Document
... You pull on a box with an applied force of 30 N. The coefficient of friction is 0.4. If the mass of the box is 2 kg, what is its acceleration? 1. Draw the box and all FOUR forces acting on it. 2. Write what you know and don’t know. 3. Write the equations, Fnet = ma and f = mN 4. Calculate the Norma ...
... You pull on a box with an applied force of 30 N. The coefficient of friction is 0.4. If the mass of the box is 2 kg, what is its acceleration? 1. Draw the box and all FOUR forces acting on it. 2. Write what you know and don’t know. 3. Write the equations, Fnet = ma and f = mN 4. Calculate the Norma ...
t = 0
... (d). From its maximum positive position to the equilibrium position, the block travels a distance A. It then goes an equal distance past the equilibrium position to its maximum negative position. It then repeats these two motions in the reverse direction to ...
... (d). From its maximum positive position to the equilibrium position, the block travels a distance A. It then goes an equal distance past the equilibrium position to its maximum negative position. It then repeats these two motions in the reverse direction to ...
Period 3 Activity Sheet: Motion and Forces
... compare to its acceleration with only one 0.5 kg mass? 3) For a given amount of force, explain how the mass of an object is related to its acceleration. ...
... compare to its acceleration with only one 0.5 kg mass? 3) For a given amount of force, explain how the mass of an object is related to its acceleration. ...
Physics 7B - AB Lecture 7 May 15 Angular Momentum Model
... the mass is distributed about the axis of rotation : I can change! Formula not really important, but the idea is that the further mass is from the axis of rotation, the greater I ...
... the mass is distributed about the axis of rotation : I can change! Formula not really important, but the idea is that the further mass is from the axis of rotation, the greater I ...
CHAPTER 14 :OSCILLATIONS One mark
... and velocity of the particle when the displacement is (a) 5cm, (b) 3 cm and (c) 0 cm. 9. A block of mass is 1 kg is fastened to a spring. The spring has a spring constant of 50 Nm–1. The block is pulled to a distance x= = 10 cm from its equilibrium position at x= 0 on a frictionless surface from res ...
... and velocity of the particle when the displacement is (a) 5cm, (b) 3 cm and (c) 0 cm. 9. A block of mass is 1 kg is fastened to a spring. The spring has a spring constant of 50 Nm–1. The block is pulled to a distance x= = 10 cm from its equilibrium position at x= 0 on a frictionless surface from res ...
Aim: How do we explain Newton`s 3rd Law?
... 3. A traveler pulls a suitcase of mass 8.00 kg across a level surface by pulling on the handle 20.0 N at an angle of 50.0° relative to horizontal. Friction against the suitcase can be modeled by μk = 0.100. (a) Determine the acceleration of the suitcase. (b) What amount of force applied at the same ...
... 3. A traveler pulls a suitcase of mass 8.00 kg across a level surface by pulling on the handle 20.0 N at an angle of 50.0° relative to horizontal. Friction against the suitcase can be modeled by μk = 0.100. (a) Determine the acceleration of the suitcase. (b) What amount of force applied at the same ...
1, 3, 6, 10, 11, 17, 21 / 1, 4, 12, 15, 20, 24, 28, 36, 38
... force on the ball will be greater in magnitude than the weight of the ball. b. As the ball falls downward, the force of air resistance is upward. Since air resistance and the weight of the ball act in opposite directions, the net force that acts on the ball will be smaller in magnitude than the weig ...
... force on the ball will be greater in magnitude than the weight of the ball. b. As the ball falls downward, the force of air resistance is upward. Since air resistance and the weight of the ball act in opposite directions, the net force that acts on the ball will be smaller in magnitude than the weig ...
17 Energy in Simp Hrmnc Mot
... position. First write the total mechanical energy (kinetic, gravitational potential, and elastic potential energy) in terms of a coordinate system, distance measured upward and labeled y, whose origin is located at the bottom of the relaxed spring of constant k (no force applied). Then determine the ...
... position. First write the total mechanical energy (kinetic, gravitational potential, and elastic potential energy) in terms of a coordinate system, distance measured upward and labeled y, whose origin is located at the bottom of the relaxed spring of constant k (no force applied). Then determine the ...
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion continued
... Newton’s laws of force and motion 1. An object continues in a state of rest or in a state of motion at a constant speed along a straight line, unless compelled to change that state by a net force. (One object) 2. When a net external force acts on an object of mass m, the acceleration that results is ...
... Newton’s laws of force and motion 1. An object continues in a state of rest or in a state of motion at a constant speed along a straight line, unless compelled to change that state by a net force. (One object) 2. When a net external force acts on an object of mass m, the acceleration that results is ...
Download_2
... For this Activity you will be using a computer-based laboratory system with an ultrasonic motion sensor and motion software. The motion sensor acts like a stupid bat when hooked up with a computer-based laboratory system. It sends out a series of sound pulses that are too high frequency to hear. The ...
... For this Activity you will be using a computer-based laboratory system with an ultrasonic motion sensor and motion software. The motion sensor acts like a stupid bat when hooked up with a computer-based laboratory system. It sends out a series of sound pulses that are too high frequency to hear. The ...
force
... to keep the object moving with the same speed and in the same direction? Zero. Think about if friction could be eliminated~once an object is in motion, it will continue in motion at a constant velocity (same speed and straight line). Newton’s 1st Law INERTIA Remember Galileo postulated that if frict ...
... to keep the object moving with the same speed and in the same direction? Zero. Think about if friction could be eliminated~once an object is in motion, it will continue in motion at a constant velocity (same speed and straight line). Newton’s 1st Law INERTIA Remember Galileo postulated that if frict ...
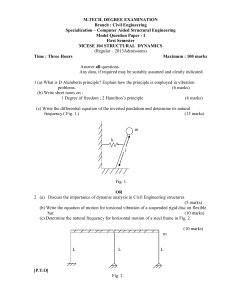
mcese 104 structural dynamics
... centre. The rotor in the machine generates a harmonic force of 3,000 kg. at a frequency 60 rad/sec. Assume 10% damping, calculate amplitude of motion of machine, force transmitted to supports and phase angle. Span of beam 3m ,E – 2 x 105 Mpa and I of beam 5000 cm4. (12 marks) ...
... centre. The rotor in the machine generates a harmonic force of 3,000 kg. at a frequency 60 rad/sec. Assume 10% damping, calculate amplitude of motion of machine, force transmitted to supports and phase angle. Span of beam 3m ,E – 2 x 105 Mpa and I of beam 5000 cm4. (12 marks) ...