50 frequently forgotten facts answer key
... d) The heat of reaction (H) of this reaction is____H = HP – HR = 35 kJ – 45 kJ = -10. kJ___ e) Sketch and label a PE diagram for this reaction: ...
... d) The heat of reaction (H) of this reaction is____H = HP – HR = 35 kJ – 45 kJ = -10. kJ___ e) Sketch and label a PE diagram for this reaction: ...
Rapid Microwave Synthesis, Characterization and Reactivity
... Powder X-ray diffraction (PXD) was conducted using a Bruker D8 diffractometer (Bruker Corporation, Billerica, MA, USA, Cu Kα source) or a PANalytical X’Pert Pro MPD powder diffractometer (Cu Kα1 source) in capillary mode. The air-sensitive samples were ground into fine powders and placed in 0.5 mm d ...
... Powder X-ray diffraction (PXD) was conducted using a Bruker D8 diffractometer (Bruker Corporation, Billerica, MA, USA, Cu Kα source) or a PANalytical X’Pert Pro MPD powder diffractometer (Cu Kα1 source) in capillary mode. The air-sensitive samples were ground into fine powders and placed in 0.5 mm d ...
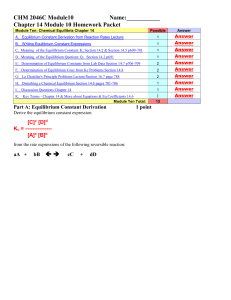
CHEM 1212 Module Ten-Chapter 16 Name
... products instead of the equilibrium concentration so as to determine the direction of the equilibrium shift. ___________________5. ____________ ________________ states that if a change is imposed on a system in equilibrium , the position of the equilibrium will shift in a direction that tends to red ...
... products instead of the equilibrium concentration so as to determine the direction of the equilibrium shift. ___________________5. ____________ ________________ states that if a change is imposed on a system in equilibrium , the position of the equilibrium will shift in a direction that tends to red ...
Unit 5 Chemical Kinetics Section 5.1 Rates of Chemical Reaction
... S2O32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) → S(s) + SO2(g) + H2O(l) A beaker containing 25 cm3 of 0.1 mol dm-3 sodium thiosulphate solution is placed over a cross drawn on a piece of paper. Then 5 cm3 of a dilute solution of hydrochloric acid is added. Timing is started as soon as the acid is added. Eventually there is ...
... S2O32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) → S(s) + SO2(g) + H2O(l) A beaker containing 25 cm3 of 0.1 mol dm-3 sodium thiosulphate solution is placed over a cross drawn on a piece of paper. Then 5 cm3 of a dilute solution of hydrochloric acid is added. Timing is started as soon as the acid is added. Eventually there is ...
Chapter 20 Thermodynamics
... 4. Dissolution of a gas decreases entropy. A gas becomes less dispersed when it dissolves in a liquid or solid. 5. Atomic size or molecular complexity In similar substances, increases in mass relate directly to entropy. In allotropic substances, increases in complexity (e.g., bond flexibility) relat ...
... 4. Dissolution of a gas decreases entropy. A gas becomes less dispersed when it dissolves in a liquid or solid. 5. Atomic size or molecular complexity In similar substances, increases in mass relate directly to entropy. In allotropic substances, increases in complexity (e.g., bond flexibility) relat ...
Thermo chemistry Dealing with
... The enthalpy change for the overall process is the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps. The heat evolved or absorbed in a chemical process is the same whether the process takes place in one or in several steps. ...
... The enthalpy change for the overall process is the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps. The heat evolved or absorbed in a chemical process is the same whether the process takes place in one or in several steps. ...
Thermochemistry - thelapierres.com
... DH0rxn = S nDH0f (products) - S mDHf0 (reactants) Hess’s Law: When reactants are converted to products, the change in enthalpy is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or in a series of steps. (Enthalpy is a state function. It doesn’t matter how you get there, only where you start an ...
... DH0rxn = S nDH0f (products) - S mDHf0 (reactants) Hess’s Law: When reactants are converted to products, the change in enthalpy is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or in a series of steps. (Enthalpy is a state function. It doesn’t matter how you get there, only where you start an ...
Rxn Types
... Single Displacement Reactions Not all single displacement reactions that can be written actually happen. The metal or non-metal must be more active than the ion it is replacing. It will depend upon the element’s Activity as ...
... Single Displacement Reactions Not all single displacement reactions that can be written actually happen. The metal or non-metal must be more active than the ion it is replacing. It will depend upon the element’s Activity as ...
Lessons 9
... determine heat of reaction, and use the data obtained to calculate the enthalpy change for a reaction compare the energy changes resulting from physical change, chemical reactions, and nuclear reactions (fission and fusion); ...
... determine heat of reaction, and use the data obtained to calculate the enthalpy change for a reaction compare the energy changes resulting from physical change, chemical reactions, and nuclear reactions (fission and fusion); ...
Entropy (Part I)
... A. expand to fill the entire container if it is heated. B. expand to fill the entire container because there are more microstates with that arrangement. C. expand to fill the entire container because the probability is less; therefore, the entropy has increased. D. expand to fill the containe ...
... A. expand to fill the entire container if it is heated. B. expand to fill the entire container because there are more microstates with that arrangement. C. expand to fill the entire container because the probability is less; therefore, the entropy has increased. D. expand to fill the containe ...
The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to form water and oxygen
... require about 20 minutes to answer. Questions 4 through 7 are short constructed response questions that should require about 7 minutes each to answer. Read each question carefully and write your response in the space provided following each question. Your responses to these questions will be scored ...
... require about 20 minutes to answer. Questions 4 through 7 are short constructed response questions that should require about 7 minutes each to answer. Read each question carefully and write your response in the space provided following each question. Your responses to these questions will be scored ...
Click Here To File
... -There are 4 unpaired electrons. -Water is a weak ligand. Thus the hybridisation involved is sp3d2 (marks to be granted if hybridisation is depicted diagrammatically) (ii) The ionisation isomer is [Co(NH3)5SO4]Br. The IUPAC name is pentaamminesulphatocobalt(III)bromide. Chemical test to distinguish ...
... -There are 4 unpaired electrons. -Water is a weak ligand. Thus the hybridisation involved is sp3d2 (marks to be granted if hybridisation is depicted diagrammatically) (ii) The ionisation isomer is [Co(NH3)5SO4]Br. The IUPAC name is pentaamminesulphatocobalt(III)bromide. Chemical test to distinguish ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.