- Lorentz Center
... by the intrinsic properties of the cell. The Fourier transform of the input (external + feedback) is given by Xi(). ...
... by the intrinsic properties of the cell. The Fourier transform of the input (external + feedback) is given by Xi(). ...
Using Music to Tap Into a Universal Neural Grammar
... Terms of Frequency Codes and Temporal Codes According to the second premise of the MBM, frequency codes and temporal codes are the fundamental building blocks of higher brain function - they are the means by which information is organized, represented and coordinated in the brain. Within the neurosc ...
... Terms of Frequency Codes and Temporal Codes According to the second premise of the MBM, frequency codes and temporal codes are the fundamental building blocks of higher brain function - they are the means by which information is organized, represented and coordinated in the brain. Within the neurosc ...
Save
... Broca,Werniche,Kussmaul) , can be identified with the consciousness formation that can be interpreted as a sort of constant,continous and simultaneous low-noise effect. When the cortex receives sufficient afferent impulses, it is said to be aroused or activated. That is, a critical number of cortica ...
... Broca,Werniche,Kussmaul) , can be identified with the consciousness formation that can be interpreted as a sort of constant,continous and simultaneous low-noise effect. When the cortex receives sufficient afferent impulses, it is said to be aroused or activated. That is, a critical number of cortica ...
1. Cell body - greinerudsd
... travels down to the axon of the first neuron. 2. When the signal reaches the end of the axon, the axon releases chemicals called neurotransmitters. ...
... travels down to the axon of the first neuron. 2. When the signal reaches the end of the axon, the axon releases chemicals called neurotransmitters. ...
Slide ()
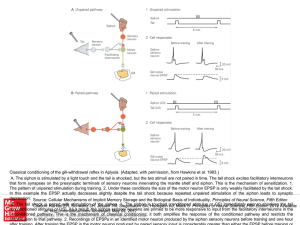
... Classical conditioning of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. (Adapted, with permission, from Hawkins et al. 1983.) A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses ...
... Classical conditioning of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. (Adapted, with permission, from Hawkins et al. 1983.) A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses ...
Ectopic brain tissue in the orbit
... undifferentiated, while in our patient clear neuroectodermal differentiation occurred? Likewise, it is unlikely that this is a microphthalmia with cyst since no formed globe was present. Finally, meningoencephalocoele and encephalocoele are unlikely since there was no continuity between the orbit an ...
... undifferentiated, while in our patient clear neuroectodermal differentiation occurred? Likewise, it is unlikely that this is a microphthalmia with cyst since no formed globe was present. Finally, meningoencephalocoele and encephalocoele are unlikely since there was no continuity between the orbit an ...
Text 4-Nervous system: Organization and Physiology
... ACTION POTENTIAL (axon conduction) GRADED POTENTIAL (cell-cell communication at synapse) ...
... ACTION POTENTIAL (axon conduction) GRADED POTENTIAL (cell-cell communication at synapse) ...
GABA A Receptor
... both positive and negative control of the degree of excitability of the neuron – Decreasing the voltage to a less negative value makes the membrane of the neuron more excitable while increasing this voltage to a more negative value makes the neuron less excitable. Sodium ion concentration is high in ...
... both positive and negative control of the degree of excitability of the neuron – Decreasing the voltage to a less negative value makes the membrane of the neuron more excitable while increasing this voltage to a more negative value makes the neuron less excitable. Sodium ion concentration is high in ...
Ch. 9: The Nervous System: The Body's Control Center
... nerves, named for corresponding vertebrae Ends at L2 in pointed structure called conus medullaris; hanging from conus medullaris is cauda equine (horses tail), which dangles loosely and floats in bath of cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) Has 2 widened areas, cervical and lumbar enlargements; contain neuro ...
... nerves, named for corresponding vertebrae Ends at L2 in pointed structure called conus medullaris; hanging from conus medullaris is cauda equine (horses tail), which dangles loosely and floats in bath of cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) Has 2 widened areas, cervical and lumbar enlargements; contain neuro ...
Discovering spatial working memory fields in prefrontal cortex
... the computer monitor and the room is dark, the monkey must use working memory to perform the task. Thus the oculomotor paradigm offers an unprecedented degree of experimental control. Funahashi et al. found that many neurons in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex including and surrounding the princip ...
... the computer monitor and the room is dark, the monkey must use working memory to perform the task. Thus the oculomotor paradigm offers an unprecedented degree of experimental control. Funahashi et al. found that many neurons in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex including and surrounding the princip ...
Nervous and Endocrine System
... • At the end of class you should be able to: – Understand the various parts of the nervous system and explain their functions. – Understand how the hormones of the endocrine system differ from the nervous system? ...
... • At the end of class you should be able to: – Understand the various parts of the nervous system and explain their functions. – Understand how the hormones of the endocrine system differ from the nervous system? ...
The Nervous System and Neurons
... 2. List the 4 main parts and describe the purpose of the 4 main parts of a neuron. 3. The nervous system is divided into 2 parts. What are they and what do they include? 4. Describe the internal and external environment of a neuron in resting potential. How is resting potential reached? 5. What is a ...
... 2. List the 4 main parts and describe the purpose of the 4 main parts of a neuron. 3. The nervous system is divided into 2 parts. What are they and what do they include? 4. Describe the internal and external environment of a neuron in resting potential. How is resting potential reached? 5. What is a ...
Chapter - Heartland Community College
... A. The resting potential of a typical neuron is -70 mV within the neuron. B. There is a difference in electrical potential between the sides of the cell membrane. C. There is a voltage difference between the inside and the outside of the cell membrane. D. The resting potential is the difference in e ...
... A. The resting potential of a typical neuron is -70 mV within the neuron. B. There is a difference in electrical potential between the sides of the cell membrane. C. There is a voltage difference between the inside and the outside of the cell membrane. D. The resting potential is the difference in e ...
Baars - neurofeedback - Aspen2008
... Procedural learning appears to require conscious access during acquisition, and then becomes less conscious with practice, coinciding with less cortical involvement. ...
... Procedural learning appears to require conscious access during acquisition, and then becomes less conscious with practice, coinciding with less cortical involvement. ...
Discovering spatial working memory fields in prefrontal cortex
... the computer monitor and the room is dark, the monkey must use working memory to perform the task. Thus the oculomotor paradigm offers an unprecedented degree of experimental control. Funahashi et al. found that many neurons in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex including and surrounding the princip ...
... the computer monitor and the room is dark, the monkey must use working memory to perform the task. Thus the oculomotor paradigm offers an unprecedented degree of experimental control. Funahashi et al. found that many neurons in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex including and surrounding the princip ...
IOSR Journal of Computer Science (IOSR-JCE) e-ISSN: 2278-0661, p-ISSN: 2278-8727 PP 24-28 www.iosrjournals.org
... Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) [1] technology is a new and fast evolving field that seeks direct interaction between the human neural system and machines, aiming to augment human capabilities by enabling people (especially disabled) to communicate and control devices by mere “thinking” or expressing ...
... Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) [1] technology is a new and fast evolving field that seeks direct interaction between the human neural system and machines, aiming to augment human capabilities by enabling people (especially disabled) to communicate and control devices by mere “thinking” or expressing ...
brain-power-ppttm
... Handles all sensory information that passes between the spinal cord and the forebrain. It is also involved in body movement in relation to auditory ...
... Handles all sensory information that passes between the spinal cord and the forebrain. It is also involved in body movement in relation to auditory ...
Slide ()
... Internal capsule (A) and MRIs through internal capsule (B) and midbrain (C). The locations of the descending axons in the internal capsule and basis pedunculi are shown on the MRIs. The letters "FATL" abbreviate Face, Arm, Trunk, and Leg. In the midbrain, the descending cortical fibers (filled middl ...
... Internal capsule (A) and MRIs through internal capsule (B) and midbrain (C). The locations of the descending axons in the internal capsule and basis pedunculi are shown on the MRIs. The letters "FATL" abbreviate Face, Arm, Trunk, and Leg. In the midbrain, the descending cortical fibers (filled middl ...
Core studies summary
... Psychological research into memory strongly suggests that there are many factors which would make eye-witnesses unreliable and the Devlin Committee (1973) recommended that juries should be instructed that it is not safe to convict on the basis of eye-witness testimony alone. Eyewitness testimony is ...
... Psychological research into memory strongly suggests that there are many factors which would make eye-witnesses unreliable and the Devlin Committee (1973) recommended that juries should be instructed that it is not safe to convict on the basis of eye-witness testimony alone. Eyewitness testimony is ...
nervous system text a - powerpoint presentation
... ganglia. Developmentally, this type of neuron starts out as a bipolar neuron. ...
... ganglia. Developmentally, this type of neuron starts out as a bipolar neuron. ...