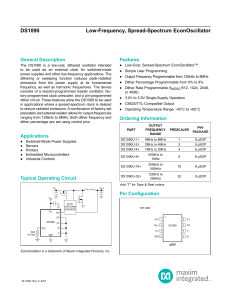
LTC6900 - Low Power, 1kHz to 20MHz Resistor
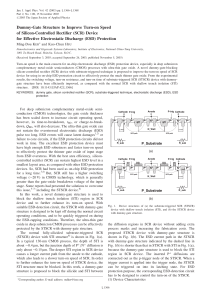
... the DIV input (Pin 4). Tie DIV to GND or drive it below 0.5V to select ÷1. This is the highest frequency range, with the master output frequency passed directly to OUT. The DIV pin may be floated or driven to midsupply to select ÷10, the intermediate frequency range. The lowest frequency range, ÷100, ...
... the DIV input (Pin 4). Tie DIV to GND or drive it below 0.5V to select ÷1. This is the highest frequency range, with the master output frequency passed directly to OUT. The DIV pin may be floated or driven to midsupply to select ÷10, the intermediate frequency range. The lowest frequency range, ÷100, ...
A New Piezoelectric Tube Scanner for Simultaneous Sensing and
... establishing a feedback loop that uses vpx as a measurement. This removes the need for incorporating a displacement sensor into scanner apparatus. When used for simultaneous sensing and actuation the tube with this electrode arrangement has a number of advantages compared with an identical tube with ...
... establishing a feedback loop that uses vpx as a measurement. This removes the need for incorporating a displacement sensor into scanner apparatus. When used for simultaneous sensing and actuation the tube with this electrode arrangement has a number of advantages compared with an identical tube with ...
Cavity magnetron

The cavity magnetron is a high-powered vacuum tube that generates microwaves using the interaction of a stream of electrons with a magnetic field while moving past a series of open metal cavities (cavity resonators). Bunches of electrons passing by the openings to the cavities excite radio wave oscillations in the cavity, much as a guitar's strings excite sound in its sound box. The frequency of the microwaves produced, the resonant frequency, is determined by the cavities' physical dimensions. Unlike other microwave tubes, such as the klystron and traveling-wave tube (TWT), the magnetron cannot function as an amplifier, increasing the power of an applied microwave signal, it serves solely as an oscillator, generating a microwave signal from direct current power supplied to the tube.The first form of magnetron tube, the split-anode magnetron, was invented by Albert Hull in 1920, but it wasn't capable of high frequencies and was little used. Similar devices were experimented with by many teams through the 1920s and 30s. On November 27, 1935, Hans Erich Hollmann applied for a patent for the first multiple cavities magnetron, which he received on July 12, 1938, but the more stable klystron was preferred for most German radars during World War II. The cavity magnetron tube was later improved by John Randall and Harry Boot in 1940 at the University of Birmingham, England. The high power of pulses from their device made centimeter-band radar practical for the Allies of World War II, with shorter wavelength radars allowing detection of smaller objects from smaller antennas. The compact cavity magnetron tube drastically reduced the size of radar sets so that they could be installed in anti-submarine aircraft and escort ships.In the post-war era the magnetron became less widely used in the radar role. This was because the magnetron's output changes from pulse to pulse, both in frequency and phase. This makes the signal unsuitable for pulse-to-pulse comparisons, which is widely used for detecting and removing ""clutter"" from the radar display. The magnetron remains in use in some radars, but has become much more common as a low-cost microwave source for microwave ovens. In this form, approximately one billion magnetrons are in use today.