Macromolecular Crystallography in India, IUCr, 2017
... dimerization of the two nucleases that nick each of the strands to cause dsDNA break). However, the structure clearly suggested that the convergence of the enzymes would leave the nucle ...
... dimerization of the two nucleases that nick each of the strands to cause dsDNA break). However, the structure clearly suggested that the convergence of the enzymes would leave the nucle ...
Molecular Cloning of engrafted: A Gene Involved in the
... We took advantage of a relatively small visible deletion that removes all of the cytological region 48A and part of 48B as an aid to the genomic cloning of the 48A region. This deleted chromosome lacks any engrailed function. We were able to establish the orientation of the entry point clones at 48B ...
... We took advantage of a relatively small visible deletion that removes all of the cytological region 48A and part of 48B as an aid to the genomic cloning of the 48A region. This deleted chromosome lacks any engrailed function. We were able to establish the orientation of the entry point clones at 48B ...
Document
... a process that has now become standard in many laboratories worldwide- gel electrophoresis. -Laboratories rely heavily on this proven and reliable technique for separating a wide variety of samples, from DNA used in forensics and for mapping genes, to proteins useful in determining evolutionary rela ...
... a process that has now become standard in many laboratories worldwide- gel electrophoresis. -Laboratories rely heavily on this proven and reliable technique for separating a wide variety of samples, from DNA used in forensics and for mapping genes, to proteins useful in determining evolutionary rela ...
Highly efficient semi-quantitative genotyping of single
... The mitochondrial locus 16519T/C [2] was used as target for the evaluation of the benefits of ICEMS for the determination of allelic frequencies in DNA mixtures. 16519 represents a highly polymorphic marker within the mitochondrial genome. Both allelic states are common within populations and the pr ...
... The mitochondrial locus 16519T/C [2] was used as target for the evaluation of the benefits of ICEMS for the determination of allelic frequencies in DNA mixtures. 16519 represents a highly polymorphic marker within the mitochondrial genome. Both allelic states are common within populations and the pr ...
In Vitro Protein Expression Kit for Disulfide - Sigma
... Introduction Thank you for your purchase of the In Vitro Protein Expression Kit (iPE-SS Kit) for use with disulfide bond containing proteins. ...
... Introduction Thank you for your purchase of the In Vitro Protein Expression Kit (iPE-SS Kit) for use with disulfide bond containing proteins. ...
Evolutionary Classification
... The genes of many organisms show important similarities at the molecular level. Similarities in DNA can be used to help determine classification and evolutionary Slide ...
... The genes of many organisms show important similarities at the molecular level. Similarities in DNA can be used to help determine classification and evolutionary Slide ...
Meiosis and Reproduction
... • Some combinations of alleles, produced during meiosis and fertilization might be more advantageous • This is what leads to natural selection. Individuals with more advantageous traits will survive to reproduce and pass on those traits. • Darwin realized that slow changes in inherited traits, due t ...
... • Some combinations of alleles, produced during meiosis and fertilization might be more advantageous • This is what leads to natural selection. Individuals with more advantageous traits will survive to reproduce and pass on those traits. • Darwin realized that slow changes in inherited traits, due t ...
Disrupting antibiotic resistance propagation by inhibiting
... coli F plasmid by Lederberg and Tatum in 1946 (2). Conjugative DNA transfer is also the central mechanism by which antibiotic resistance and virulence factors are propagated in bacterial populations (reviewed in ref. 3). Indeed, it is well established that antibiotic resistance can be rapidly acquir ...
... coli F plasmid by Lederberg and Tatum in 1946 (2). Conjugative DNA transfer is also the central mechanism by which antibiotic resistance and virulence factors are propagated in bacterial populations (reviewed in ref. 3). Indeed, it is well established that antibiotic resistance can be rapidly acquir ...
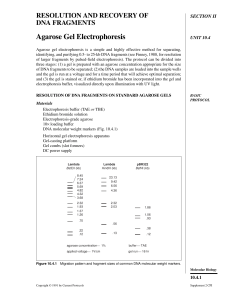
Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
... A bellows-type camera equipped with a Polaroid film holder provides a convenient means for gel photography (see sketch 10.4A). An orange filter (Kodak Wratten #23A) is required to achieve a desirable film image of light transmitted by fluorescing DNA. A clear UV blocking filter (Kodak Wratten #2B) i ...
... A bellows-type camera equipped with a Polaroid film holder provides a convenient means for gel photography (see sketch 10.4A). An orange filter (Kodak Wratten #23A) is required to achieve a desirable film image of light transmitted by fluorescing DNA. A clear UV blocking filter (Kodak Wratten #2B) i ...
Preparation of MyoD mRNA for the differentiation of stem cells into
... Stem cells have been extensively studied by scientists as they have the ability to differentiate into different somatic cells, or diploid cells, and carry out different functions. However, somatic cells could also be induced to differentiate back into stem cells and then be differentiated into other ...
... Stem cells have been extensively studied by scientists as they have the ability to differentiate into different somatic cells, or diploid cells, and carry out different functions. However, somatic cells could also be induced to differentiate back into stem cells and then be differentiated into other ...
Table of Contents - NAU jan.ucc.nau.edu web server
... special sequence of DNA . The promoter determines the direction, which strand to read, and direction to take RNA polymerase binds to the promoter. Once the polymerase is attached to the promoter DNA, the DNA strands unwind and ...
... special sequence of DNA . The promoter determines the direction, which strand to read, and direction to take RNA polymerase binds to the promoter. Once the polymerase is attached to the promoter DNA, the DNA strands unwind and ...
BB30055: Genes and genomes
... SSR - Simple Sequence Repeats /STR – short tandem repeats 1-13 bp repeats e.g. (A)n ; (AC)n 2% of genome (dinucleotides - 0.5%) Used as genetic markers (especially for disease mapping) ...
... SSR - Simple Sequence Repeats /STR – short tandem repeats 1-13 bp repeats e.g. (A)n ; (AC)n 2% of genome (dinucleotides - 0.5%) Used as genetic markers (especially for disease mapping) ...
An enlarged largest subunit or Plasmodium falciparum RNA
... sequences of clone gl5 and the cDNA clones were colinear (Fig. 1C. and ID.). Oligonucleotide probes B and C, derived from the 5' region of clone gl5, hybridized with a 12 kb genomic Xbal fragment (Fig. 2B.). Probe B and C selected a clone, XI, from a Xbal genomic DNA library. Clone XI contained the ...
... sequences of clone gl5 and the cDNA clones were colinear (Fig. 1C. and ID.). Oligonucleotide probes B and C, derived from the 5' region of clone gl5, hybridized with a 12 kb genomic Xbal fragment (Fig. 2B.). Probe B and C selected a clone, XI, from a Xbal genomic DNA library. Clone XI contained the ...
the three dynamic levels of dna consciousness
... in the theory of DNA consciousness has become more of a science that involves genetic pathways that underlay the neurologic correlates of consciousness (NCC). However, what evidence do we have to support the first concept of the theory of DNA consciousness i.e. DNA is a degree of consciousness? The ...
... in the theory of DNA consciousness has become more of a science that involves genetic pathways that underlay the neurologic correlates of consciousness (NCC). However, what evidence do we have to support the first concept of the theory of DNA consciousness i.e. DNA is a degree of consciousness? The ...
Electrophoresis and Hardy Wienberg notes
... • p2 = the percentage of individuals with three repeats of the STR sequence on both chromosomes • 2pq = the percentage of individuals with one chromosome with three repeats and one with five repeats • q2 = the percentage of individuals with five repeats of the STR sequence on both chromosomes ...
... • p2 = the percentage of individuals with three repeats of the STR sequence on both chromosomes • 2pq = the percentage of individuals with one chromosome with three repeats and one with five repeats • q2 = the percentage of individuals with five repeats of the STR sequence on both chromosomes ...
Cleavage of a model DNA replication fork by a Type I restriction
... site and an unmethylated site, which is a target for restriction cleavage. Generation of an unmethylated site should be generally rare, but it can occur in certain mutants with replication fork crowding, as described below. Therefore, it is possible that some relationship exists between restriction ...
... site and an unmethylated site, which is a target for restriction cleavage. Generation of an unmethylated site should be generally rare, but it can occur in certain mutants with replication fork crowding, as described below. Therefore, it is possible that some relationship exists between restriction ...
Motif Finding Problem
... • Located within the RR are the Transcription Factor Binding Sites (TFBS), also known as motifs, specific for a given transcription factor • TFs influence gene expression by binding to a specific location in the respective gene’s regulatory region - TFBS ...
... • Located within the RR are the Transcription Factor Binding Sites (TFBS), also known as motifs, specific for a given transcription factor • TFs influence gene expression by binding to a specific location in the respective gene’s regulatory region - TFBS ...
Epigenetic differences arise during the lifetime of
... indicate how an appreciation of epigenetics is missing from our understanding of how different phenotypes can be originated from the same genotype. DNA methylation 兩 epigenetics 兩 histones ...
... indicate how an appreciation of epigenetics is missing from our understanding of how different phenotypes can be originated from the same genotype. DNA methylation 兩 epigenetics 兩 histones ...
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSRJECE)
... the realm of molecular electronics. Molecular electronics attempts to find the use of single molecule or group of molecules to function as basic element of electronic devices. Molecular electronic uses material having dimensions below 100 nm, such as organic molecules, carbon nanotubes, and nanowire ...
... the realm of molecular electronics. Molecular electronics attempts to find the use of single molecule or group of molecules to function as basic element of electronic devices. Molecular electronic uses material having dimensions below 100 nm, such as organic molecules, carbon nanotubes, and nanowire ...
The “m”
... steps. (1) Look on the left side of the chart to find the large row of codons that begin with C. (2) Move across this row until you get to the column of ...
... steps. (1) Look on the left side of the chart to find the large row of codons that begin with C. (2) Move across this row until you get to the column of ...
Table of Contents: Introduction
... Hello, and welcome to the January 2013 issue of DNA Tribes® Digest. This month’s feature article will explore genetic evidence for the origins of European populations, based on a detailed comparison to neighboring world regions using autosomal STR data. In particular, this analysis will explore evid ...
... Hello, and welcome to the January 2013 issue of DNA Tribes® Digest. This month’s feature article will explore genetic evidence for the origins of European populations, based on a detailed comparison to neighboring world regions using autosomal STR data. In particular, this analysis will explore evid ...
Genotyping of Ryanodine receptor 1 (RYR1) gene associated with
... et al., 2007). Although, these two approaches are effective and sensitive, problems with reproducibility and costly of these techniques have been a major barricade, respectively. Therefore, most of researchers have widely employed PCR-RFLP using Hhal restriction enzyme for determining the C1843T var ...
... et al., 2007). Although, these two approaches are effective and sensitive, problems with reproducibility and costly of these techniques have been a major barricade, respectively. Therefore, most of researchers have widely employed PCR-RFLP using Hhal restriction enzyme for determining the C1843T var ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.