3 Two-Dimensional Kinematics
... characteristic of vectors. (Recall that vectors are quantities that have both magnitude and direction.) As for one-dimensional kinematics, we use arrows to represent vectors. The length of the arrow is proportional to the vector’s magnitude. The arrow’s length is indicated by hash marks in Figure 3. ...
... characteristic of vectors. (Recall that vectors are quantities that have both magnitude and direction.) As for one-dimensional kinematics, we use arrows to represent vectors. The length of the arrow is proportional to the vector’s magnitude. The arrow’s length is indicated by hash marks in Figure 3. ...
letters - Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris
... along the axis and ,5 km across the axis; that is, a short wavelength increase in travel-time difference of 35–40% in the lower crust. If the whole anomaly is produced by the presence of melt then over 45% of the lower crust could be molten, assuming horizontally aligned, spheroidal inclusions with ...
... along the axis and ,5 km across the axis; that is, a short wavelength increase in travel-time difference of 35–40% in the lower crust. If the whole anomaly is produced by the presence of melt then over 45% of the lower crust could be molten, assuming horizontally aligned, spheroidal inclusions with ...
1 Issues to address at the FDR. - LIGO
... strength of ?? Tesla will be grouped on two set of four and secured below the suspension and at the end of the suspension table The damping measurement result should hold true also for the new OFI suspension prototype (OFIS-Proto2). OFIS-Proto2 differs from the previous one in the connection of the ...
... strength of ?? Tesla will be grouped on two set of four and secured below the suspension and at the end of the suspension table The damping measurement result should hold true also for the new OFI suspension prototype (OFIS-Proto2). OFIS-Proto2 differs from the previous one in the connection of the ...
PHYSICS COURSE DESCRIPTION - McCall
... 3. Explain how an object can “fall” around the Earth 4. Explain why gravity has no effect on a satellite orbiting the Earth 5. Relate length of period to altitude of a satellite orbiting the Earth 6. Define elliptical orbit 7. Compare/contrast the speed of the parts of a satellite’s elliptical orbit ...
... 3. Explain how an object can “fall” around the Earth 4. Explain why gravity has no effect on a satellite orbiting the Earth 5. Relate length of period to altitude of a satellite orbiting the Earth 6. Define elliptical orbit 7. Compare/contrast the speed of the parts of a satellite’s elliptical orbit ...
Seismic evaluation of old masonry buildings. Part I: Method
... Another disadvantage of the method is that it does not account directly for hysteretic energy dissipation. Thus, in this type of analysis, this phenomenon can only be accounted for in an approximate manner, for instance by means of changing the viscous damping coefficient, and/or by means of a behav ...
... Another disadvantage of the method is that it does not account directly for hysteretic energy dissipation. Thus, in this type of analysis, this phenomenon can only be accounted for in an approximate manner, for instance by means of changing the viscous damping coefficient, and/or by means of a behav ...
Linear Momentum and Collisions
... small car moving with the same speed. The more momentum an object has, the harder it is to stop it, and the greater effect it will have if it is brought to rest by bnpact or collision. A football player is more likely to be stunned if tackled by a beavy opponent running at top speed than by a lighte ...
... small car moving with the same speed. The more momentum an object has, the harder it is to stop it, and the greater effect it will have if it is brought to rest by bnpact or collision. A football player is more likely to be stunned if tackled by a beavy opponent running at top speed than by a lighte ...
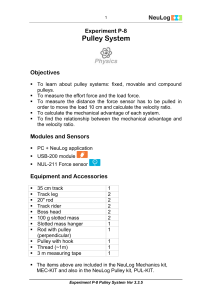
Pulley System - NeuLog Sensors
... cable fits into the groove and passes over the wheel. A fixed pulley is fastened to one spot. The fixed pulley has no gains in force or distance, but it changes the direction of the force. A movable pulley moves along a rope. It decreases the force, but the rope must be pulled for a longer distance. ...
... cable fits into the groove and passes over the wheel. A fixed pulley is fastened to one spot. The fixed pulley has no gains in force or distance, but it changes the direction of the force. A movable pulley moves along a rope. It decreases the force, but the rope must be pulled for a longer distance. ...
Chapter 2 and 3 - Fayetteville State University
... In order for this force to do work, it must point along the direction of motion. In this case, it is perpendicular to the direction of motion so the work is zero. Feedback C: Incorrect. See section 3.1. Question 3.02 TRUE or FALSE: If an object moves from one point in space to another, then work has ...
... In order for this force to do work, it must point along the direction of motion. In this case, it is perpendicular to the direction of motion so the work is zero. Feedback C: Incorrect. See section 3.1. Question 3.02 TRUE or FALSE: If an object moves from one point in space to another, then work has ...
Going Down
... sand, it will quickly come to rest. If you roll it on a surface that is hard and smooth, such as a bowling alley, the ball will roll for a long time with little change in velocity. You could imagine that if all friction were eliminated, the ball might roll at the same velocity forever. Galileo did m ...
... sand, it will quickly come to rest. If you roll it on a surface that is hard and smooth, such as a bowling alley, the ball will roll for a long time with little change in velocity. You could imagine that if all friction were eliminated, the ball might roll at the same velocity forever. Galileo did m ...
1) An anchor is dropped in the water plummets to the ocean floor
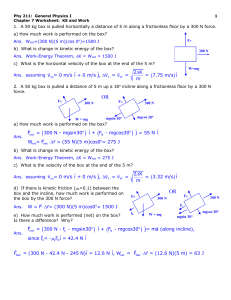
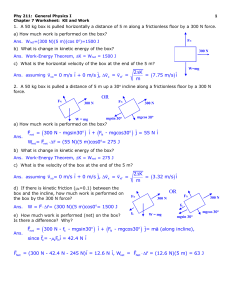
... a) What is the KE at the start of the trial, v = 0 mph? Ans. Ko = 0 J b) What is the KE at the end of the quarter mile? Ans. Kf = ½ mv2 = 2.07x106 J c) How much work is performed on the Corvette during this trial? Ans. Wnet = K = Kf - Ko = 2.07x106 J d) What is the average net power in (W or J/s) g ...
... a) What is the KE at the start of the trial, v = 0 mph? Ans. Ko = 0 J b) What is the KE at the end of the quarter mile? Ans. Kf = ½ mv2 = 2.07x106 J c) How much work is performed on the Corvette during this trial? Ans. Wnet = K = Kf - Ko = 2.07x106 J d) What is the average net power in (W or J/s) g ...
Ph211_CH7_worksheet-f06
... a) What is the KE at the start of the trial, v = 0 mph? Ans. Ko = 0 J b) What is the KE at the end of the quarter mile? Ans. Kf = ½ mv2 = 2.07x106 J c) How much work is performed on the Corvette during this trial? Ans. Wnet = K = Kf - Ko = 2.07x106 J d) What is the average net power in (W or J/s) g ...
... a) What is the KE at the start of the trial, v = 0 mph? Ans. Ko = 0 J b) What is the KE at the end of the quarter mile? Ans. Kf = ½ mv2 = 2.07x106 J c) How much work is performed on the Corvette during this trial? Ans. Wnet = K = Kf - Ko = 2.07x106 J d) What is the average net power in (W or J/s) g ...
Pearson Physics Level 20 Unit II Dynamics
... action force: a force initiated by object A on object B apparent weight: the negative of the normal force acting on an object coefficient of friction: proportionality constant relating the magnitude of the force of friction to the magnitude of the normal force field: a three-dimensional region of in ...
... action force: a force initiated by object A on object B apparent weight: the negative of the normal force acting on an object coefficient of friction: proportionality constant relating the magnitude of the force of friction to the magnitude of the normal force field: a three-dimensional region of in ...