Interpret The Graph Below
... acted upon by an unbalanced force • Objects at rest tend to stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force • The more mass an object has, the more inertia it has – More massive objects are harder to start moving and ...
... acted upon by an unbalanced force • Objects at rest tend to stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force • The more mass an object has, the more inertia it has – More massive objects are harder to start moving and ...
dynamics
... Newton’s second law answers the question of what happens to an object that has a nonzero resultant force acting on it. Newton’s second law states that; if a net force acts on a body, the body will accelerate. The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the resultant force acting on it ...
... Newton’s second law answers the question of what happens to an object that has a nonzero resultant force acting on it. Newton’s second law states that; if a net force acts on a body, the body will accelerate. The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the resultant force acting on it ...
IPC Review - Humble ISD
... A force does work on an object if a component of the force is perpendicular to the displacement of the object. is parallel to the displacement of the object. perpendicular to the displacement of the object moves the object along a path that returns the object to its starting position. d. parallel to ...
... A force does work on an object if a component of the force is perpendicular to the displacement of the object. is parallel to the displacement of the object. perpendicular to the displacement of the object moves the object along a path that returns the object to its starting position. d. parallel to ...
PHY2053-S10 Exam II Chapters 6-10
... lump of clay is suspended from a cord 4.0 m long. When the pitcher throws his fastball aimed at the clay, the ball becomes embedded in the clay and the two swing up to a maximum height of 0.35 m. If the mass of the baseball is 0.21 kg, find the speed of the pitch. ( Hint: Use conservation of moment ...
... lump of clay is suspended from a cord 4.0 m long. When the pitcher throws his fastball aimed at the clay, the ball becomes embedded in the clay and the two swing up to a maximum height of 0.35 m. If the mass of the baseball is 0.21 kg, find the speed of the pitch. ( Hint: Use conservation of moment ...
Learning Standard # 1
... Explain the difference between speed and velocity. Distinguish the difference between Velocity and acceleration. Graphically represent and interpret distance - time, velocity – time, and acceleration and time. Understand that gravity causes objects to accelerate towards earth’s center. Solve acceler ...
... Explain the difference between speed and velocity. Distinguish the difference between Velocity and acceleration. Graphically represent and interpret distance - time, velocity – time, and acceleration and time. Understand that gravity causes objects to accelerate towards earth’s center. Solve acceler ...
StewartCalcET8_13_04
... Since the gravitational force of the sun on a planet is so much larger than the forces exerted by other celestial bodies, we can safely ignore all bodies in the universe except the sun and one planet revolving about it. We use a coordinate system with the sun at the origin and we let r = r(t) be the ...
... Since the gravitational force of the sun on a planet is so much larger than the forces exerted by other celestial bodies, we can safely ignore all bodies in the universe except the sun and one planet revolving about it. We use a coordinate system with the sun at the origin and we let r = r(t) be the ...
01) A car has a mass of 1000 kilograms
... 6. The weight of a flying aeroplane is mainly balanced by a) weight of the displaced air b) force of propelled air c) vertical component of the thrust created by air current striking the lower surface of the plane. d) upward thrust created by the pressure difference between the upper and lower surfa ...
... 6. The weight of a flying aeroplane is mainly balanced by a) weight of the displaced air b) force of propelled air c) vertical component of the thrust created by air current striking the lower surface of the plane. d) upward thrust created by the pressure difference between the upper and lower surfa ...
PPT - Hss-1.us
... needs to be testable, so you can determine if it is true or not. For example, you think about your observations and you propose that the types of clouds, cumuliform or stratiform, are related to how fast the temperature cools off with height. So you state that for cumulus clouds to form the air need ...
... needs to be testable, so you can determine if it is true or not. For example, you think about your observations and you propose that the types of clouds, cumuliform or stratiform, are related to how fast the temperature cools off with height. So you state that for cumulus clouds to form the air need ...
Raising and Lowering
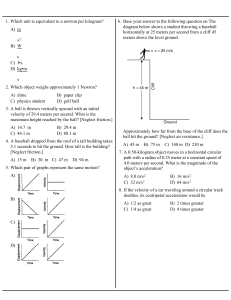
... negative velocity. Draw a motion diagram for the box. Is the net force on the box, up, down or zero? Draw a force diagram for the box. Acceleration is positive, e.g. velocity might change from -10 to -5, an increase of +5. The net force = mass x acceleration which is upwards since acceleration is ...
... negative velocity. Draw a motion diagram for the box. Is the net force on the box, up, down or zero? Draw a force diagram for the box. Acceleration is positive, e.g. velocity might change from -10 to -5, an increase of +5. The net force = mass x acceleration which is upwards since acceleration is ...
Name - Manasquan Public Schools
... Florida, averaging 58 mi/hr for the journey and has traveled over 1550 miles so far but has stopped to refuel is________________. ...
... Florida, averaging 58 mi/hr for the journey and has traveled over 1550 miles so far but has stopped to refuel is________________. ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.