IMFUFA- Roskilde Universitetscenter- postbox 260
... The force of gravity on the surface of such a particle will be so strong, that the particle "swallows itself” and becomes a mini-black hole. This has never been observed.and will probably never be, since the Planck-energy Mp∙c2 = 1018 GeV is far beyond the range of even the largest accelerators. Per ...
... The force of gravity on the surface of such a particle will be so strong, that the particle "swallows itself” and becomes a mini-black hole. This has never been observed.and will probably never be, since the Planck-energy Mp∙c2 = 1018 GeV is far beyond the range of even the largest accelerators. Per ...
Chapter 8 Microcanonical ensemble
... In the case of the ideal gas free expansion, eliminating dynamical constraints meant increasing the volume. The phase space volume is a monotonically increasing function of the configuration volume V and, since S is by definition proportional to the phase space volume (eq. (8.2)), the statistical S ...
... In the case of the ideal gas free expansion, eliminating dynamical constraints meant increasing the volume. The phase space volume is a monotonically increasing function of the configuration volume V and, since S is by definition proportional to the phase space volume (eq. (8.2)), the statistical S ...
Computation of hadronic two-point functions in Lattice QCD
... field theories: not directly measurable parameters need to be adjusted as functions of a scale µ at which QCD is evaluated, to keep physical observables (e.g. hadron masses) constant and well defined. In QCD this is possible and no new terms need to be introduced as µ is sent to infinity. QCD is a r ...
... field theories: not directly measurable parameters need to be adjusted as functions of a scale µ at which QCD is evaluated, to keep physical observables (e.g. hadron masses) constant and well defined. In QCD this is possible and no new terms need to be introduced as µ is sent to infinity. QCD is a r ...
Introduction to the Physics of Waves and Sound
... The above assumptions are made with the technical equivalent of artistic license. Since they greatly simply the system while preserving much of the essential nature of physical oscillation, they are useful for purposes of explanation, and introductory physics texts almost invariably use them. Real ...
... The above assumptions are made with the technical equivalent of artistic license. Since they greatly simply the system while preserving much of the essential nature of physical oscillation, they are useful for purposes of explanation, and introductory physics texts almost invariably use them. Real ...
SC81 Physics Curriculum Map 2010/2011 Revised 7/29/2010
... 1. Predict how the force will change between two masses when the distance between them increases or decreases. Predict how the force will change between two masses when the mass of one or both of them increases or ...
... 1. Predict how the force will change between two masses when the distance between them increases or decreases. Predict how the force will change between two masses when the mass of one or both of them increases or ...
Physics Regents Review Sheet
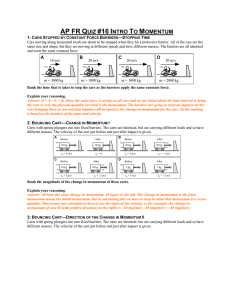
... _____ what holds the Earth in its path around the Sun _____ Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation _____ what G represents _____ how weight (force due to gravity) is related to distance of separation _____ Kepler’s Laws Momentum _____ what momentum is _____ when an object has momentum _____ how momen ...
... _____ what holds the Earth in its path around the Sun _____ Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation _____ what G represents _____ how weight (force due to gravity) is related to distance of separation _____ Kepler’s Laws Momentum _____ what momentum is _____ when an object has momentum _____ how momen ...
chapter7_PC
... not have to be the same as the sign of the angular speed The instantaneous angular acceleration is defined as the limit of the average acceleration as the ...
... not have to be the same as the sign of the angular speed The instantaneous angular acceleration is defined as the limit of the average acceleration as the ...
Conceptual Physics
... 23. If a ball is thrown up at 10 m/s, what will be the speed of the ball when it’s caught back at the original point of the throw? 24. If you throw a ball straight up, what is the ball’s instantaneous speed at the top of its path? 25. If you throw a ball straight up, what is the ball’s acceleration ...
... 23. If a ball is thrown up at 10 m/s, what will be the speed of the ball when it’s caught back at the original point of the throw? 24. If you throw a ball straight up, what is the ball’s instantaneous speed at the top of its path? 25. If you throw a ball straight up, what is the ball’s acceleration ...
Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem for Rotational Motion
... Imagine an object that moves in a complete circle. The object rotates through the angle of ...
... Imagine an object that moves in a complete circle. The object rotates through the angle of ...
Electromagnetic Fields
... • In application to AMO problems, wavelengths are almost always >> the size of the system: >>R. This suggests the dipole approximation, where transverse/longitudinal seems hardly to matter. Isn’t the dipole approximation always valid in practical environments? • There exists a simple gauge transfor ...
... • In application to AMO problems, wavelengths are almost always >> the size of the system: >>R. This suggests the dipole approximation, where transverse/longitudinal seems hardly to matter. Isn’t the dipole approximation always valid in practical environments? • There exists a simple gauge transfor ...