mL water c. compressing 1 mol Ne at constant temperature from 1.5 L to 0.5 L d. raising the temperature of 100 g Cu from 275 K to 295 K e. grinding a large crystal of KCl to powder 10. Hydrogen for use in ammonia production is produced by the reaction CH4(g) + H2O(g) ↔ ...
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry
... are not state functions. • Whether the battery is shorted out or is discharged by running the fan, its E is the same. – But q and w are different in the two cases. ...
... are not state functions. • Whether the battery is shorted out or is discharged by running the fan, its E is the same. – But q and w are different in the two cases. ...
Question Paper - Revision Science
... (Total for Question 2 = 4 marks) 3 Which of the following mixtures would form the best buffer solution with pH 9 for use in a school laboratory? A Ethanoic acid and sodium ethanoate B Sodium chloride and sodium hydroxide C Hydrocyanic acid and sodium cyanide D Ammonium chloride and ammonia (Total fo ...
... (Total for Question 2 = 4 marks) 3 Which of the following mixtures would form the best buffer solution with pH 9 for use in a school laboratory? A Ethanoic acid and sodium ethanoate B Sodium chloride and sodium hydroxide C Hydrocyanic acid and sodium cyanide D Ammonium chloride and ammonia (Total fo ...
C:\Users\mrh70950\Documents\My Files\WordPerfect
... accounts for the formation of all three products. ...
... accounts for the formation of all three products. ...
document
... 7. Polyatomic Ion F. A multiplier. It is used to balance equations. 8. Synthesis Reaction G. A reaction in which two reactant compounds switch ions. 9. Decomposition Reaction H. This number tells the number of atoms of one element in a 10. Single Displacement Reaction compound. I. Bonds formed by ga ...
... 7. Polyatomic Ion F. A multiplier. It is used to balance equations. 8. Synthesis Reaction G. A reaction in which two reactant compounds switch ions. 9. Decomposition Reaction H. This number tells the number of atoms of one element in a 10. Single Displacement Reaction compound. I. Bonds formed by ga ...
unit 4 practice
... hydroxide solutions of the same concentration. Which statement is correct? A. The initial pH values of both acids are equal. B. At the equivalence points, the solutions of both titrations have pH values ...
... hydroxide solutions of the same concentration. Which statement is correct? A. The initial pH values of both acids are equal. B. At the equivalence points, the solutions of both titrations have pH values ...
Chpt6 - Dr. Erdal ONURHAN
... - Thermal Energy is due to random motion of atoms and molecules. It is generally calculated from temperature measurements. Temperature is not a measure of thermal energy itself. - Chemical Energy is stored within the structural units of chemical substances. When a chemical reaction takes place, chem ...
... - Thermal Energy is due to random motion of atoms and molecules. It is generally calculated from temperature measurements. Temperature is not a measure of thermal energy itself. - Chemical Energy is stored within the structural units of chemical substances. When a chemical reaction takes place, chem ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.