Magmatic processes at slow spreading ridges
... of the crust–mantle boundary. In contrast, electromagnetic methods are relatively insensitive to sharp structural boundaries, but are sensitive to the large-scale distribution of crustal temperature and to the presence, amount and interconnectedness of conductive crustal fluids. In combination, the ...
... of the crust–mantle boundary. In contrast, electromagnetic methods are relatively insensitive to sharp structural boundaries, but are sensitive to the large-scale distribution of crustal temperature and to the presence, amount and interconnectedness of conductive crustal fluids. In combination, the ...
File
... 1. A pitcher releases a fastball that moves toward home plate. Other than the force exerted by the pitcher, what are two forces that act on the ball as it travels between the pitcher and home plate? How does each of these forces change the ball’s motion? Classify the forces acting on the ball as bal ...
... 1. A pitcher releases a fastball that moves toward home plate. Other than the force exerted by the pitcher, what are two forces that act on the ball as it travels between the pitcher and home plate? How does each of these forces change the ball’s motion? Classify the forces acting on the ball as bal ...
Packet 8: Impulse Momentum
... 1. Two pop cans are at rest on a stand. A firecracker is placed between the cans and lit. The firecracker explodes and exerts equal and opposite forces on the two cans. Assuming the system of two cans to be isolated, the post-explosion momentum of the system ____. A) is dependent upon the mass and v ...
... 1. Two pop cans are at rest on a stand. A firecracker is placed between the cans and lit. The firecracker explodes and exerts equal and opposite forces on the two cans. Assuming the system of two cans to be isolated, the post-explosion momentum of the system ____. A) is dependent upon the mass and v ...
1 - OnCourse
... How can waves be categorized? What do these types of waves depend on? What are the characteristics of all waves? What is sound? What is the relationship between perceived qualities and physical quantities? What is the Doppler Effect? How many charges are there and what part of the atom is charged? W ...
... How can waves be categorized? What do these types of waves depend on? What are the characteristics of all waves? What is sound? What is the relationship between perceived qualities and physical quantities? What is the Doppler Effect? How many charges are there and what part of the atom is charged? W ...
Adams2010-MechanicalVibrations.pdf
... and organs. In fact, it is well known that the resonant frequency of the human intestinal tract (approx. 4-8 Hz) should be avoided at all costs when designing high performance aircraft and reusable launch vehicles because sustained exposure can cause serious internal trauma (Leatherwood and Dempsey, ...
... and organs. In fact, it is well known that the resonant frequency of the human intestinal tract (approx. 4-8 Hz) should be avoided at all costs when designing high performance aircraft and reusable launch vehicles because sustained exposure can cause serious internal trauma (Leatherwood and Dempsey, ...
FREE Sample Here - Find the cheapest test bank for your
... B) keep rolling without slowing down if no friction acted upon it. C) roll as long as its inertia nudged it along. D) roll in the opposite direction. Answer: B Diff: 1 Topic: Galileo's Concept of Inertia 4) When Galileo rolled a ball down an incline and up another incline, he found that the ball rol ...
... B) keep rolling without slowing down if no friction acted upon it. C) roll as long as its inertia nudged it along. D) roll in the opposite direction. Answer: B Diff: 1 Topic: Galileo's Concept of Inertia 4) When Galileo rolled a ball down an incline and up another incline, he found that the ball rol ...
Seismic low-velocity layer at the top of subducting slabs
... circum-Pacific subduction zones show such signals, which can be explained as low-velocity channels 2–8 km thick. Velocity anomalies within low-velocity channels are largest at shallowest depths, up to 14% slower than surroundings at depths less than 150 km, diminishing to <3% at greater depths. This ...
... circum-Pacific subduction zones show such signals, which can be explained as low-velocity channels 2–8 km thick. Velocity anomalies within low-velocity channels are largest at shallowest depths, up to 14% slower than surroundings at depths less than 150 km, diminishing to <3% at greater depths. This ...
gge_orals_nov8_2006 - Department of Earth and Planetary
... be detectable as ultra-low velocity zones (ULVZ) at the base of the mantle [Buffett et al, 2000; Kanda and Stevenson, 2006]. Remarkably, multiple assessments of core-reflected and diffracted seismic phases have found patches of ULVZs tens of kilometers thick at the base of the mantle that appear to ...
... be detectable as ultra-low velocity zones (ULVZ) at the base of the mantle [Buffett et al, 2000; Kanda and Stevenson, 2006]. Remarkably, multiple assessments of core-reflected and diffracted seismic phases have found patches of ULVZs tens of kilometers thick at the base of the mantle that appear to ...
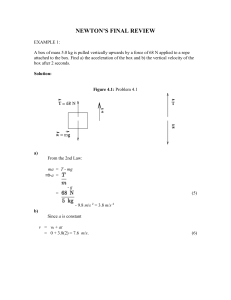
Final Newtons Review
... 6.9 meters from its rest position. PSYW 40. A 4.44-kg bucket suspended by a rope is accelerated upwards from an initial rest position. If the tension in the rope is a constant value of 83.1 Newtons, then determine the speed (in m/s) of the bucket after 1.59 seconds. PSYW 41. A 22.6-N horizontal forc ...
... 6.9 meters from its rest position. PSYW 40. A 4.44-kg bucket suspended by a rope is accelerated upwards from an initial rest position. If the tension in the rope is a constant value of 83.1 Newtons, then determine the speed (in m/s) of the bucket after 1.59 seconds. PSYW 41. A 22.6-N horizontal forc ...
Conceptual Physical Science, 5e (Hewitt
... B) keep rolling without slowing down if no friction acted upon it. C) roll as long as its inertia nudged it along. D) roll in the opposite direction. Answer: B Diff: 1 Topic: Galileo's Concept of Inertia 4) When Galileo rolled a ball down an incline and up another incline, he found that the ball rol ...
... B) keep rolling without slowing down if no friction acted upon it. C) roll as long as its inertia nudged it along. D) roll in the opposite direction. Answer: B Diff: 1 Topic: Galileo's Concept of Inertia 4) When Galileo rolled a ball down an incline and up another incline, he found that the ball rol ...
Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions
... breaks up into a pair of other particles called pions ('# and '") that are oppositely charged but equal in mass, as illustrated in Figure 9.3. Assuming the kaon is initially at rest, prove that the two pions must have momenta that are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. ...
... breaks up into a pair of other particles called pions ('# and '") that are oppositely charged but equal in mass, as illustrated in Figure 9.3. Assuming the kaon is initially at rest, prove that the two pions must have momenta that are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. ...
13_InstructorSolutions
... EVALUATE: The amplitude and the maximum speed depend on the total energy of the system but the angular frequency is independent of the amount of energy in the system and just depends on the force constant of the spring and the mass of the object. IDENTIFY: K = 12 mv 2 , U grav = mgy and U el = 12 kx ...
... EVALUATE: The amplitude and the maximum speed depend on the total energy of the system but the angular frequency is independent of the amount of energy in the system and just depends on the force constant of the spring and the mass of the object. IDENTIFY: K = 12 mv 2 , U grav = mgy and U el = 12 kx ...
crustal velocity structure of the rukwa rift in the western
... mafic composition. This finding is important for understanding the occurrence of lower crustal earthquakes in east Africa, because it suggests that at least some of the crust in east Africa could be sufficiently strong at mid- and lower crustal depths to support brittle deformation. ...
... mafic composition. This finding is important for understanding the occurrence of lower crustal earthquakes in east Africa, because it suggests that at least some of the crust in east Africa could be sufficiently strong at mid- and lower crustal depths to support brittle deformation. ...
Chapter 15 Periodic Motion
... Looking Ahead: Rotational oscillations • A horizontal disk suspended at its center by a thin fiber forms a type of torsional oscillator. • A pendulum is any object that swings about a pivot. A simple pendulum consists of a small object (the bob) attached to a very light wire or rod. • You will learn ...
... Looking Ahead: Rotational oscillations • A horizontal disk suspended at its center by a thin fiber forms a type of torsional oscillator. • A pendulum is any object that swings about a pivot. A simple pendulum consists of a small object (the bob) attached to a very light wire or rod. • You will learn ...