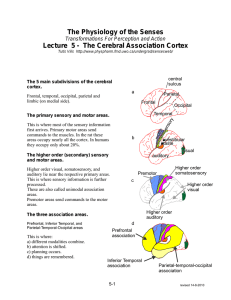
The Cerebral Association Cortex
... All adjacent areas of cortex are extensively interconnected as are selected distant areas. These fiber tracts form the white matter of the cortex which contains several million miles of axons. These extensive interconnections predisposes the cortex to epilepsy. A locus of abnormal activity in one ar ...
... All adjacent areas of cortex are extensively interconnected as are selected distant areas. These fiber tracts form the white matter of the cortex which contains several million miles of axons. These extensive interconnections predisposes the cortex to epilepsy. A locus of abnormal activity in one ar ...
Neurons, Hormones, and the Brain
... includes the axon terminal, synaptic cleft, and receptor sites on receiving cell. Neurotransmitter: Chemical substance that is released by transmitting neuron at the synapse and alters the activity of the receiving neuron. ©2002 Prentice Hall ...
... includes the axon terminal, synaptic cleft, and receptor sites on receiving cell. Neurotransmitter: Chemical substance that is released by transmitting neuron at the synapse and alters the activity of the receiving neuron. ©2002 Prentice Hall ...
Keshara Senanayake Page # 1 -an individual nerve cells is called
... (postsynaptic neuron). >both dendrites and the cell bodies of neurons are covered with synapses >synapses include the synaptic terminal of the presynaptic neuron, the gap, and the specialized membrane of the post synaptic neuron (contains receptors for neurotransmitters) -when action potential reach ...
... (postsynaptic neuron). >both dendrites and the cell bodies of neurons are covered with synapses >synapses include the synaptic terminal of the presynaptic neuron, the gap, and the specialized membrane of the post synaptic neuron (contains receptors for neurotransmitters) -when action potential reach ...
Nervous_System__Ch_7__S2015
... (e) Satellite cells and Schwann cells (which form myelin) surround neurons in the PNS. ...
... (e) Satellite cells and Schwann cells (which form myelin) surround neurons in the PNS. ...
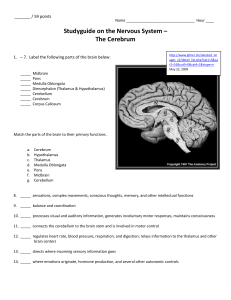
Major Parts of the Brain:
... 8. _____ sensations, complex movements, conscious thoughts, memory, and other intellectual functions 9. _____ balance and coordination 10. _____ processes visual and auditory information, generates involuntary motor responses, maintains consciousness 11. _____ connects the cerebellum to the brain st ...
... 8. _____ sensations, complex movements, conscious thoughts, memory, and other intellectual functions 9. _____ balance and coordination 10. _____ processes visual and auditory information, generates involuntary motor responses, maintains consciousness 11. _____ connects the cerebellum to the brain st ...
ch 16 sensory motor systems
... merges into the next. Each stage has been identified by EEG recordings . 2) Most dreaming occurs during rapid eye movement sleep. C. Learning and Memory 1. Learning is the ability to acquire new knowledge or skills through instruction or experience. Memory is the process by which that knowledge is r ...
... merges into the next. Each stage has been identified by EEG recordings . 2) Most dreaming occurs during rapid eye movement sleep. C. Learning and Memory 1. Learning is the ability to acquire new knowledge or skills through instruction or experience. Memory is the process by which that knowledge is r ...
Nervous System PowerPoint
... close and the ion gates for sodium open up. Positive ions flood into the cell making it positive. This rapid inflow is referred to as depolarization. After the impulse, the gates return to the resting condition with extra potassium gates open. The flow of potassium ions out of the cell restores ...
... close and the ion gates for sodium open up. Positive ions flood into the cell making it positive. This rapid inflow is referred to as depolarization. After the impulse, the gates return to the resting condition with extra potassium gates open. The flow of potassium ions out of the cell restores ...
Ramón y Cajal, 19 th century
... dendritic shape. This leads to changes in neuronal connectivity which, in turn, adapts neuronal activity. The goal is that by these changes neurons achieve a homeostatic equilibrium of their activity. ...
... dendritic shape. This leads to changes in neuronal connectivity which, in turn, adapts neuronal activity. The goal is that by these changes neurons achieve a homeostatic equilibrium of their activity. ...
Full Text PDF - Jaypee Journals
... layer of neuroepithelial cells, called the matrix layer (Fig. 5A). As this layer thickens, it gradually acquires the configuration of a pseudostratified epithelium. The nuclei of neuroectodermal cells become arranged in more and more layers, but all these cells remain in contact with the external an ...
... layer of neuroepithelial cells, called the matrix layer (Fig. 5A). As this layer thickens, it gradually acquires the configuration of a pseudostratified epithelium. The nuclei of neuroectodermal cells become arranged in more and more layers, but all these cells remain in contact with the external an ...
Neural Networks (NN)
... If the step activation function is used (i.e., the neuron's output is 0 if the input is less than zero, and 1 if the input is greater than or equal to 0) then the neuron acts just like the biological neuron described earlier (subtracting the threshold from the weighted sum and comparing with zero is ...
... If the step activation function is used (i.e., the neuron's output is 0 if the input is less than zero, and 1 if the input is greater than or equal to 0) then the neuron acts just like the biological neuron described earlier (subtracting the threshold from the weighted sum and comparing with zero is ...
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE)
... most common tests undertaken to confirm the presence of brain tumor and to identify its location for selected specialist treatment options. Currently, there are different treatment options available for brain tumor. These options include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. The choice for t ...
... most common tests undertaken to confirm the presence of brain tumor and to identify its location for selected specialist treatment options. Currently, there are different treatment options available for brain tumor. These options include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. The choice for t ...
Physiology2 - Sheet#8 - Dr.Loai Alzgoul - Done By: Mais
... *in the past , people discovered morphine as a pain relief . After that they discovered its receptor in the body which they called µ receptors (morphine receptors ) . BUT since we have special receptors for morphine then there must be something similar to morphine structure in our bodies. That was" ...
... *in the past , people discovered morphine as a pain relief . After that they discovered its receptor in the body which they called µ receptors (morphine receptors ) . BUT since we have special receptors for morphine then there must be something similar to morphine structure in our bodies. That was" ...
The Nervous System - Optum360Coding.com
... controls unconscious movements in skeletal muscle for coordination, posture, balance; injury/trauma characterized by lack of muscle coordination, abnormal gait, may affect speech muscles; some cognitive functions such as attention, language, emotional functions such as fear and pleasure responses; d ...
... controls unconscious movements in skeletal muscle for coordination, posture, balance; injury/trauma characterized by lack of muscle coordination, abnormal gait, may affect speech muscles; some cognitive functions such as attention, language, emotional functions such as fear and pleasure responses; d ...
ch4_1 - Homework Market
... many synapses. • Final cellular activity is a summation of these many excitatory and inhibitory synaptic signals. ...
... many synapses. • Final cellular activity is a summation of these many excitatory and inhibitory synaptic signals. ...
Areas of Research Interest
... information that people remember about false events versus the types of information they remember about real events. One objective is that if we know how the two memories differ, we might be able to tell when the memories people retrieve are actually false. References Burns, D. J., Martens, N. J, Be ...
... information that people remember about false events versus the types of information they remember about real events. One objective is that if we know how the two memories differ, we might be able to tell when the memories people retrieve are actually false. References Burns, D. J., Martens, N. J, Be ...
• In vertebrates
... neurons are distributed according to the body part that generates sensory input or receives motor input Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... neurons are distributed according to the body part that generates sensory input or receives motor input Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
The Nervous System
... 1. What part of the brain do you use to do your math homework? 2. What part of the brain do you mostly use to create a drawing? 3. What part of the brain helps a basketball player maintain her balance while driving for a lay-up? 4. What part of the body protects the spinal cord? To which body system ...
... 1. What part of the brain do you use to do your math homework? 2. What part of the brain do you mostly use to create a drawing? 3. What part of the brain helps a basketball player maintain her balance while driving for a lay-up? 4. What part of the body protects the spinal cord? To which body system ...
Central Nervous System
... – The association areas, in turn, communicate with the motor cortex and with other sensory association areas to analyze, recognize, and act on sensory inputs. ...
... – The association areas, in turn, communicate with the motor cortex and with other sensory association areas to analyze, recognize, and act on sensory inputs. ...
cognitive processes and memory
... attention, our motivation, how much we practice, our state of consciousness when we learn something and our state of consciousness when we recall it, and interference from other events and experiences. Cognitive psychologists study cognition, all the mental activities associated with thinking, knowi ...
... attention, our motivation, how much we practice, our state of consciousness when we learn something and our state of consciousness when we recall it, and interference from other events and experiences. Cognitive psychologists study cognition, all the mental activities associated with thinking, knowi ...
Concept Analysis Diagram - Intracranial Regulation
... The brain is a complex organ that controls many functions of the body. The brain receives and interprets stimuli from both internal and external sources. Intracranial regulation includes normal and abnormal processes of cranial function. This process includes the brain and the central nervous system ...
... The brain is a complex organ that controls many functions of the body. The brain receives and interprets stimuli from both internal and external sources. Intracranial regulation includes normal and abnormal processes of cranial function. This process includes the brain and the central nervous system ...
Lesson 1 - SEL at Meigs
... stronger cell connections each time you repeat a thought or action. To do this, we will be building our own neuron models out of food! You will be given four different types of food so that each food item can be used for a different part of the neuron. Facilitator discusses diagram: Say: The dia ...
... stronger cell connections each time you repeat a thought or action. To do this, we will be building our own neuron models out of food! You will be given four different types of food so that each food item can be used for a different part of the neuron. Facilitator discusses diagram: Say: The dia ...
VL 3 - Memory and Attention
... " Recency effects reflect limited STM capacity, ceases with time " Primacy effects reflect transfer to LTM via rehearsal " Primacy effect more robust than recency: less affected by interference or delay ...
... " Recency effects reflect limited STM capacity, ceases with time " Primacy effects reflect transfer to LTM via rehearsal " Primacy effect more robust than recency: less affected by interference or delay ...
Chapter 9 - Nervous System
... A particular neuron of a pool may receive excitatory or inhibitory stimulation; if the net effect is excitatory but subthreshold, the neuron becomes more excitable to incoming stimulation (a condition called facilitation). D. Convergence (p. 217) ...
... A particular neuron of a pool may receive excitatory or inhibitory stimulation; if the net effect is excitatory but subthreshold, the neuron becomes more excitable to incoming stimulation (a condition called facilitation). D. Convergence (p. 217) ...
The Nervous System
... Identify and discuss the two main parts of the nervous system. Explain how the nervous system functions as the central control system of the body. Identify factors that may lead to disorders of the nervous system. http://thekidshouldseethis.com/post/21915392227 ...
... Identify and discuss the two main parts of the nervous system. Explain how the nervous system functions as the central control system of the body. Identify factors that may lead to disorders of the nervous system. http://thekidshouldseethis.com/post/21915392227 ...