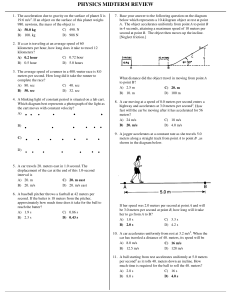
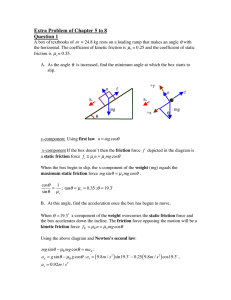
Causation as Folk Science
... just be weak enough to conform peacefully with our physics. But the much neglected fact is that it never was! All our standard physical theories exhibit one or other form of indeterminism. 4 (See Earman, 1986; Alper et al., 2000) That means, that we can always find circumstances in which the full sp ...
... just be weak enough to conform peacefully with our physics. But the much neglected fact is that it never was! All our standard physical theories exhibit one or other form of indeterminism. 4 (See Earman, 1986; Alper et al., 2000) That means, that we can always find circumstances in which the full sp ...
Forces - Chabot College
... Goals for Chapter 4 • To learn the relationship between mass, acceleration, and force: Newton’s Second Law of Motion: F = ma a = F/m • To relate mass (quantity of matter) and weight (force on that matter from gravity) ...
... Goals for Chapter 4 • To learn the relationship between mass, acceleration, and force: Newton’s Second Law of Motion: F = ma a = F/m • To relate mass (quantity of matter) and weight (force on that matter from gravity) ...
Newton`s Laws Review Sheet
... 2. You have a hammer with a loose head, which is about to fall off the top. Why is it better to hit the bottom (butt) of the hammer against the table to tighten it, rather than hitting the top of the hammer against the table? This is due to Newton’s First Law. When you hit your hammer against the ta ...
... 2. You have a hammer with a loose head, which is about to fall off the top. Why is it better to hit the bottom (butt) of the hammer against the table to tighten it, rather than hitting the top of the hammer against the table? This is due to Newton’s First Law. When you hit your hammer against the ta ...
Force and Motion
... Net force causes You are right if you are thinking “all forces together.” The motion of motion an object depends on the net force acting on it. There is almost always more than one force present because gravity acts on all objects. ...
... Net force causes You are right if you are thinking “all forces together.” The motion of motion an object depends on the net force acting on it. There is almost always more than one force present because gravity acts on all objects. ...
Rotary
... A changing angular velocity indicates the presence of an angular acceleration in rigid body, typically measured in rad s −2. The average angular acceleration ...
... A changing angular velocity indicates the presence of an angular acceleration in rigid body, typically measured in rad s −2. The average angular acceleration ...
Document
... mass and radius. Which reaches the bottom of the incline first? 1. The cylinder 2. The hoop 3. Both at same time "An object's moment of inertia determines how much it resists rotational motion. The cylinder has a smaller moment of inertia, so it’s easier “to get going”. Less energy goes into rolling ...
... mass and radius. Which reaches the bottom of the incline first? 1. The cylinder 2. The hoop 3. Both at same time "An object's moment of inertia determines how much it resists rotational motion. The cylinder has a smaller moment of inertia, so it’s easier “to get going”. Less energy goes into rolling ...
Generation of Gravitational Force
... these accelerometers sense linear or centrifugal acceleration and acceleration due to gravity but these are not direct sensors of gravity. There is no direct sensor available for gravity because no other property of Gravitational field is known. If there is a direct sensor of gravity which is not ba ...
... these accelerometers sense linear or centrifugal acceleration and acceleration due to gravity but these are not direct sensors of gravity. There is no direct sensor available for gravity because no other property of Gravitational field is known. If there is a direct sensor of gravity which is not ba ...
Problem Set 4 Momentum and Continuous Mass Flow Solutions
... the horizontal direction, the center of mass does not accelerate and hence remains at rest and in the same place. So we will calculate the position of the center of mass before the person started walking and after the person finished walking, and set them equal to find out how far the cart has moved ...
... the horizontal direction, the center of mass does not accelerate and hence remains at rest and in the same place. So we will calculate the position of the center of mass before the person started walking and after the person finished walking, and set them equal to find out how far the cart has moved ...
Part III: Movement Analysis – Learning Outcomes
... Gravity is a force that occurs naturally and pulls a body towards the centre of the earth at a rate of 9.81 meters per second squared. Gravitational pull always occurs through the centre of mass of an object. The location of the centre of gravity depends on the arrangement of mass within the body. I ...
... Gravity is a force that occurs naturally and pulls a body towards the centre of the earth at a rate of 9.81 meters per second squared. Gravitational pull always occurs through the centre of mass of an object. The location of the centre of gravity depends on the arrangement of mass within the body. I ...
has occurred over the past 14 billion years COSMIC DOWNSIZING
... holes lurking in their cores. This research suggests that not all supermassive black holes were formed in the quasar era. These mighty objects have apparently been assembling from the earliest times until the present. The supermassive black holes that are still active, however, do not exhibit the sa ...
... holes lurking in their cores. This research suggests that not all supermassive black holes were formed in the quasar era. These mighty objects have apparently been assembling from the earliest times until the present. The supermassive black holes that are still active, however, do not exhibit the sa ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.