
Lecture 13 11-20-02
... volume of titrant needed to reach the equivalence point, we draw a vertical line that intersects the x-axis at this volume. Next, we determine the pH for two or three volumes before the equivalence point and for two or three volumes after the equivalence point. To save time we only calculate pH valu ...
... volume of titrant needed to reach the equivalence point, we draw a vertical line that intersects the x-axis at this volume. Next, we determine the pH for two or three volumes before the equivalence point and for two or three volumes after the equivalence point. To save time we only calculate pH valu ...
Supercritical Burning of Liquid Oxygen (LOX) Droplet with Detailed
... A numerical study of the supercritical combustion of a liquid oxygen (LOX) droplet in a stagnant environment of hot hydrogen is carried out with a detailed chemistry model. Special attention is devoted to ignition process and diffusion flame structure. Ignition consists typically of the propagation ...
... A numerical study of the supercritical combustion of a liquid oxygen (LOX) droplet in a stagnant environment of hot hydrogen is carried out with a detailed chemistry model. Special attention is devoted to ignition process and diffusion flame structure. Ignition consists typically of the propagation ...
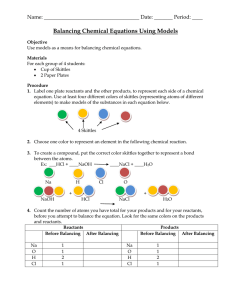
Balancing Chemical Equations Using Models
... 6. Then add any coefficients if they are needed, and count how many atoms we now have. ___HCl + ____NaOH ____NaCl + ____H2O For our example we have the same number of each atom for both products and reactants, we do not need to add any coefficients to balance the equation. Reactants Before Balancing ...
... 6. Then add any coefficients if they are needed, and count how many atoms we now have. ___HCl + ____NaOH ____NaCl + ____H2O For our example we have the same number of each atom for both products and reactants, we do not need to add any coefficients to balance the equation. Reactants Before Balancing ...
CHAPTER 19 TRANSITION METALS AND COORDINATION
... electrons that can be removed. Stable ions of the representative metals are determined by how many s and p valence electrons can be removed. In general, representative metals lose all of the s and p valence electrons to form their stable ions. Transition metals generally lose the s electron(s) to fo ...
... electrons that can be removed. Stable ions of the representative metals are determined by how many s and p valence electrons can be removed. In general, representative metals lose all of the s and p valence electrons to form their stable ions. Transition metals generally lose the s electron(s) to fo ...
5 Steps to a 5 AP Chemistry, 2008-2009 Edition
... previous years. We have revised our presentation to reflect this change. We have also significantly revised the reaction chapter to mirror the extensive changes made in the reaction question on the AP exam. The AP Chemistry exam certainly isn’t easy, but the rewards are worth it—college credit and t ...
... previous years. We have revised our presentation to reflect this change. We have also significantly revised the reaction chapter to mirror the extensive changes made in the reaction question on the AP exam. The AP Chemistry exam certainly isn’t easy, but the rewards are worth it—college credit and t ...
ioan stamatin
... 2. understand the implications of design decisions in a research activity or in the global engineering marketplace to appropriate physical phenomena in vary stuff through material science 3. are able to formulate and analyze problems, think creatively, communicate effectively, synthesize information ...
... 2. understand the implications of design decisions in a research activity or in the global engineering marketplace to appropriate physical phenomena in vary stuff through material science 3. are able to formulate and analyze problems, think creatively, communicate effectively, synthesize information ...
Oxygen Carriers Materials for Chemical
... past century, which is mainly due to industrial activities. During the same time period the global average temperature has increased by approximately 0.6 °C [9]. Figure 1 shows the observed changes in global mean temperature in the past 140 years. ...
... past century, which is mainly due to industrial activities. During the same time period the global average temperature has increased by approximately 0.6 °C [9]. Figure 1 shows the observed changes in global mean temperature in the past 140 years. ...
Glossary of terms used in photocatalysis and radiation catalysis
... tation marks” indicates that it is NOT defined in this Glossary (see [11]). In addition, an underlined word marks its importance in the respective entry. Synonyms appear in non-bolded roman type immediately below the main term. The same convention as in the “Glossary of terms used in photochemistry” ...
... tation marks” indicates that it is NOT defined in this Glossary (see [11]). In addition, an underlined word marks its importance in the respective entry. Synonyms appear in non-bolded roman type immediately below the main term. The same convention as in the “Glossary of terms used in photochemistry” ...
Type - Enrico Fermi High
... An experiment is performed to determine the number of particles in 1 mole of a substance (the actual number is called Avogadro’s number, we will learn about this later in the year), you get an answer of 8.23 × 10 22 particles. What is your percent error? ...
... An experiment is performed to determine the number of particles in 1 mole of a substance (the actual number is called Avogadro’s number, we will learn about this later in the year), you get an answer of 8.23 × 10 22 particles. What is your percent error? ...
Chemical thermodynamics - Mahesh Tutorials Science
... The first law talks about the conservation of energy in a process but does not speak of the feasibility of a process. It does not tell whether a process will happen on its own i.e. whether the process is spontaneous or not. A spontaneous process is one which happens on its own. Example, heat always ...
... The first law talks about the conservation of energy in a process but does not speak of the feasibility of a process. It does not tell whether a process will happen on its own i.e. whether the process is spontaneous or not. A spontaneous process is one which happens on its own. Example, heat always ...
mclintock.ch6 [Compatibility Mode]
... ► The numbers and kinds of atoms must be the same on both sides of the reaction arrow. ► Numbers in front of formulas are called coefficients; they multiply all the atoms in a formula. ► The symbol 2 NaHCO3 indicates two units of sodium bicarbonate, which contains 2 Na, 2 H, 2 C, and 6 O. ► Substanc ...
... ► The numbers and kinds of atoms must be the same on both sides of the reaction arrow. ► Numbers in front of formulas are called coefficients; they multiply all the atoms in a formula. ► The symbol 2 NaHCO3 indicates two units of sodium bicarbonate, which contains 2 Na, 2 H, 2 C, and 6 O. ► Substanc ...
Answers - logo Pre-U Chemistry Textbook
... ∆rH = –577 kJ mol–1, which is highly exothermic so gases produced will expand rapidly at the high temperatures. Also, there are __ 32 more moles of products than reactants. ...
... ∆rH = –577 kJ mol–1, which is highly exothermic so gases produced will expand rapidly at the high temperatures. Also, there are __ 32 more moles of products than reactants. ...
Molecular theory of partial molar volume and its applications to
... to combine the KB theory with molecular simulation are still limited to small molecules [34–38]. Another approach is to employ molecular liquid theories [39,40], such as the reference hypernetted chain (RHNC) [41] and the reference interaction site model (RISM) [42,43] theories, which yield the RDF ...
... to combine the KB theory with molecular simulation are still limited to small molecules [34–38]. Another approach is to employ molecular liquid theories [39,40], such as the reference hypernetted chain (RHNC) [41] and the reference interaction site model (RISM) [42,43] theories, which yield the RDF ...
Learning Outcomes
... (f) define relative atomic mass, Ar .............................................................................................. 18 (g) define relative molecular mass, Mr, and calculate relative molecular mass (and relative formula mass) as the sum of relative atomic masses........................ ...
... (f) define relative atomic mass, Ar .............................................................................................. 18 (g) define relative molecular mass, Mr, and calculate relative molecular mass (and relative formula mass) as the sum of relative atomic masses........................ ...
2016-2018 Syllabus - Cambridge International Examinations
... final result.’ Page 39: Section C5.3.4 Suggesting improvements, paragraph after list, 6th line, now reads ‘may relate to sources of error or uncertainty identified by the candidate or to other sources of error or uncertainty.’ The changes below were introduced for version 1 of this syllabus. Part of ...
... final result.’ Page 39: Section C5.3.4 Suggesting improvements, paragraph after list, 6th line, now reads ‘may relate to sources of error or uncertainty identified by the candidate or to other sources of error or uncertainty.’ The changes below were introduced for version 1 of this syllabus. Part of ...
LMM Auger spectra of Cu, Zn, Ga, and Ge, II. Relationship with the L
... of the L, , hole. At first glance this may not seem to be the case because of the relatively large oneelectron 3d bandwidth. In the Coster-Kronig process however the 3d and I., hole are, initially at least, on the same atom and therefore the 3d hole will not behave as a single-particle excitation an ...
... of the L, , hole. At first glance this may not seem to be the case because of the relatively large oneelectron 3d bandwidth. In the Coster-Kronig process however the 3d and I., hole are, initially at least, on the same atom and therefore the 3d hole will not behave as a single-particle excitation an ...
Chemistry, Biology
... process of observation and experimentation, Galileo Galilei used experiments to overturn Aristotle’s ideas of the motion of objects, for example the flawed idea that heavy objects fall faster than lighter ones, which dominated physics for about 2000 years. The greatest contribution to the developmen ...
... process of observation and experimentation, Galileo Galilei used experiments to overturn Aristotle’s ideas of the motion of objects, for example the flawed idea that heavy objects fall faster than lighter ones, which dominated physics for about 2000 years. The greatest contribution to the developmen ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.












![mclintock.ch6 [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003971396_1-780a12aa3165c9221aca3ac594a06674-300x300.png)









