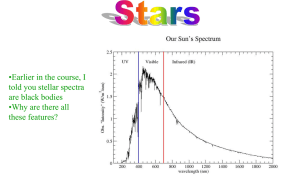
Example
... Rolling, Torque, and Angular Momentum In this chapter we will cover the following topics: -Rolling of circular objects and its relationship with friction -Redefinition of torque as a vector to describe rotational problems that are more complicated than the rotation of a rigid body about a fixed axis ...
... Rolling, Torque, and Angular Momentum In this chapter we will cover the following topics: -Rolling of circular objects and its relationship with friction -Redefinition of torque as a vector to describe rotational problems that are more complicated than the rotation of a rigid body about a fixed axis ...
Chapter 1 Introduction
... roughly 73% of the total. The total energy density adds up to a “critical density” which suggests that the universe is geometrically flat (as discussed below). This combination of theory and observations forms the entire theoretical basis of Big Bang cosmology, and produces very specific prediction ...
... roughly 73% of the total. The total energy density adds up to a “critical density” which suggests that the universe is geometrically flat (as discussed below). This combination of theory and observations forms the entire theoretical basis of Big Bang cosmology, and produces very specific prediction ...
Rotation Torque, Rolling, & Angular Momentum
... A) Static (because the wheel never actually moves, or “skids” along the surface… if it were perfect it would simply touch down on the ground, then lift up as it rolled) ...
... A) Static (because the wheel never actually moves, or “skids” along the surface… if it were perfect it would simply touch down on the ground, then lift up as it rolled) ...
Circular Motion
... cm from the rotation axis. Calculate its centripetal acceleration, in “g’s.” ...
... cm from the rotation axis. Calculate its centripetal acceleration, in “g’s.” ...
12 The Milky Way - Journigan-wiki
... which these stars orbit has a mass of 4 million solar masses, yet nothing is seen there. Therefore, many astronomers almost inescapably conclude that a massive black hole lies at the heart of our galaxy. This evidence is perhaps the best yet that black holes actually exist. ...
... which these stars orbit has a mass of 4 million solar masses, yet nothing is seen there. Therefore, many astronomers almost inescapably conclude that a massive black hole lies at the heart of our galaxy. This evidence is perhaps the best yet that black holes actually exist. ...
Milky Way
... The Milky Way – Artist’s Conception •Our galaxy is hard to study because we are inside it •We are in the galactic plane, filled with obscuring dust •Other galaxies are hard to study because they are far away •Generalize from far away to nearby and vice versa ...
... The Milky Way – Artist’s Conception •Our galaxy is hard to study because we are inside it •We are in the galactic plane, filled with obscuring dust •Other galaxies are hard to study because they are far away •Generalize from far away to nearby and vice versa ...
MSci Astrophysics 210PHY412
... In clusters, t and Z must be same for all stars Hence differences must be due to M Stellar evolution assumes that the differences in cluster stars are due only (or mainly) to initial M ...
... In clusters, t and Z must be same for all stars Hence differences must be due to M Stellar evolution assumes that the differences in cluster stars are due only (or mainly) to initial M ...
Tutorial #6 Solutions
... From Newton’s third law, the downward force exerted on the air by the helicopter is equal and opposite to the upward force on the helicopter (the engine’s thrust). If we neglect air resistance, the thrust and gravity are the only vertical forces acting, so Newton’s second law for the helicopter (pos ...
... From Newton’s third law, the downward force exerted on the air by the helicopter is equal and opposite to the upward force on the helicopter (the engine’s thrust). If we neglect air resistance, the thrust and gravity are the only vertical forces acting, so Newton’s second law for the helicopter (pos ...
Slides for Chapters 9, 10, 11 and Review
... S ECTION 10.2: T ORQUE FOR R IGID B ODY Example 10.3. (setup as in Example 9.8) We wrap a light, non-stretching cable around a solid cylinder with mass M and radius R. The cylinder rotates with negligible friction about a stationary horizontal axis. We tie the free and of the cable to a block of ma ...
... S ECTION 10.2: T ORQUE FOR R IGID B ODY Example 10.3. (setup as in Example 9.8) We wrap a light, non-stretching cable around a solid cylinder with mass M and radius R. The cylinder rotates with negligible friction about a stationary horizontal axis. We tie the free and of the cable to a block of ma ...
PHYSICS (861) - Indiaeducation.net
... expression for this acceleration using r Triangle Law to find ∆ v . Magnitude and r direction of a same as that of ∆ v ; Centripetal acceleration; the cause of this acceleration is a force - also called centripetal force; the name only indicates its direction, it is not a new type of force, it could ...
... expression for this acceleration using r Triangle Law to find ∆ v . Magnitude and r direction of a same as that of ∆ v ; Centripetal acceleration; the cause of this acceleration is a force - also called centripetal force; the name only indicates its direction, it is not a new type of force, it could ...
1.9 Simple Harmonic Motion
... Not only the mass oscillates when it is released, but also the spring itself. The period of oscillation is affected by the mass of the spring. ...
... Not only the mass oscillates when it is released, but also the spring itself. The period of oscillation is affected by the mass of the spring. ...
- Lorentz Center
... Interesting systems - AW UMa Pribulla & Rucinski (2008) find higher mass ratio q = 0.1 and suggest that AW UMa may not be a contact binary? ...
... Interesting systems - AW UMa Pribulla & Rucinski (2008) find higher mass ratio q = 0.1 and suggest that AW UMa may not be a contact binary? ...
Astrophysics with the Computer: Finding the Gravitational Potential
... The movement of stars within a galaxy is governed by the gravitational potential in the galaxy which is produced by all the visible and nonvisible matter in the galaxy. So the stars of the disk, of the bulge, and of the halo as well as the gas in the disk influence the kinematics of any star, say in ...
... The movement of stars within a galaxy is governed by the gravitational potential in the galaxy which is produced by all the visible and nonvisible matter in the galaxy. So the stars of the disk, of the bulge, and of the halo as well as the gas in the disk influence the kinematics of any star, say in ...
10841 Physics (Pink) P1
... Four options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Each question has only ONE correct answer. Write only the letter (A – D) next to the question number (1.1 – 1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.11 C. ...
... Four options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Each question has only ONE correct answer. Write only the letter (A – D) next to the question number (1.1 – 1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.11 C. ...
Mechanics Notes II Forces, Inertia and Motion The mathematics of
... This is also an amazing result, and nature didn’t have be be so simple! It shows that if the amount of material (or ”ρV mass”) is doubled, the acceleration is cut in half for the same constant force. Experiment will also show that n times the amount of ”ρV mass” results in an acceleration equal to 1 ...
... This is also an amazing result, and nature didn’t have be be so simple! It shows that if the amount of material (or ”ρV mass”) is doubled, the acceleration is cut in half for the same constant force. Experiment will also show that n times the amount of ”ρV mass” results in an acceleration equal to 1 ...
Conceptual Physics
... 33. What is the resultant velocity of a boat going across a river the boat's speedometer reads 4 m/s West and the river is flowing 3 m/s South? Draw your solution and then use the Pythagorean Theorem to verify the ...
... 33. What is the resultant velocity of a boat going across a river the boat's speedometer reads 4 m/s West and the river is flowing 3 m/s South? Draw your solution and then use the Pythagorean Theorem to verify the ...
Chapter 1: An Introduction to Philosophy of Science
... It is important to understand that the validity is not another name for ‘good’. In particular, valid arguments can have false conclusions. This leads to the important distinction between a sound arguments and valid arguments. A sound argument is one that is valid and has true premises. The conclusio ...
... It is important to understand that the validity is not another name for ‘good’. In particular, valid arguments can have false conclusions. This leads to the important distinction between a sound arguments and valid arguments. A sound argument is one that is valid and has true premises. The conclusio ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.