Curriculum Map - Biology
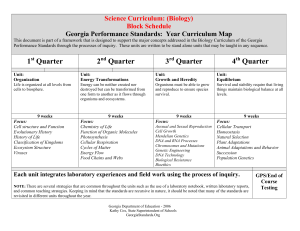
... Georgia Performance Standards: Year Curriculum Map This document is part of a framework that is designed to support the major concepts addressed in the Biology Curriculum of the Georgia Performance Standards through the processes of inquiry. These units are written to be stand alone units that may b ...
... Georgia Performance Standards: Year Curriculum Map This document is part of a framework that is designed to support the major concepts addressed in the Biology Curriculum of the Georgia Performance Standards through the processes of inquiry. These units are written to be stand alone units that may b ...
First Trimester Kevin Hoffmeyer`s Biology
... Chapters 6.2-6.3, 32.1-32.2, and 28.1-28.2: Molecular Movement, Excretory System, Nervous System 1. What is the basic unit of a plasma membrane? What properties allow this unit to form membranes? 2. Describe the four main functions of specific proteins embedded in the cell membrane. 3. What are two ...
... Chapters 6.2-6.3, 32.1-32.2, and 28.1-28.2: Molecular Movement, Excretory System, Nervous System 1. What is the basic unit of a plasma membrane? What properties allow this unit to form membranes? 2. Describe the four main functions of specific proteins embedded in the cell membrane. 3. What are two ...
Cells - Open Equal Free
... your skin cells and the cells that make up your teeth are very different from the cells that make up the gums around them. Cells are different so that they can do different jobs. ...
... your skin cells and the cells that make up your teeth are very different from the cells that make up the gums around them. Cells are different so that they can do different jobs. ...
Exam 2A key
... 5. Pick either the fish or bird respiratory system and explain the features that make it especially efficient. Make specific reference to each of the basic requirements of systems that exchange materials with the environment by diffusion and highlight the countercurrent exchange mechanism seen in f ...
... 5. Pick either the fish or bird respiratory system and explain the features that make it especially efficient. Make specific reference to each of the basic requirements of systems that exchange materials with the environment by diffusion and highlight the countercurrent exchange mechanism seen in f ...
Immune system notes
... mother is creating antibodies against pathogens baby is being exposed to ...
... mother is creating antibodies against pathogens baby is being exposed to ...
AMA 179 powerpoint
... Internal respiration: exchange of gases in all body cells, oxygen is released into cells from the capillaries and carbon dioxide is sent from the cells into the ...
... Internal respiration: exchange of gases in all body cells, oxygen is released into cells from the capillaries and carbon dioxide is sent from the cells into the ...
Exam 2B key
... concentrations in the water and blood from coming into equilibrium. Bird lung (quite similar): Distance – very thin epithelia, Area – large surface area to the lungs, Gradients – pumping air through the lungs and especially the countercurrent exchange mechanism that has air and blood flowing in oppo ...
... concentrations in the water and blood from coming into equilibrium. Bird lung (quite similar): Distance – very thin epithelia, Area – large surface area to the lungs, Gradients – pumping air through the lungs and especially the countercurrent exchange mechanism that has air and blood flowing in oppo ...
CEE 210 Environmental Biology for Engineers
... from nonliving cells Very sensitive if plating conditions are optimal Fast and nondestructive, but cannot detect cell densities less than 107 cells per ml Only practical application is in the research laboratory Requires a fixed standard to relate chemical activity to cell mass and/or cell numbers P ...
... from nonliving cells Very sensitive if plating conditions are optimal Fast and nondestructive, but cannot detect cell densities less than 107 cells per ml Only practical application is in the research laboratory Requires a fixed standard to relate chemical activity to cell mass and/or cell numbers P ...
Cellular Hierarchy
... relate to actual plants and animals? As you may have already guessed, the microscopic differences between plant and animal cells translate into macroscopic (larger) differences in organisms. This fact is explained by the cellular hierarchy. As we will discover during this chapter, differences in cel ...
... relate to actual plants and animals? As you may have already guessed, the microscopic differences between plant and animal cells translate into macroscopic (larger) differences in organisms. This fact is explained by the cellular hierarchy. As we will discover during this chapter, differences in cel ...
Chapter 3: Cells
... Lecture Notes The cell is the body’s most basic unit of structure and function. The human body contains about 75 trillion cells. Cell size is measured in micrometersm), which are also called microns. 1 micrometer = 1/1000 millimeter (0.001 mm). A human egg cell is about 140 m and is just barely ...
... Lecture Notes The cell is the body’s most basic unit of structure and function. The human body contains about 75 trillion cells. Cell size is measured in micrometersm), which are also called microns. 1 micrometer = 1/1000 millimeter (0.001 mm). A human egg cell is about 140 m and is just barely ...
ParScore Scantrons for Lecture Tests Introduction to Microbiology Use Your Textbook Wisely
... Fungi, protistans, plants and animals ...
... Fungi, protistans, plants and animals ...
Name - SchoolNotes
... o ONLY one 4. List and describe the four type of microscopes. What types of specimens do you look at with them? Simple- has one lens Compound light-has two or more lenses to magnify small objects so they can easily be seen with the naked eye, magnifies 400 x Stereomicroscope-uses two eyes to v ...
... o ONLY one 4. List and describe the four type of microscopes. What types of specimens do you look at with them? Simple- has one lens Compound light-has two or more lenses to magnify small objects so they can easily be seen with the naked eye, magnifies 400 x Stereomicroscope-uses two eyes to v ...
Cell Structure
... cisternae, it is called smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER); SER is involved in lipid or steroid synthesis. The ribosomes synthesize the proteins required for cell structure and function by using information coding for the protein’s structure from the linear DNA-like mRNA molecules. This mRNA, which ...
... cisternae, it is called smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER); SER is involved in lipid or steroid synthesis. The ribosomes synthesize the proteins required for cell structure and function by using information coding for the protein’s structure from the linear DNA-like mRNA molecules. This mRNA, which ...
Biology
... a) DNA was taken from a sheep’s somatic cell and fused into an egg cell from a different sheep, then the cells grow to an embryo, then the embryo is inserted into the sheep that provided the egg. b) DNA was taken from a sheep’s embryo and fused with a different sheep’s egg cell, then the cells grow ...
... a) DNA was taken from a sheep’s somatic cell and fused into an egg cell from a different sheep, then the cells grow to an embryo, then the embryo is inserted into the sheep that provided the egg. b) DNA was taken from a sheep’s embryo and fused with a different sheep’s egg cell, then the cells grow ...
Unit D Chapter 1 Notes
... Oxygen, carbon dioxide, most nutrients, and cell wastes are exchanged between the body’s cells and red blood cells in the capillaries. Oxygen is needed by the cells to do their work. Lesson 3: How Does Your Body Get Rid of Cell Wastes? As body cells carry out life activities, they produce wastes. C ...
... Oxygen, carbon dioxide, most nutrients, and cell wastes are exchanged between the body’s cells and red blood cells in the capillaries. Oxygen is needed by the cells to do their work. Lesson 3: How Does Your Body Get Rid of Cell Wastes? As body cells carry out life activities, they produce wastes. C ...
Cells and tissues
... Cells and tissues • cells are basic units of life • are required for nutrition to the body, supply of oxygen and removal of waste • need to be able to reproduce, called mitosis • tissues are groups of similar cells with specialised function • types are epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous ...
... Cells and tissues • cells are basic units of life • are required for nutrition to the body, supply of oxygen and removal of waste • need to be able to reproduce, called mitosis • tissues are groups of similar cells with specialised function • types are epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous ...
ALAT Chapter 4
... Gross anatomy = structures visible to the eye Histology = microscopic view of tissue Physiology = function of parts of an organism Functions to survive, grow & reproduce ...
... Gross anatomy = structures visible to the eye Histology = microscopic view of tissue Physiology = function of parts of an organism Functions to survive, grow & reproduce ...
Topic One: Chemistry of Living Things
... II. Cell Theory has three parts: 1. _______________________________________________________________________ Unicellular – single celled organisms (amoeba, paramecium) Multicellular – have more than 1 cell; may be only a few (vorticella), or many trillions of cells (humans). Almost all structures in ...
... II. Cell Theory has three parts: 1. _______________________________________________________________________ Unicellular – single celled organisms (amoeba, paramecium) Multicellular – have more than 1 cell; may be only a few (vorticella), or many trillions of cells (humans). Almost all structures in ...
Workplace Science - Continuing Education at KPR
... cell divides to form two new cells. You consist of a great many cells, but like all other organisms, you started life as a single cell. How did you develop from a single cell into an organism with trillions of cells? The answer is cell division. After cells grow to their maximum size, they divide in ...
... cell divides to form two new cells. You consist of a great many cells, but like all other organisms, you started life as a single cell. How did you develop from a single cell into an organism with trillions of cells? The answer is cell division. After cells grow to their maximum size, they divide in ...
Body Organization
... Body Organization • The body has an hierarchical organization. – Hierarchy is the arrangement of a particular set of items that are represented as being "above," "below," or "at the same level as" one another. ...
... Body Organization • The body has an hierarchical organization. – Hierarchy is the arrangement of a particular set of items that are represented as being "above," "below," or "at the same level as" one another. ...
1.2 From Cells to Organisms
... A. Organism is an individual living thing. B. Unicellular organisms a. Unicellular organism are one celled organisms that carry out all of the processes of life within a single cell. b. Examples of unicellular organisms are diatoms, bacteria, protozoa, unicellular algae, and unicellular fungi or yea ...
... A. Organism is an individual living thing. B. Unicellular organisms a. Unicellular organism are one celled organisms that carry out all of the processes of life within a single cell. b. Examples of unicellular organisms are diatoms, bacteria, protozoa, unicellular algae, and unicellular fungi or yea ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.























