SCB255 Course Title: Cell Biology Department
... 4. Illustrate various signal transduction mechanisms. 5. Identify the components of the cytoskeleton, cell junctions and the extracellular matrix. 6. Define the stages of and the regulatory components of the cell division cycle. 7. Explain the cellular mechanisms involved in cancer and apoptosis. 8. ...
... 4. Illustrate various signal transduction mechanisms. 5. Identify the components of the cytoskeleton, cell junctions and the extracellular matrix. 6. Define the stages of and the regulatory components of the cell division cycle. 7. Explain the cellular mechanisms involved in cancer and apoptosis. 8. ...
Chapter 1 - apel slice
... Make a graphic organizer like the one at the right to compare and contrast onion characteristics that you observe. Write the characteristics that you see without using a microscope in one circle, those you see using a microscope in the other circle, and characteristics that are the same in the cente ...
... Make a graphic organizer like the one at the right to compare and contrast onion characteristics that you observe. Write the characteristics that you see without using a microscope in one circle, those you see using a microscope in the other circle, and characteristics that are the same in the cente ...
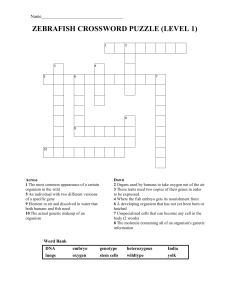
Zebrafish Crossword Puzzles
... 5 The type of environment where wild zebrafish live 6 A possible answer to a problem 8 Element in air and dissolved in water that both humans and fish need 9 These traits need two copies of their gene to be expressed 10 Unspecialized cells that can become any cell in the body (2 words) 11 A change i ...
... 5 The type of environment where wild zebrafish live 6 A possible answer to a problem 8 Element in air and dissolved in water that both humans and fish need 9 These traits need two copies of their gene to be expressed 10 Unspecialized cells that can become any cell in the body (2 words) 11 A change i ...
Bio II Chapter 32 - Marissa Junior/Senior High School
... sponges. (Sponges have no true tissue.) Can be 2 or 3 layers, depending upon the organisms. Every organ and tissue arises from a germ layer. ...
... sponges. (Sponges have no true tissue.) Can be 2 or 3 layers, depending upon the organisms. Every organ and tissue arises from a germ layer. ...
PACT Review for 7th Grade Science
... A group of specialized cells that work together to perform the same function. There are four basic types of tissue in the human body: Nerve tissue—carries impulses back and forth to the brain from the body Muscle tissue—contracts and shortens, making body parts move Epithelial tissue—covers th ...
... A group of specialized cells that work together to perform the same function. There are four basic types of tissue in the human body: Nerve tissue—carries impulses back and forth to the brain from the body Muscle tissue—contracts and shortens, making body parts move Epithelial tissue—covers th ...
26 120 515 Molecular Biology of Eukaryotes
... Nancy Craig et al., Molecular Biology: Principles of Genome Function ...
... Nancy Craig et al., Molecular Biology: Principles of Genome Function ...
Fall Semester Review Pre-AP Science 7
... 37. Define homeostasis. The ability of an organism to maintain stability when the environment changes; staying the same 38. Complete the concept map below by describing and giving examples for each of the three types of homeostasis. (Pg. 340-331) ...
... 37. Define homeostasis. The ability of an organism to maintain stability when the environment changes; staying the same 38. Complete the concept map below by describing and giving examples for each of the three types of homeostasis. (Pg. 340-331) ...
abbey secondary school
... Photosynthesis is very important process not only to plants but also to animals. Verify this statement by:a) Giving conditions necessary for the process. b) Explaining three significant roles of the process to the living organisms. ...
... Photosynthesis is very important process not only to plants but also to animals. Verify this statement by:a) Giving conditions necessary for the process. b) Explaining three significant roles of the process to the living organisms. ...
Subject Guide to Biology Browsing the Biology Collection
... The Basics of Biology [QH 307.2 .S75 2004 Ref] – contains information about biological topics such as cells, genetics, and organs. The Cambridge Dictionary of Human Biology and Evolution [QP 34.5 .M24 2005 Ref] – provides definitions of various biological terms such as “genome mutation.” The D ...
... The Basics of Biology [QH 307.2 .S75 2004 Ref] – contains information about biological topics such as cells, genetics, and organs. The Cambridge Dictionary of Human Biology and Evolution [QP 34.5 .M24 2005 Ref] – provides definitions of various biological terms such as “genome mutation.” The D ...
PowerPoint
... • Cells: basic structural and functional units of life – respond to their environment – maintain homeostasis at the cellular level – modify structure and function over time ...
... • Cells: basic structural and functional units of life – respond to their environment – maintain homeostasis at the cellular level – modify structure and function over time ...
PowerPoint
... • Cells: basic structural and functional units of life – respond to their environment – maintain homeostasis at the cellular level – modify structure and function over time ...
... • Cells: basic structural and functional units of life – respond to their environment – maintain homeostasis at the cellular level – modify structure and function over time ...
Name
... 20. What type of muscle are your heart and stomach made of and why? A. Voluntary because we want our brain to have control over these organs. B. Involuntary because we want them to work automatically. C. Voluntary because we want them to work automatically. D. Involuntary because we want our brain ...
... 20. What type of muscle are your heart and stomach made of and why? A. Voluntary because we want our brain to have control over these organs. B. Involuntary because we want them to work automatically. C. Voluntary because we want them to work automatically. D. Involuntary because we want our brain ...
bachelor of science biotechnology
... Upon successful completion of this program, a student will be able to: 1. Gain an understanding and appreciation of the complexity of biological pathways that are fundamental to living organisms. a. Identify signaling cascades that allow cells to respond appropriately to changes in their environment ...
... Upon successful completion of this program, a student will be able to: 1. Gain an understanding and appreciation of the complexity of biological pathways that are fundamental to living organisms. a. Identify signaling cascades that allow cells to respond appropriately to changes in their environment ...
GAS EXCHANGE in “Animals”
... Figure 36.13a The mechanism of stomatal opening and closing Figure 36.13b The mechanism of stomatal opening and closing ...
... Figure 36.13a The mechanism of stomatal opening and closing Figure 36.13b The mechanism of stomatal opening and closing ...
BIOGRAPHICAL SKETCH A. Personal Statement
... ubiquitin leads to activation or inhibition of NF-κB signaling in human cancer cells. I was trained to decipher cell-signaling events in cancer cells by utilizing in vitro cell free systems to recapitulate and define molecular mechanisms. From my postdoctoral training in cancer biology in the distin ...
... ubiquitin leads to activation or inhibition of NF-κB signaling in human cancer cells. I was trained to decipher cell-signaling events in cancer cells by utilizing in vitro cell free systems to recapitulate and define molecular mechanisms. From my postdoctoral training in cancer biology in the distin ...
File
... Deduce two processes that occur in human cells during this part of the cell cycle, but not during the other part. ...
... Deduce two processes that occur in human cells during this part of the cell cycle, but not during the other part. ...
View/Open - seafdec/aqd
... to cyanobacteria which produce a diverse range of secondary metabolites including hepatotoxins, neurotoxins and cytotoxins cyst – a non-motile, resistant, dormant stage debris – organic waste from dead cells or unused food definitive host – the host in which the parasite undergoes sexual reproductio ...
... to cyanobacteria which produce a diverse range of secondary metabolites including hepatotoxins, neurotoxins and cytotoxins cyst – a non-motile, resistant, dormant stage debris – organic waste from dead cells or unused food definitive host – the host in which the parasite undergoes sexual reproductio ...
An Introduction to Cells
... interphase, and cytokinesis, and explain their significance. • 3-9 Discuss the regulation of the cell life cycle. ...
... interphase, and cytokinesis, and explain their significance. • 3-9 Discuss the regulation of the cell life cycle. ...
PDF 0.8 MB - National Centers for Systems Biology
... Method and Logic in Quantitative Biology (II) Smith and Waterman 1981. Identification of common molecular subsequences Felsenstein 1981. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. Eisen JA. 1998. A phylogenomic study of the MutS family of proteins. Eisen MB et al., 1998. ...
... Method and Logic in Quantitative Biology (II) Smith and Waterman 1981. Identification of common molecular subsequences Felsenstein 1981. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. Eisen JA. 1998. A phylogenomic study of the MutS family of proteins. Eisen MB et al., 1998. ...
Eukaryotic Organisms
... 1) Flibasidiella neoformans – causes a form of meningitis C) Ascomycetes 1) Saccharomyces – used in making bread, beer and wine 2) Candida albicans – causes thrush, vaginal yeast infection and a severe skin infection in children (diaper rash) 3) Pneumocystis jiroveci – causes a lung infection that i ...
... 1) Flibasidiella neoformans – causes a form of meningitis C) Ascomycetes 1) Saccharomyces – used in making bread, beer and wine 2) Candida albicans – causes thrush, vaginal yeast infection and a severe skin infection in children (diaper rash) 3) Pneumocystis jiroveci – causes a lung infection that i ...
Year 10 TRIPLE Biology Learning Cycle 3 Overview
... Week 1: Pupils to be given a short exam paper consisting of biology, chemistry and physics questions from LC1 & 2. These are marked weekly by the member of staff not on Y10 timetable and handed back the following week. ...
... Week 1: Pupils to be given a short exam paper consisting of biology, chemistry and physics questions from LC1 & 2. These are marked weekly by the member of staff not on Y10 timetable and handed back the following week. ...
cells-3a1 - WordPress.com
... The two kinds you need to be most familiar with are ‘typical’ animal and plant cells. ...
... The two kinds you need to be most familiar with are ‘typical’ animal and plant cells. ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.