Nonlinear-optical properties of a noninteracting Bose gas
... p ! h̄k momentum eigenstate (k is the wave vector of the incident electromagnetic f ield). The states jq# are then eigenstates of the free particle Hamiltonian H0 with eigenenergies ...
... p ! h̄k momentum eigenstate (k is the wave vector of the incident electromagnetic f ield). The states jq# are then eigenstates of the free particle Hamiltonian H0 with eigenenergies ...
Pasechnik
... In difference from Vainshtein’s approach within the dispersion approach we have two dispersion relations for axial anomaly including both structures ...
... In difference from Vainshtein’s approach within the dispersion approach we have two dispersion relations for axial anomaly including both structures ...
Symmetry in Electron-Atom Collisions and Photoionization Process
... It is thus natural to expect that the quantum mechanical description of the two processes, (a) atomic photoionization and (b) electron-ion collision, must be related. Indeed it is, but the relationship is subtle. The difficulty in relating the two processes comes from the fact that even if the final ...
... It is thus natural to expect that the quantum mechanical description of the two processes, (a) atomic photoionization and (b) electron-ion collision, must be related. Indeed it is, but the relationship is subtle. The difficulty in relating the two processes comes from the fact that even if the final ...
Stacey Carpenter
... Here's how it's done in physics: Remember Newton's 2nd Law of Motion, Fnet=ma? Will it make a difference how long you apply the force? Descartes (Need to check this.) took the equation from Newton's 2nd Law, F = ma, and looked at what would happen if the force was applied for a period of time. Ft ...
... Here's how it's done in physics: Remember Newton's 2nd Law of Motion, Fnet=ma? Will it make a difference how long you apply the force? Descartes (Need to check this.) took the equation from Newton's 2nd Law, F = ma, and looked at what would happen if the force was applied for a period of time. Ft ...
An introduction to the concept of symmetry - Pierre
... It must be invariant under space translation, time translation, rotations and Lorentz transformation The laws of physics are independent of the state of motion and the position of observers This equation must satisfies three local gauge invariance on the internal space of the particles (quantu ...
... It must be invariant under space translation, time translation, rotations and Lorentz transformation The laws of physics are independent of the state of motion and the position of observers This equation must satisfies three local gauge invariance on the internal space of the particles (quantu ...
Monday, October 25, 2004
... The total external force exerted on the system of total mass M causes the center of mass to move at an acceleration given by a F / M as if all the mass of the system is concentrated on the center of mass. Consider a massless rod with two balls attached at either end. The position of the center o ...
... The total external force exerted on the system of total mass M causes the center of mass to move at an acceleration given by a F / M as if all the mass of the system is concentrated on the center of mass. Consider a massless rod with two balls attached at either end. The position of the center o ...
10SuExamF
... of inertia is I = (2/5)M(R)2. (Note: So, it is ISN’T a uniform disk, & the disk moment of inertia, Idisk = (½)MR2 should NOT be used!!) At time t = 0, it starts from rest (initial angular velocity ω0 = 0) & begins to rotate counterclockwise about an axis passing through center of the sphere & R perp ...
... of inertia is I = (2/5)M(R)2. (Note: So, it is ISN’T a uniform disk, & the disk moment of inertia, Idisk = (½)MR2 should NOT be used!!) At time t = 0, it starts from rest (initial angular velocity ω0 = 0) & begins to rotate counterclockwise about an axis passing through center of the sphere & R perp ...
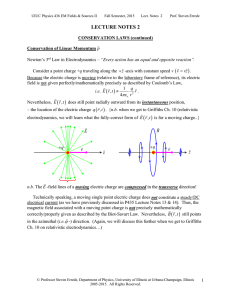
Lecture Notes 02: Conservation Laws (Continued): Conservation of Linear Momentum, Maxwell's Stress Tensor
... Thus, here, for this special case, Newton’s 3rd law is obeyed simply by the mechanical linear momentum associated with this system – the linear momentum carried by the EM field(s) in this special-case situation is zero. Note that this special-case situation is related to the case of parallel electri ...
... Thus, here, for this special case, Newton’s 3rd law is obeyed simply by the mechanical linear momentum associated with this system – the linear momentum carried by the EM field(s) in this special-case situation is zero. Note that this special-case situation is related to the case of parallel electri ...
General Physics I Homework Set 5
... drops to the ground afterward (but soon recovers to fly hap(b) What is the angular velocity of the bar just as it reaches the ground? pily away). What is the angular velocity of the bar (a) just afterit is hit by the bird, and (b) just as it reaches the ground? 10.92. A small block with mass 0.250 k ...
... drops to the ground afterward (but soon recovers to fly hap(b) What is the angular velocity of the bar just as it reaches the ground? pily away). What is the angular velocity of the bar (a) just afterit is hit by the bird, and (b) just as it reaches the ground? 10.92. A small block with mass 0.250 k ...
The Fundamental Physics of Electromagnetic Waves
... determined the correct formula for blackbody radiation. A proper derivation of that empirical equation, however, was another matter altogether and according to Planck was the hardest work of his life. (Planck, 1901 and 1920) Planck started with the Helmholtz equation (U = A + TS) and then introduced ...
... determined the correct formula for blackbody radiation. A proper derivation of that empirical equation, however, was another matter altogether and according to Planck was the hardest work of his life. (Planck, 1901 and 1920) Planck started with the Helmholtz equation (U = A + TS) and then introduced ...
Linear Momentum and Collisions
... A car with mass 1.5×103 kg traveling east at a speed of 25 m/s collides at an intersection with a 2.5×103 kg van traveling north at a speed of 20 m/s. Find the magnitude and direction of the velocity of the wreckage after the collision, assuming that the vehicles undergo a perfectly inelastic collis ...
... A car with mass 1.5×103 kg traveling east at a speed of 25 m/s collides at an intersection with a 2.5×103 kg van traveling north at a speed of 20 m/s. Find the magnitude and direction of the velocity of the wreckage after the collision, assuming that the vehicles undergo a perfectly inelastic collis ...
Rescattering of Ultra Low-Energy Electrons for Single
... parent ion with low velocities and, accordingly, large elastic scattering cross sections. Thus, after acceleration in the laser field they are effectively redistributed to larger momenta depleting at the same time the intensity at P e close to zero. Since recent purely classical “over-the-barrier” c ...
... parent ion with low velocities and, accordingly, large elastic scattering cross sections. Thus, after acceleration in the laser field they are effectively redistributed to larger momenta depleting at the same time the intensity at P e close to zero. Since recent purely classical “over-the-barrier” c ...