554534 - Physics
... The graphs below illustrate light rays that are passing from air into a transparent medium. Which graph shows a light ray entering the medium with the highest refractive index? A) ...
... The graphs below illustrate light rays that are passing from air into a transparent medium. Which graph shows a light ray entering the medium with the highest refractive index? A) ...
Physical properties
... based on differences in their solubility. • A process by which a chemical compound is separated into components by crystallization. In fractional crystallization the compound is mixed with a solvent, heated, and then gradually cooled so that, as each of its constituent components crystallizes, it ca ...
... based on differences in their solubility. • A process by which a chemical compound is separated into components by crystallization. In fractional crystallization the compound is mixed with a solvent, heated, and then gradually cooled so that, as each of its constituent components crystallizes, it ca ...
Light Slides
... particular interest to us. Figure 33-2 shows the relative sensitivity of the human eye to light of various wavelengths. The center of the visible region is about 555 nm, which produces the sensation that we call yellow-green The limits of this visible spectrum are not well defined because the eye-se ...
... particular interest to us. Figure 33-2 shows the relative sensitivity of the human eye to light of various wavelengths. The center of the visible region is about 555 nm, which produces the sensation that we call yellow-green The limits of this visible spectrum are not well defined because the eye-se ...
Waves and Particles
... Radar: radio detection and ranging, a system that uses reflected radio waves to determine the velocity and location of objects ...
... Radar: radio detection and ranging, a system that uses reflected radio waves to determine the velocity and location of objects ...
Honors Chemistry Review Packet KEY
... 6. Liquids and gases both have an indefinite shape; while the shape of a solid is definite, the shape of a liquid is indefinite. 7. It is reversible because solid mercury can be melted back into a liquid again. 8. Platinum and copper can have the same mass and volume (extensive properties). They can ...
... 6. Liquids and gases both have an indefinite shape; while the shape of a solid is definite, the shape of a liquid is indefinite. 7. It is reversible because solid mercury can be melted back into a liquid again. 8. Platinum and copper can have the same mass and volume (extensive properties). They can ...
LIGHT: What is it?
... Electrons release light when falling down to the lower energy level. Photons - bundles/packets of energy released when the electrons fall. Light: Stream of Photons ...
... Electrons release light when falling down to the lower energy level. Photons - bundles/packets of energy released when the electrons fall. Light: Stream of Photons ...
light - pennsphysics
... • waves by which light energy travels • Other examples: radio waves, microwaves, X rays • all are radiated by vibrating electrons within an atom ...
... • waves by which light energy travels • Other examples: radio waves, microwaves, X rays • all are radiated by vibrating electrons within an atom ...
Optics
... 1) To demonstrate the laws of reflection using a plane mirror. 2)To locate an image in a plane mirror the method of no parallax ...
... 1) To demonstrate the laws of reflection using a plane mirror. 2)To locate an image in a plane mirror the method of no parallax ...
The Origin Of The Earth
... Free oxygen begins to accumulate Ozone is synthesized Aerobic metabolism can begin ...
... Free oxygen begins to accumulate Ozone is synthesized Aerobic metabolism can begin ...
Grade 10 Optics Unit Outline
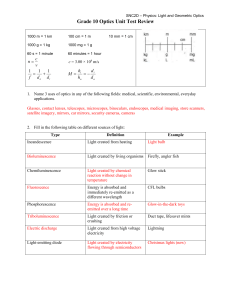
... Fluorescence – absorbs and immediately re-emits energy as light Phosphorescence – absorbs energy but slowly re-emits light over long period of time ...
... Fluorescence – absorbs and immediately re-emits energy as light Phosphorescence – absorbs energy but slowly re-emits light over long period of time ...
Chapter 1 Matter and Change
... - contain only one kind of atom - cannot be broken down by physical or chemical means - unique physical and chemical properties ...
... - contain only one kind of atom - cannot be broken down by physical or chemical means - unique physical and chemical properties ...
Light Lessons from Dr. Lighthead
... Light Fact 5: • When charged particles from the sun are captured by the Earth’s magnetic field it creates an effect we call the AURORA BOREALIS or Northern Lights ...
... Light Fact 5: • When charged particles from the sun are captured by the Earth’s magnetic field it creates an effect we call the AURORA BOREALIS or Northern Lights ...
Summer 2006 Chemistry Practice103 final Carbonic acid, H2CO3 (aq)
... a. absorbing ultraviolet light energy from the sun and emitting it as infrared radiation. b. absorbing ultraviolet light energy from the sun and storing it as molecular vibrations. c. absorbing infrared light energy from the sun and storing it as molecular vibrations. d. absorbing ultraviolet light ...
... a. absorbing ultraviolet light energy from the sun and emitting it as infrared radiation. b. absorbing ultraviolet light energy from the sun and storing it as molecular vibrations. c. absorbing infrared light energy from the sun and storing it as molecular vibrations. d. absorbing ultraviolet light ...
File
... • Light energy comes from both natural and artificial sources • Light travels directly from a luminous source (object that emit light) or indirectly from a non-luminous source (object reflects light) to your eyes ...
... • Light energy comes from both natural and artificial sources • Light travels directly from a luminous source (object that emit light) or indirectly from a non-luminous source (object reflects light) to your eyes ...
Part5-Electromagneti..
... Components perpendicular to this plane tend to reflect more strongly than components parallel to this plane. ...
... Components perpendicular to this plane tend to reflect more strongly than components parallel to this plane. ...
15.4 How Light Behaves
... the extent to which a light beam is deflected on entering or leaving the medium. The symbol for the index of refraction is n, so that n = c / v. ...
... the extent to which a light beam is deflected on entering or leaving the medium. The symbol for the index of refraction is n, so that n = c / v. ...
Photopolymer
A photopolymer is a polymer that changes its properties when exposed to light, often in the ultraviolet or visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum. These changes are often manifested structurally, for example hardening of the material occurs as a result of cross-linking when exposed to light. An example is shown below depicting a mixture of monomers, oligomers, and photoinitiators that conform into a hardened polymeric material through a process called curing,.A wide variety of technologically useful applications rely on photopolymers, for example some enamels and varnishes depend on photopolymer formulation for proper hardening upon exposure to light. In some instances, an enamel can cure in a fraction of a second when exposed to light, as opposed to thermally cured enamels which can require half an hour or longer. Curable materials are widely used for medical, printing, and photoresist technologies. Changes in structural and chemical properties can be induced internally by chromophores that the polymer subunit already possesses, or externally by addition of photosensitive molecules. Typically a photopolymer consists of a mixture of multifunctional monomers and oligomers in order to achieve the desired physical properties, and therefore a wide variety of monomers and oligomers have been developed that can polymerize in the presence of light either through internal or external initiation. Photopolymers undergo a process called curing, where oligomers are cross-linked upon exposure to light, forming what is known as a network polymer. The result of photo curing is the formation of a thermoset network of polymers. One of the advantages of photo-curing is that it can be done selectively using high energy light sources, for example lasers, however, most systems are not readily activated by light, and in this case a photoinitiator is required. Photoinitiators are compounds that upon radiation of light decompose into reactive species that activate polymerization of specific functional groups on the oligomers. An example of a mixture that undergoes cross-linking when exposed to light is shown below. The mixture consists of monomeric styrene and oligomeric acrylates.Most commonly, photopolymerized systems are typically cured through UV radiation, since ultraviolet light is more energetic; however, the development of dye-based photoinitiator systems have allowed for the use of visible light, having potential advantages of processes that are more simple and safe to handle. UV curing in industrial processes has greatly expanded over the past several decades. Many traditional thermally cured and solvent-based technologies can be replaced by photopolymerization technologies. The advantages of photopolymerization over thermally cured polymerization include high rates of polymerization and environmental benefits from elimination of volatile organic solvents.There are two general routes for photoinitiation: free radical and ionic. The general process involves doping a batch of neat polymer with small amounts of photoinitiator, followed by selective radiation of light, resulting a highly cross-linked product. Many of these reactions do not require solvent which eliminates termination path via reaction of initiators with solvent and impurities, in addition to decreasing the overall cost.