Chemistry Simulations
... This simulation allows the students to see how they can put energy into the system to overcome the activation energy. They can increase the temperature as well as the number of molecules. There is also a timer feature, so students can measure how long it takes for a reaction to occur, and how the ra ...
... This simulation allows the students to see how they can put energy into the system to overcome the activation energy. They can increase the temperature as well as the number of molecules. There is also a timer feature, so students can measure how long it takes for a reaction to occur, and how the ra ...
SCH4U Exam Review
... 30. Barium sulphate, BaSO4, is so insoluble that is can be swallowed without significant danger, even though Ba2+ is toxic. At 25C, 1.00 L of water dissolves only 0.00245 g of BaSO4. (a) How many moles of BaSO4 dissolve per liter? (b) What are the molar concentrations of Ba2+ and SO42- in a saturat ...
... 30. Barium sulphate, BaSO4, is so insoluble that is can be swallowed without significant danger, even though Ba2+ is toxic. At 25C, 1.00 L of water dissolves only 0.00245 g of BaSO4. (a) How many moles of BaSO4 dissolve per liter? (b) What are the molar concentrations of Ba2+ and SO42- in a saturat ...
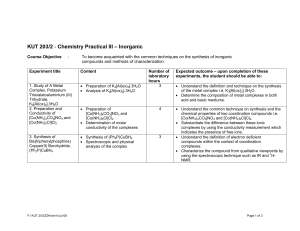
KUT 203/2 - Chemistry Practical III (Inorganic Chemistry)
... • Understand the correlation between the colors of transition metal or metal ion with its oxidation state i.e. VO2+ (yellow), VO2+ (blue) etc. • Determine the composition of a metal complex of which the metal exists in various oxidation states by using the titration technique. • Synthesize several c ...
... • Understand the correlation between the colors of transition metal or metal ion with its oxidation state i.e. VO2+ (yellow), VO2+ (blue) etc. • Determine the composition of a metal complex of which the metal exists in various oxidation states by using the titration technique. • Synthesize several c ...
AS CHECKLISTS File
... Explain the term isotopes as atoms of an element with different numbers of neutrons and different masses. State that 12C is used as the standard measurement of ...
... Explain the term isotopes as atoms of an element with different numbers of neutrons and different masses. State that 12C is used as the standard measurement of ...
Class_X–Science__term_I
... 1) Chemical reaction:-Chemical reaction is a change in which one or more new substances are formed. 2) Chemical Equations:-Representation of a chemical reaction in terms of symbols and formulae of the reactants and products is known as chemical equation. 3) Balanced Chemical equations:-The chemical ...
... 1) Chemical reaction:-Chemical reaction is a change in which one or more new substances are formed. 2) Chemical Equations:-Representation of a chemical reaction in terms of symbols and formulae of the reactants and products is known as chemical equation. 3) Balanced Chemical equations:-The chemical ...
Chapter 3: Stoichiometry
... Actual yield is found by measuring the quantity of product formed in the experiment. Theoretical yield is calculated from reaction stoichiometry. ...
... Actual yield is found by measuring the quantity of product formed in the experiment. Theoretical yield is calculated from reaction stoichiometry. ...
Unit #8 - consumerchem
... b) For all products to the right of the arrow. c) If more than one reactant or product, separate them with a "plus" sign. 4) 2. Once the correct formula is written: NEVER change the subscript(s). 5) 3. Set up a chart: a) with all atom types down the left side ...
... b) For all products to the right of the arrow. c) If more than one reactant or product, separate them with a "plus" sign. 4) 2. Once the correct formula is written: NEVER change the subscript(s). 5) 3. Set up a chart: a) with all atom types down the left side ...
Combining the Benefits of Homogeneous and Heterogeneous
... Gas-expanded liquids (GXLs) result from the pressurized dissolution of a gas, such as CO2, into organics like THF or acetonitrile. The GXL's physical properties can be tuned with the composition of the mixture, i.e. the amount of antisolvent gas added to the organic. Ford et al. [14] reported the Ka ...
... Gas-expanded liquids (GXLs) result from the pressurized dissolution of a gas, such as CO2, into organics like THF or acetonitrile. The GXL's physical properties can be tuned with the composition of the mixture, i.e. the amount of antisolvent gas added to the organic. Ford et al. [14] reported the Ka ...
Analysing Acids and Bases
... An indicator is used during acid-base titration to identify the equivalence point of the reaction. An acid-base indicator is a substance whose colour depends on the concentration of H3O+ ions in a solution. Indicators are weak acids with their acid form being one colour and their conjugate base ...
... An indicator is used during acid-base titration to identify the equivalence point of the reaction. An acid-base indicator is a substance whose colour depends on the concentration of H3O+ ions in a solution. Indicators are weak acids with their acid form being one colour and their conjugate base ...
Document
... atom or ion that is bonded to more than one atom or molecule. Some of the most interesting ions have a metal ion surrounded by a number of ligands. Ligands are molecules, such as ammonia, NH3, or anions, such as cyanide, CN −, that readily bond to metal ions. Figure 5 shows a model of one complex io ...
... atom or ion that is bonded to more than one atom or molecule. Some of the most interesting ions have a metal ion surrounded by a number of ligands. Ligands are molecules, such as ammonia, NH3, or anions, such as cyanide, CN −, that readily bond to metal ions. Figure 5 shows a model of one complex io ...
School of Chemistry and Physics Westville Campus, Durban
... 2.0 mole of silver nitrate reacts with 1.6 moles of HCl in a precipitation reaction to produce AgCl and nitric acid. The following reaction occurred: ...
... 2.0 mole of silver nitrate reacts with 1.6 moles of HCl in a precipitation reaction to produce AgCl and nitric acid. The following reaction occurred: ...
Chapter 4 Student Notes
... A redox equation is balanced if: it is balanced for atoms on each side. the total electrons lost and gained are equal. the reducing agent: the oxidizing agent: Our equation now looks like this: ...
... A redox equation is balanced if: it is balanced for atoms on each side. the total electrons lost and gained are equal. the reducing agent: the oxidizing agent: Our equation now looks like this: ...
Stoichiometry_files/5-Limiting React Lab 1.cwk (WP).
... 8.) When the reaction is over pour the contents of the beaker through the DRY filter paper & funnel. (You will need to use another beaker to catch the liquid) 9.) When the contents are filtered, spread your filter paper over a paper towel, LABEL it with your name and put it in the cabinets on the ba ...
... 8.) When the reaction is over pour the contents of the beaker through the DRY filter paper & funnel. (You will need to use another beaker to catch the liquid) 9.) When the contents are filtered, spread your filter paper over a paper towel, LABEL it with your name and put it in the cabinets on the ba ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.