Refraction of Light
... strange image of a distant object. A fata morgana actually is a superposition of several images of one object. Typically one image is upright more or less above two inverted images that may be mingled together. The images may undergo rapid changes as the air layers move slightly up and down relative ...
... strange image of a distant object. A fata morgana actually is a superposition of several images of one object. Typically one image is upright more or less above two inverted images that may be mingled together. The images may undergo rapid changes as the air layers move slightly up and down relative ...
HIGH - Electrical and Computer Engineering
... IGH-SPEED optical intensity modulators have been widely used in analog fiber-optic transmission systems, community access television (CATV) distribution systems, radio frequency (RF) phase shifters, and analog/digital microwave links [1], [2]. They are also attractive as an external modulator in wav ...
... IGH-SPEED optical intensity modulators have been widely used in analog fiber-optic transmission systems, community access television (CATV) distribution systems, radio frequency (RF) phase shifters, and analog/digital microwave links [1], [2]. They are also attractive as an external modulator in wav ...
Manual(Exp.1) - Manuals for PHYSLAB
... Electromagnetic spectrum from X-ray tube composed by continuous spectrum and steep line spectrum. Line spectrum comes from excitation of target atom and continuous spectrum comes from decelerated atom. At low temperatures, atoms tend to be in their ground state; at progressively higher temperatures ...
... Electromagnetic spectrum from X-ray tube composed by continuous spectrum and steep line spectrum. Line spectrum comes from excitation of target atom and continuous spectrum comes from decelerated atom. At low temperatures, atoms tend to be in their ground state; at progressively higher temperatures ...
1, 2, 5, 6, 7 Time: 08:00
... 18. Use models to demonstrate how light & sound waves differ in how they are absorbed, reflected, & transmitted through different types of media. 19. Integrate qualitative information to explain that common communication devices use electromagnetic waves to encode & transmit information. ...
... 18. Use models to demonstrate how light & sound waves differ in how they are absorbed, reflected, & transmitted through different types of media. 19. Integrate qualitative information to explain that common communication devices use electromagnetic waves to encode & transmit information. ...
RTD Part 2 - County Central High School
... A fluorescent tube operates by exciting mercury atoms from their ground state to an excited state. The return of the atoms to a lower energy level results in the emission of electromagnetic radiation that cannot be seen. Through a process called fluorescence, a phosphor powder coating on the inside ...
... A fluorescent tube operates by exciting mercury atoms from their ground state to an excited state. The return of the atoms to a lower energy level results in the emission of electromagnetic radiation that cannot be seen. Through a process called fluorescence, a phosphor powder coating on the inside ...
... of animals with neither eyes nor brains, he completed postdoctoral fellowships at Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institution and WHOI. After a year as an assistant scientist at WHOI, he accepted a position in the Biology Department at Duke University. He is interested in all aspects of vision in oceani ...
Chemistry 30 Review of Basic Chemistry 20
... ionic rules described above. Then use a prefix in front of the word “hydrate”. Example: CuSO4 6H2O is: copper (II) sulfate hexahydrate Example: aluminum chloride trihydrate is: ...
... ionic rules described above. Then use a prefix in front of the word “hydrate”. Example: CuSO4 6H2O is: copper (II) sulfate hexahydrate Example: aluminum chloride trihydrate is: ...
HOMEWORK ANSWERS (Light and Geometric Optics)
... 7) Briefly describe how you could demonstrate that white light is composed of many different colours. a. White light can be separated into its different colors thorough a prism. Blue light refracted most; red light refracted least. SOURCES OF LIGHT 1) In grade 9 science, you studied the differences ...
... 7) Briefly describe how you could demonstrate that white light is composed of many different colours. a. White light can be separated into its different colors thorough a prism. Blue light refracted most; red light refracted least. SOURCES OF LIGHT 1) In grade 9 science, you studied the differences ...
Refraction - Kelso High School
... The refractive index of a medium depends upon the frequency (colour) of the incident light. When light enters a glass prism, it separates into its component colours and produces a spectrum. This happens because each colour (frequency) is refracted by a different amount. Since violet is refracted mor ...
... The refractive index of a medium depends upon the frequency (colour) of the incident light. When light enters a glass prism, it separates into its component colours and produces a spectrum. This happens because each colour (frequency) is refracted by a different amount. Since violet is refracted mor ...
Shedding Light on Light in the Ocean
... of animals with neither eyes nor brains, he completed postdoctoral fellowships at Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institution and WHOI. After a year as an assistant scientist at WHOI, he accepted a position in the Biology Department at Duke University. He is interested in all aspects of vision in oceani ...
... of animals with neither eyes nor brains, he completed postdoctoral fellowships at Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institution and WHOI. After a year as an assistant scientist at WHOI, he accepted a position in the Biology Department at Duke University. He is interested in all aspects of vision in oceani ...
Chapter 3 Note Packet
... of the same elements in the same proportion by mass, no matter how large or small the sample. Example: Water is always composed of 2 Hydrogen to 1 Oxygen ...
... of the same elements in the same proportion by mass, no matter how large or small the sample. Example: Water is always composed of 2 Hydrogen to 1 Oxygen ...
i. introduction
... manipulate plant morphology and physiology using photoselective filters have been going on for decades especially in green house environments. In this regard, use of coloured shadenets or photo-selective nets is an emerging technological approach. On top of physical protective functions and environm ...
... manipulate plant morphology and physiology using photoselective filters have been going on for decades especially in green house environments. In this regard, use of coloured shadenets or photo-selective nets is an emerging technological approach. On top of physical protective functions and environm ...
Physics notes – Wave-like properties of light
... Theoretically the intensity of light is halved after passing through a polarising sheet. If a second sheet is placed in tandem with its polarising direction perpendicular to the first sheet, it is expected to block the rest from passing through. Example 1 What do you think a third sheet will do to t ...
... Theoretically the intensity of light is halved after passing through a polarising sheet. If a second sheet is placed in tandem with its polarising direction perpendicular to the first sheet, it is expected to block the rest from passing through. Example 1 What do you think a third sheet will do to t ...
Waves Review (Key)
... days of the universe. Infrared thermal-imaging cameras are used to detect heat loss in insulated systems, to observe changing blood flow in the skin, and to detect overheating of electrical apparatus. Other applications include environmental monitoring, remote temperature sensing, short-ranged wirel ...
... days of the universe. Infrared thermal-imaging cameras are used to detect heat loss in insulated systems, to observe changing blood flow in the skin, and to detect overheating of electrical apparatus. Other applications include environmental monitoring, remote temperature sensing, short-ranged wirel ...
Chemistry Essentials Unit 2
... Of course not!!!!! We can find similarities to create types of matter Can be classified into 2 broad categories pure substances mixtures ...
... Of course not!!!!! We can find similarities to create types of matter Can be classified into 2 broad categories pure substances mixtures ...
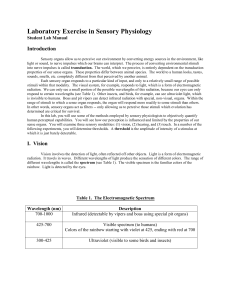
Laboratory Exercise in Sensory Physiology
... type has peak sensitivity to red, one type to blue, and one type to green. There are two main advantages to having three types of cones. First it expands the overall range of wavelengths of light, which are visible. Second it allows us to perceive colors. This is because any given wavelength stimul ...
... type has peak sensitivity to red, one type to blue, and one type to green. There are two main advantages to having three types of cones. First it expands the overall range of wavelengths of light, which are visible. Second it allows us to perceive colors. This is because any given wavelength stimul ...
Polarization of EM waves
... • Can be explained in terms of oscillations of dipole atoms when excited by an EM wave • Derivation explains polarization as well • This is why the sky is blue! • The higher frequencies are scattered more by the molecules in the atmosphere • Reds and oranges just pass through, so the sky appears blu ...
... • Can be explained in terms of oscillations of dipole atoms when excited by an EM wave • Derivation explains polarization as well • This is why the sky is blue! • The higher frequencies are scattered more by the molecules in the atmosphere • Reds and oranges just pass through, so the sky appears blu ...
SENIOR SCIENCE, Physics 1 When light goes from one material
... Index of refraction can change for a gas such as air. What causes the change and what is a consequence of such a change? a. An increase in temperature reduces index of refraction slightly causing light to travel slightly slower at higher temperature. b. An increase in temperature reduces air's index ...
... Index of refraction can change for a gas such as air. What causes the change and what is a consequence of such a change? a. An increase in temperature reduces index of refraction slightly causing light to travel slightly slower at higher temperature. b. An increase in temperature reduces air's index ...
Photopolymer
A photopolymer is a polymer that changes its properties when exposed to light, often in the ultraviolet or visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum. These changes are often manifested structurally, for example hardening of the material occurs as a result of cross-linking when exposed to light. An example is shown below depicting a mixture of monomers, oligomers, and photoinitiators that conform into a hardened polymeric material through a process called curing,.A wide variety of technologically useful applications rely on photopolymers, for example some enamels and varnishes depend on photopolymer formulation for proper hardening upon exposure to light. In some instances, an enamel can cure in a fraction of a second when exposed to light, as opposed to thermally cured enamels which can require half an hour or longer. Curable materials are widely used for medical, printing, and photoresist technologies. Changes in structural and chemical properties can be induced internally by chromophores that the polymer subunit already possesses, or externally by addition of photosensitive molecules. Typically a photopolymer consists of a mixture of multifunctional monomers and oligomers in order to achieve the desired physical properties, and therefore a wide variety of monomers and oligomers have been developed that can polymerize in the presence of light either through internal or external initiation. Photopolymers undergo a process called curing, where oligomers are cross-linked upon exposure to light, forming what is known as a network polymer. The result of photo curing is the formation of a thermoset network of polymers. One of the advantages of photo-curing is that it can be done selectively using high energy light sources, for example lasers, however, most systems are not readily activated by light, and in this case a photoinitiator is required. Photoinitiators are compounds that upon radiation of light decompose into reactive species that activate polymerization of specific functional groups on the oligomers. An example of a mixture that undergoes cross-linking when exposed to light is shown below. The mixture consists of monomeric styrene and oligomeric acrylates.Most commonly, photopolymerized systems are typically cured through UV radiation, since ultraviolet light is more energetic; however, the development of dye-based photoinitiator systems have allowed for the use of visible light, having potential advantages of processes that are more simple and safe to handle. UV curing in industrial processes has greatly expanded over the past several decades. Many traditional thermally cured and solvent-based technologies can be replaced by photopolymerization technologies. The advantages of photopolymerization over thermally cured polymerization include high rates of polymerization and environmental benefits from elimination of volatile organic solvents.There are two general routes for photoinitiation: free radical and ionic. The general process involves doping a batch of neat polymer with small amounts of photoinitiator, followed by selective radiation of light, resulting a highly cross-linked product. Many of these reactions do not require solvent which eliminates termination path via reaction of initiators with solvent and impurities, in addition to decreasing the overall cost.