Chapter 24 – The Body`s Defenses against Pathogens State
... People who share contaminated needles to inject themselves with drugs are at a high risk for contracting HIV. People who have sex with IV drug abusers are also at high risk. ...
... People who share contaminated needles to inject themselves with drugs are at a high risk for contracting HIV. People who have sex with IV drug abusers are also at high risk. ...
The Human Organization
... Substances that are made of more than one element are called compounds. A compound is two or more elements that are chemically combined. Think: What elements make up the compounds carbon ...
... Substances that are made of more than one element are called compounds. A compound is two or more elements that are chemically combined. Think: What elements make up the compounds carbon ...
WEB . WHRSD . ORG - Whitman-Hanson Regional School District
... of very few elements. The six most common are C, H, N, O, P, and S. 1.2 Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids). 1.3 Explain the role of enzymes as catalysts that lower the activa ...
... of very few elements. The six most common are C, H, N, O, P, and S. 1.2 Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids). 1.3 Explain the role of enzymes as catalysts that lower the activa ...
Multicellularity
... granules” in its egg cells. (You do not have to remember these details; this is just an example to help you understand). When the egg is fertilized, the P granules move to the end of the cell where the sperm entered. When the fertilized egg goes through its first division, only one of the two cells ...
... granules” in its egg cells. (You do not have to remember these details; this is just an example to help you understand). When the egg is fertilized, the P granules move to the end of the cell where the sperm entered. When the fertilized egg goes through its first division, only one of the two cells ...
2.1 Cell Theory
... 2. Reproduction—the ability of organisms to reproduce their own kind, 3. Growth and development—consistent growth and development controlled by inherited DNA, 4. Energy processing—the use of chemical energy to power an organism’s activities and chemical ...
... 2. Reproduction—the ability of organisms to reproduce their own kind, 3. Growth and development—consistent growth and development controlled by inherited DNA, 4. Energy processing—the use of chemical energy to power an organism’s activities and chemical ...
1.1 Modern Cell Theory- All organisms (living things) are composed
... of cells. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Many organisms are single-celled and that one cell must carry out all the basic functions of life. Other organisms are multicellular and the cells that form these organisms can be organized at various levels to carry ...
... of cells. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Many organisms are single-celled and that one cell must carry out all the basic functions of life. Other organisms are multicellular and the cells that form these organisms can be organized at various levels to carry ...
Daily Tasks 11-16 through 11-24
... have. Predict who gave you each trait. Traits Dominant Recessive Hair type Curly or Straight wavy Hair color Dark Light Dimples Having No dimples dimples Earlobes Free Attached ...
... have. Predict who gave you each trait. Traits Dominant Recessive Hair type Curly or Straight wavy Hair color Dark Light Dimples Having No dimples dimples Earlobes Free Attached ...
Anatomy Powerpoint
... collagenous tissue located in the wall of the aorta and the elastic ligament of the spine Fibrocollagenous: Flexible and has great strength, located in the sclera in eyes and in the dermis of skin Irregular: Fibers are arranged in random directions Loose: Lacks fibrous reinforcement which makes it m ...
... collagenous tissue located in the wall of the aorta and the elastic ligament of the spine Fibrocollagenous: Flexible and has great strength, located in the sclera in eyes and in the dermis of skin Irregular: Fibers are arranged in random directions Loose: Lacks fibrous reinforcement which makes it m ...
Biology Review
... 30. If the cell cycle is controlled by enzymes, what might result if the genes that control the production of these enzymes are damaged? ...
... 30. If the cell cycle is controlled by enzymes, what might result if the genes that control the production of these enzymes are damaged? ...
Cell
... ● The gel-like fluid inside of a cell made of mostly water. The other organelles are embedded in the cytoplasm ● Made up of mostly water and salt ● Cytoplasm is responsible for giving a cell its shape. It helps to fill out the cell and keeps organelles in their place. Without cytoplasm, the cell wou ...
... ● The gel-like fluid inside of a cell made of mostly water. The other organelles are embedded in the cytoplasm ● Made up of mostly water and salt ● Cytoplasm is responsible for giving a cell its shape. It helps to fill out the cell and keeps organelles in their place. Without cytoplasm, the cell wou ...
Hydrophobic – water fearing (non-polar substances) Hydrophilic
... Example: Sodium-potassium pump ATP Na+ (moving out) K+ (coming in) ...
... Example: Sodium-potassium pump ATP Na+ (moving out) K+ (coming in) ...
Regents Packet Green
... 5. Proteins are made from amino acids. a. Proteins make most of the chemicals used to build and run an organism’s body, so as far as your body is concerned, proteins are by far the most important of these three organic molecules. b. It is the SHAPE of proteins and how they fit together with other mo ...
... 5. Proteins are made from amino acids. a. Proteins make most of the chemicals used to build and run an organism’s body, so as far as your body is concerned, proteins are by far the most important of these three organic molecules. b. It is the SHAPE of proteins and how they fit together with other mo ...
11 Animal physiology
... Disease may result when the body is invaded by pathogens. Pathogens can be species specific, although others can cross the species divide and have a range of host organisms. A first line of defence against pathogens that invade may be provided by phagocytic white cells – these are able to engulf and ...
... Disease may result when the body is invaded by pathogens. Pathogens can be species specific, although others can cross the species divide and have a range of host organisms. A first line of defence against pathogens that invade may be provided by phagocytic white cells – these are able to engulf and ...
Chapter 30/34: Intro to Your Body Organization of the Human Body
... How does the body get 100 trillion cells to work together and perform different jobs? What are the levels of organization? Cells tissues organs organ systems Cell: basic unit of structure and function in living things Specialized cells: a cell that is uniquely suited to perform a particular fu ...
... How does the body get 100 trillion cells to work together and perform different jobs? What are the levels of organization? Cells tissues organs organ systems Cell: basic unit of structure and function in living things Specialized cells: a cell that is uniquely suited to perform a particular fu ...
Document
... There are 5 Kingdoms 1. Monerans (monera) – also called BACTERIA 2. Protists (protista) 3. Fungi 4. Plants 5. Animals ...
... There are 5 Kingdoms 1. Monerans (monera) – also called BACTERIA 2. Protists (protista) 3. Fungi 4. Plants 5. Animals ...
Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
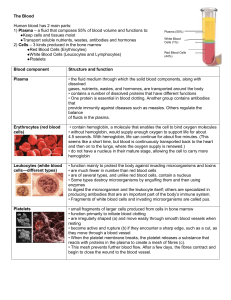
... The Blood Human blood has 2 main parts: 1) Plasma – a fluid that composes 55% of blood volume and functions to: ●Keep cells and tissues moist ●Transport soluble nutrients, wastes, antibodies and hormones 2) Cells – 3 kinds produced in the bone marrow ●Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes) ●White Blood Cell ...
... The Blood Human blood has 2 main parts: 1) Plasma – a fluid that composes 55% of blood volume and functions to: ●Keep cells and tissues moist ●Transport soluble nutrients, wastes, antibodies and hormones 2) Cells – 3 kinds produced in the bone marrow ●Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes) ●White Blood Cell ...
EXTENSION Movement within the cell Why are cells so small?
... Most human cells are between 10 and 15 micrometres (μm) in diameter (1 μm is onethousandth of a millimetre). Nerve cells may have extensions that are up to a metre long and muscle cells may be up to 30 cm long. However, both nerve and muscle cells are too thin to be seen with the naked eye. Human eg ...
... Most human cells are between 10 and 15 micrometres (μm) in diameter (1 μm is onethousandth of a millimetre). Nerve cells may have extensions that are up to a metre long and muscle cells may be up to 30 cm long. However, both nerve and muscle cells are too thin to be seen with the naked eye. Human eg ...
Levels of Organization
... The nervous system detects and interprets information from the environment outside the body and from within the body; controls most body functions. The immune system fights ...
... The nervous system detects and interprets information from the environment outside the body and from within the body; controls most body functions. The immune system fights ...
Tissue Level of Organization
... – calcium & phosphate---give it its hardness – interwoven collagen fibers provide strength ...
... – calcium & phosphate---give it its hardness – interwoven collagen fibers provide strength ...
Tissue Level of Organization
... – calcium & phosphate---give it its hardness – interwoven collagen fibers provide strength ...
... – calcium & phosphate---give it its hardness – interwoven collagen fibers provide strength ...
The AV node
... and this conformational change releases the phosphate group on the cytoplasm side. This release allows the channel to revert to its original shape and as a result, the potassium ions are released inside the cell. ...
... and this conformational change releases the phosphate group on the cytoplasm side. This release allows the channel to revert to its original shape and as a result, the potassium ions are released inside the cell. ...
Tissues & Muscle
... from separating under tension and cardiac muscles cells from pulling apart during contraction ...
... from separating under tension and cardiac muscles cells from pulling apart during contraction ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.