cell membrane and passive transport
... CLE 3210.1.5 - Compare different models to explain the movement of materials into and out of the cell. SPI 3210.1.8 - Compare active and passive transport. RLE 2010.2.1 - Recognize the importance of homeostasis as a survival mechanism. ...
... CLE 3210.1.5 - Compare different models to explain the movement of materials into and out of the cell. SPI 3210.1.8 - Compare active and passive transport. RLE 2010.2.1 - Recognize the importance of homeostasis as a survival mechanism. ...
Characteristics of Life Notes
... A control mechanism then compares the actual room temperature to the set temperature. Let’s say the set temperature is 21C (70F). When the temperature falls below 21C, the thermostat kicks on by sending an electronic message to the furnace. When the sensor on the thermostat indicates that the ...
... A control mechanism then compares the actual room temperature to the set temperature. Let’s say the set temperature is 21C (70F). When the temperature falls below 21C, the thermostat kicks on by sending an electronic message to the furnace. When the sensor on the thermostat indicates that the ...
Middle East Jeopardy
... The organ that produces 3 digestive enzymes, then delivers the enzymes to the small intestine. What is the pancreas? ...
... The organ that produces 3 digestive enzymes, then delivers the enzymes to the small intestine. What is the pancreas? ...
Ch 41 Notes
... Individuals who eat only plant proteins need to eat specific plant combinations to get all the essential amino acids ...
... Individuals who eat only plant proteins need to eat specific plant combinations to get all the essential amino acids ...
Anatomy and Physiology of Animals
... Animals are very complex organisms, yet the structural basis of all animals begins with cells. A cell is the most basic structure of an animal and is considered the building block from which an animal’s body is made. All cells of an embryo have the same number and kinds of genes because they all des ...
... Animals are very complex organisms, yet the structural basis of all animals begins with cells. A cell is the most basic structure of an animal and is considered the building block from which an animal’s body is made. All cells of an embryo have the same number and kinds of genes because they all des ...
Z00-302(1.1)
... Main compartments of a plant cell. Cells, either prokaryote or eukaryote, are highly organized sets of molecules. In fact, cells have many internal compartments with specific functions. Let's say a cellular compartment is a space, delimited or not by membrane, where a necessary or important functio ...
... Main compartments of a plant cell. Cells, either prokaryote or eukaryote, are highly organized sets of molecules. In fact, cells have many internal compartments with specific functions. Let's say a cellular compartment is a space, delimited or not by membrane, where a necessary or important functio ...
animals classification
... • Digest food within the body • Most of them have embryonic layers (these layers form tissues, organs, systems) • Cells are connected to eachother by extracellular proteins (connective tissue) • Most animals have diploid life cycle • Most animals have muscle tissue for movement, nerve for impulses. ...
... • Digest food within the body • Most of them have embryonic layers (these layers form tissues, organs, systems) • Cells are connected to eachother by extracellular proteins (connective tissue) • Most animals have diploid life cycle • Most animals have muscle tissue for movement, nerve for impulses. ...
AP Biology
... body plan. The protostomes are currently divided into two major groups: the lophotrochozoans and the ecdysozoans, based on a larval developmental stage. We are not going to be concerned with this distinction. Rather, the major animal Phyla and characteristics you should focus on are given below. ...
... body plan. The protostomes are currently divided into two major groups: the lophotrochozoans and the ecdysozoans, based on a larval developmental stage. We are not going to be concerned with this distinction. Rather, the major animal Phyla and characteristics you should focus on are given below. ...
The Chemistry of Living Systems
... Molecules in plants and animals The four types of Living creatures are such complex organisms that even today we have biological much to learn about the chemical reactions that take place inside us. molecules Scientists classify the organic molecules in living things into four basic groups: carbohyd ...
... Molecules in plants and animals The four types of Living creatures are such complex organisms that even today we have biological much to learn about the chemical reactions that take place inside us. molecules Scientists classify the organic molecules in living things into four basic groups: carbohyd ...
Chapter 35-1 - Human Body Systems
... • Can you name the 11 organ systems found in the human body? • What are the main functions of each organ system? ...
... • Can you name the 11 organ systems found in the human body? • What are the main functions of each organ system? ...
Unit 1 – Biology – Cells PowerPoint
... A stem cell is an _______________ cell of an organism which is capable of giving rise to ______ other cells type. Stem cells from human ________ and adult ______ marrow can be cloned and made to differentiate into many different types of human cells. Scientific research is trying to find ways that s ...
... A stem cell is an _______________ cell of an organism which is capable of giving rise to ______ other cells type. Stem cells from human ________ and adult ______ marrow can be cloned and made to differentiate into many different types of human cells. Scientific research is trying to find ways that s ...
Directed Reading 11.2 - Blair Community Schools
... to opposite poles of the cell. _____________________ 7. The homologous chromosomes separate. The chromosomes of each pair are pulled to opposite poles of the cell by the spindle fibers. The chromatids do not separate at their centromeres. _____________________ 8. The chromosomes condense, and the nu ...
... to opposite poles of the cell. _____________________ 7. The homologous chromosomes separate. The chromosomes of each pair are pulled to opposite poles of the cell by the spindle fibers. The chromatids do not separate at their centromeres. _____________________ 8. The chromosomes condense, and the nu ...
Developmental Gene Regulation and the
... body plans could have existed earlier, but have fossilized poorly. Indeed some such organisms apparently left traces of themselves in Vendian age deposits, in the form of burrows and tracks that only a bilaterally symmetrical animal could have produced (see, for example, Fedonkin, 1994). Thus the gr ...
... body plans could have existed earlier, but have fossilized poorly. Indeed some such organisms apparently left traces of themselves in Vendian age deposits, in the form of burrows and tracks that only a bilaterally symmetrical animal could have produced (see, for example, Fedonkin, 1994). Thus the gr ...
Intro to the Circulatory System
... Which is CORRECT about gas exchange in humans A. The diaphragm rises and air is pulled into the lungs B. Air is forced down the windpipe when a person inhales C. The breathing rate is controlled by the hypothalamus in the brain D. Hemoglobin carries carbon dioxide and oxygen in ...
... Which is CORRECT about gas exchange in humans A. The diaphragm rises and air is pulled into the lungs B. Air is forced down the windpipe when a person inhales C. The breathing rate is controlled by the hypothalamus in the brain D. Hemoglobin carries carbon dioxide and oxygen in ...
An optimized green fluorescent protein biosensor for the inhibitory
... Ahmed Abdelfattah, Yiqun Wang, Robert E. Campbell* University of Alberta POSTER The human brain controls all sensory perception, thought and almost all motor movements. This function is achieved by relaying electrical signals through neurons in the central nervous system. These electrical signals ar ...
... Ahmed Abdelfattah, Yiqun Wang, Robert E. Campbell* University of Alberta POSTER The human brain controls all sensory perception, thought and almost all motor movements. This function is achieved by relaying electrical signals through neurons in the central nervous system. These electrical signals ar ...
What is an Animal? - Tanque Verde Unified District
... predators • These are rigid and must be shed for the animal to grow larger • Exoskeletons are often possessed by invertebrates, animals that lack a spine (ex: crabs, beetles, spiders) ...
... predators • These are rigid and must be shed for the animal to grow larger • Exoskeletons are often possessed by invertebrates, animals that lack a spine (ex: crabs, beetles, spiders) ...
Ch48Immunity - Environmental
... immune system attacks own molecules & cells lupus antibodies against many molecules released by normal breakdown of cells ...
... immune system attacks own molecules & cells lupus antibodies against many molecules released by normal breakdown of cells ...
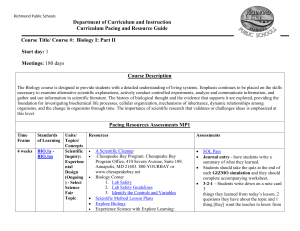
NEW Biology Part II CPR
... Meetings: 180 days Course Description The Biology course is designed to provide students with a detailed understanding of living systems. Emphasis continues to be placed on the skills necessary to examine alternative scientific explanations, actively conduct controlled experiments, analyze and commu ...
... Meetings: 180 days Course Description The Biology course is designed to provide students with a detailed understanding of living systems. Emphasis continues to be placed on the skills necessary to examine alternative scientific explanations, actively conduct controlled experiments, analyze and commu ...
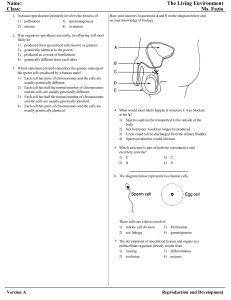
Reproduction and Development
... resemble those of a developing embryo in their ability to reproduce repeatedly, forming exact copies of themselves. They may also form many other different kinds of cells. Stem cells in bone marrow offer a dramatic example. They can give rise to all of the structures in the blood: red blood cells, p ...
... resemble those of a developing embryo in their ability to reproduce repeatedly, forming exact copies of themselves. They may also form many other different kinds of cells. Stem cells in bone marrow offer a dramatic example. They can give rise to all of the structures in the blood: red blood cells, p ...
Punnett Square Worksheet 1
... they eat more and more of the herbivores, decreasing the herbivore population. It then becomes harder and harder for the carnivores to find herbivores to eat, and the population of carnivores decreases. In this way, the carnivores and herbivores stay in a relatively stable equilibrium, each limiting ...
... they eat more and more of the herbivores, decreasing the herbivore population. It then becomes harder and harder for the carnivores to find herbivores to eat, and the population of carnivores decreases. In this way, the carnivores and herbivores stay in a relatively stable equilibrium, each limiting ...
Biology 11 – Human Anatomy Lecture
... 4. Normal Body Temperature (37C) is maintained mainly by muscle metabolism, and is essential for chemical reactions. a. Low body temperature slows metabolic reactions b. High body temperature can denature enzymes 5. Atmospheric pressure is the force that air exerts on our body surface; needed for b ...
... 4. Normal Body Temperature (37C) is maintained mainly by muscle metabolism, and is essential for chemical reactions. a. Low body temperature slows metabolic reactions b. High body temperature can denature enzymes 5. Atmospheric pressure is the force that air exerts on our body surface; needed for b ...
Study Guide for Final Exam - SBCC Biological Sciences Department
... examples of what functions each type serves. 10. What is ATP? What process creates it? What is it used for? From Study Guide 2 (Lectures 9-13) 1. Know what mitosis is, why it occurs, which cells undergo it, and what the 2 main stages of it are. 2. Define meiosis & state how the end result of it diff ...
... examples of what functions each type serves. 10. What is ATP? What process creates it? What is it used for? From Study Guide 2 (Lectures 9-13) 1. Know what mitosis is, why it occurs, which cells undergo it, and what the 2 main stages of it are. 2. Define meiosis & state how the end result of it diff ...
all systems go
... A group of cells that are similar in structure and function are called tissues. A group of two or more tissues working together to perform a specific function are arranged into organs. Two or more organs working together make up an organ system. Systems working together make up an organism. Generall ...
... A group of cells that are similar in structure and function are called tissues. A group of two or more tissues working together to perform a specific function are arranged into organs. Two or more organs working together make up an organ system. Systems working together make up an organism. Generall ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.