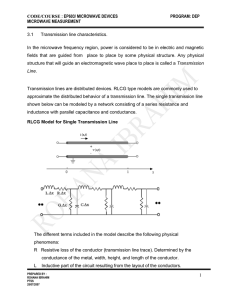
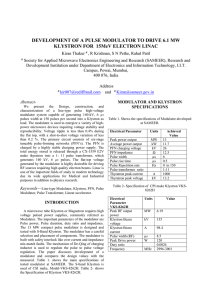
CODE/COURSE : EP603/ MICROWAVE DEVICES PROGRAM: DEP
... The wavemeter is adjusted for maximum or minimum power meter readings depending on whether the cavity is a transmission or absorption type device. With the tarnsmission-type device, the power meter will be adjusted for a maximum. It only allows frequency close to resonance to be transmitted throug ...
... The wavemeter is adjusted for maximum or minimum power meter readings depending on whether the cavity is a transmission or absorption type device. With the tarnsmission-type device, the power meter will be adjusted for a maximum. It only allows frequency close to resonance to be transmitted throug ...
a single layer biofuel cell as potential coating for implantable low
... We therefore utilized the above derived average ohmic polarizations (given per electrode area) to calculate cell voltages and thus power densities for fuel cells having the same total area, but different electrode proportions. Fig. 6 displays the maximum power densities achievable for different rati ...
... We therefore utilized the above derived average ohmic polarizations (given per electrode area) to calculate cell voltages and thus power densities for fuel cells having the same total area, but different electrode proportions. Fig. 6 displays the maximum power densities achievable for different rati ...
The Electromagnetic Pulse Technology (EMPT
... forming and cutting of metals by application of strong, short pulsed magnetic fields. This technique came up in the 1960’s and was adopted by many researchers within the following decade. The research work covered the fundamentals of the EMPT as well as its applications. Dietz et. al. derived a sche ...
... forming and cutting of metals by application of strong, short pulsed magnetic fields. This technique came up in the 1960’s and was adopted by many researchers within the following decade. The research work covered the fundamentals of the EMPT as well as its applications. Dietz et. al. derived a sche ...
Plasma processes as advanced methods for cavity cleaning
... allowed to drift out of the ionizing region, and so the plasma continues some distance beyond it. • The electron density is much greater than in the corresponding positive corona but they are of a predominantly lower energy, being in a region of lower potential-gradien. • The lower energy of the ele ...
... allowed to drift out of the ionizing region, and so the plasma continues some distance beyond it. • The electron density is much greater than in the corresponding positive corona but they are of a predominantly lower energy, being in a region of lower potential-gradien. • The lower energy of the ele ...
Paper - Indico
... reproducibility. Voltage ripple is less than 0.4% during the flat top, with a shot-to-shot voltage variation of less than 0.2 %. The primary circuit consists of six-stage tuneable pulse-forming networks (PFN’s). The PFN is charged by a highly stable charging power supply. The total energy stored is ...
... reproducibility. Voltage ripple is less than 0.4% during the flat top, with a shot-to-shot voltage variation of less than 0.2 %. The primary circuit consists of six-stage tuneable pulse-forming networks (PFN’s). The PFN is charged by a highly stable charging power supply. The total energy stored is ...
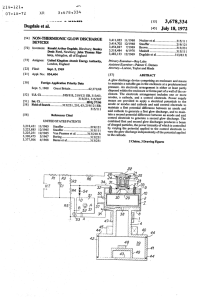
Dugdale et al. 1451 July 18, 1972
... cathode 6 and control electrode 2 and any further electrode cathode 21 is connected via resistors R1, R2, and R6, to the provided between the anode 3 and cathode 6. negative H.T. terminal of a high voltage power supply, for ex Furthermore the anode 3 may consist of a single tube having 25 ample a 30 ...
... cathode 6 and control electrode 2 and any further electrode cathode 21 is connected via resistors R1, R2, and R6, to the provided between the anode 3 and cathode 6. negative H.T. terminal of a high voltage power supply, for ex Furthermore the anode 3 may consist of a single tube having 25 ample a 30 ...
GLOSSARY
... polarization simultaneously. With this method, there is a loss of 3 dB of effective power in either linear plane, and substantial loss if the opposite sense of circular polarization is used (i.e. left vs right). See Section 3-2. CLUTTER, RADAR - Undesired radar returns or echoes resulting from man-m ...
... polarization simultaneously. With this method, there is a loss of 3 dB of effective power in either linear plane, and substantial loss if the opposite sense of circular polarization is used (i.e. left vs right). See Section 3-2. CLUTTER, RADAR - Undesired radar returns or echoes resulting from man-m ...
Electronics IEEE Projects
... through the diode. The diode remains "in conduction" until the current through it drops below a value characteristic for the device, called the holding current. Below this value, the diode switches back to its high-resistance (nonconducting) state. This behavior is bidirectional, meaning typically t ...
... through the diode. The diode remains "in conduction" until the current through it drops below a value characteristic for the device, called the holding current. Below this value, the diode switches back to its high-resistance (nonconducting) state. This behavior is bidirectional, meaning typically t ...
ch17
... • Plays important role in producing and using electrical energy • Field or flux – Exists between poles of magnet – Movement of electrons causes magnetic field ...
... • Plays important role in producing and using electrical energy • Field or flux – Exists between poles of magnet – Movement of electrons causes magnetic field ...
Cavity magnetron

The cavity magnetron is a high-powered vacuum tube that generates microwaves using the interaction of a stream of electrons with a magnetic field while moving past a series of open metal cavities (cavity resonators). Bunches of electrons passing by the openings to the cavities excite radio wave oscillations in the cavity, much as a guitar's strings excite sound in its sound box. The frequency of the microwaves produced, the resonant frequency, is determined by the cavities' physical dimensions. Unlike other microwave tubes, such as the klystron and traveling-wave tube (TWT), the magnetron cannot function as an amplifier, increasing the power of an applied microwave signal, it serves solely as an oscillator, generating a microwave signal from direct current power supplied to the tube.The first form of magnetron tube, the split-anode magnetron, was invented by Albert Hull in 1920, but it wasn't capable of high frequencies and was little used. Similar devices were experimented with by many teams through the 1920s and 30s. On November 27, 1935, Hans Erich Hollmann applied for a patent for the first multiple cavities magnetron, which he received on July 12, 1938, but the more stable klystron was preferred for most German radars during World War II. The cavity magnetron tube was later improved by John Randall and Harry Boot in 1940 at the University of Birmingham, England. The high power of pulses from their device made centimeter-band radar practical for the Allies of World War II, with shorter wavelength radars allowing detection of smaller objects from smaller antennas. The compact cavity magnetron tube drastically reduced the size of radar sets so that they could be installed in anti-submarine aircraft and escort ships.In the post-war era the magnetron became less widely used in the radar role. This was because the magnetron's output changes from pulse to pulse, both in frequency and phase. This makes the signal unsuitable for pulse-to-pulse comparisons, which is widely used for detecting and removing ""clutter"" from the radar display. The magnetron remains in use in some radars, but has become much more common as a low-cost microwave source for microwave ovens. In this form, approximately one billion magnetrons are in use today.