s - Nuffield Foundation
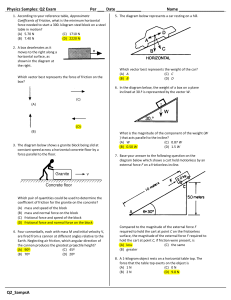
... find the frictional force acting on each can. 4 A sledge has mass 15 kg. A horizontal pull of 25 N will just move the sledge when it is on a horizontal surface of compacted snow. a Draw a diagram showing the forces acting on the sledge, modelled as a particle, when it is just on the point of sliding ...
... find the frictional force acting on each can. 4 A sledge has mass 15 kg. A horizontal pull of 25 N will just move the sledge when it is on a horizontal surface of compacted snow. a Draw a diagram showing the forces acting on the sledge, modelled as a particle, when it is just on the point of sliding ...
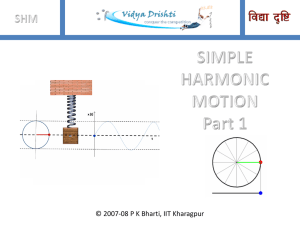
SHM Part 1 - Ask Physics
... after a regular intervals of time is called periodic motion. Therefore, revolution of the Earth around the Sun is a periodic motion. The time period of this periodic motion is roughly 365 days. Therefore, T ≈ 365 days = 365 X 24 X 60 X 60 s = 31536000 s. Hence, frequency: ...
... after a regular intervals of time is called periodic motion. Therefore, revolution of the Earth around the Sun is a periodic motion. The time period of this periodic motion is roughly 365 days. Therefore, T ≈ 365 days = 365 X 24 X 60 X 60 s = 31536000 s. Hence, frequency: ...
force=mass times acceleration
... 11. Inertia: the tendency of an object to resist a change in its motion 12. Inexhaustible: incapable of being entirely consumed or used up; renewable 13. Joule: SI unit of energy 14. Kinetic energy: The energy of a moving object 15. Law of Conservation of Energy: That energy can neither be created n ...
... 11. Inertia: the tendency of an object to resist a change in its motion 12. Inexhaustible: incapable of being entirely consumed or used up; renewable 13. Joule: SI unit of energy 14. Kinetic energy: The energy of a moving object 15. Law of Conservation of Energy: That energy can neither be created n ...
Chapter 4 Powerpoint
... constant pull of 7.5 × 105 N, how long does it take to increase the speed of the train from rest to 80 km/h? ...
... constant pull of 7.5 × 105 N, how long does it take to increase the speed of the train from rest to 80 km/h? ...
Force unit outline - Huber Heights City Schools
... Example 7: A student moves a box of books by attaching a rope to the box and pulling with a force of 90.0 N at an angle of 30.0. The box of books has a mass of 20.0 kg, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the bottom of the box and the sidewalk is 0.50. Find the acceleration of the box. ...
... Example 7: A student moves a box of books by attaching a rope to the box and pulling with a force of 90.0 N at an angle of 30.0. The box of books has a mass of 20.0 kg, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the bottom of the box and the sidewalk is 0.50. Find the acceleration of the box. ...
Physics 106P: Lecture 23 Notes
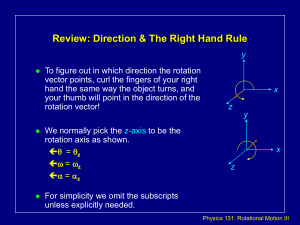
... We just used = I for rotation about an axis through the CM even though the CM was accelerating! The CM is not an inertial reference frame! Is this OK?? (After all, we can only use F = ma in an inertial reference frame). ...
... We just used = I for rotation about an axis through the CM even though the CM was accelerating! The CM is not an inertial reference frame! Is this OK?? (After all, we can only use F = ma in an inertial reference frame). ...
CHAPTER ONE
... Engineering mechanics:- is essentially a study of the external effects of a system of forces acting on a rigid body. The mechanics of rigid bodies subdivided into: ...
... Engineering mechanics:- is essentially a study of the external effects of a system of forces acting on a rigid body. The mechanics of rigid bodies subdivided into: ...
Collisions – Impulse and Momentum
... 5. Rescale the Force vs time graph (The impulse graph) so that you can clearly see the data points where contact began, and contact ended. 6. Click on the Highlight Range icon near the top left of the impulse graph to make a highlight box appear on the impulse graph. Rescale the graph and the high ...
... 5. Rescale the Force vs time graph (The impulse graph) so that you can clearly see the data points where contact began, and contact ended. 6. Click on the Highlight Range icon near the top left of the impulse graph to make a highlight box appear on the impulse graph. Rescale the graph and the high ...
4.1_simple_harmonic_motion_
... (a) when the springs are connected as in figure (a) calculate the period of oscillations when it is displaced from its equilibrium position and then released. (b) When the springs are connected instead as in figure (b) would the period change. 24. The graph in the figure shows the variation with tim ...
... (a) when the springs are connected as in figure (a) calculate the period of oscillations when it is displaced from its equilibrium position and then released. (b) When the springs are connected instead as in figure (b) would the period change. 24. The graph in the figure shows the variation with tim ...
Chapter 4 - faculty at Chemeketa
... Coin and feather fall with air present • Feather reaches terminal velocity very quickly and falls slowly at constant speed, reaching the bottom after the coin does. • Coin falls very quickly and air resistance doesn’t build up to its weight over short-falling distances, which is why the coin hits th ...
... Coin and feather fall with air present • Feather reaches terminal velocity very quickly and falls slowly at constant speed, reaching the bottom after the coin does. • Coin falls very quickly and air resistance doesn’t build up to its weight over short-falling distances, which is why the coin hits th ...