Experimental Investigations in Introductory Physics
... This reliance on observation distinguishes the natural sciences from such areas as metaphysics and astrology. However, the natural sciences also are in contrast to the discipline of mathematics. A mathematical system or theory can be created and it need only be self-consistent. This is, of course, n ...
... This reliance on observation distinguishes the natural sciences from such areas as metaphysics and astrology. However, the natural sciences also are in contrast to the discipline of mathematics. A mathematical system or theory can be created and it need only be self-consistent. This is, of course, n ...
Document
... slide the crate up along a board. If the crate has a mass of 50 kg and the board is at a 30º incline, what is the maximum force she must apply parallel to the board to move the crate at constant velocity into her truck if the coefficient of friction is .25? ...
... slide the crate up along a board. If the crate has a mass of 50 kg and the board is at a 30º incline, what is the maximum force she must apply parallel to the board to move the crate at constant velocity into her truck if the coefficient of friction is .25? ...
A ubiquitous lowvelocity layer at the base of the mantle transition zone
... and ocean stacks. We also calculated the Pds amplitudes for the 410 and 660 in the IASP91 model. The absolute amplitudes in the global stacks may be suppressed by diverse factors, such as scattering caused by the 3-D Earth heterogeneity, topography and sharpness of the discontinuities, and poor data ...
... and ocean stacks. We also calculated the Pds amplitudes for the 410 and 660 in the IASP91 model. The absolute amplitudes in the global stacks may be suppressed by diverse factors, such as scattering caused by the 3-D Earth heterogeneity, topography and sharpness of the discontinuities, and poor data ...
Physics 3
... 6. A small sphere of mass m is dropped from a great height. After it has fallen 100 m, it has attained its terminal velocity and continues to fall at that speed. The work done by air friction against the sphere during the first 100 m of fall is . [MP PMT 1990] Greater than the work done by air fric ...
... 6. A small sphere of mass m is dropped from a great height. After it has fallen 100 m, it has attained its terminal velocity and continues to fall at that speed. The work done by air friction against the sphere during the first 100 m of fall is . [MP PMT 1990] Greater than the work done by air fric ...
66 3.1 Newton`s Second Law 3.2 Gravity 3.3 The Third Law of
... Mass and Acceleration If you throw a softball and a baseball as hard as you can, why don’t they have the same speed? The difference is due to their masses. A softball has a mass of about 0.20 kg, but a baseball’s mass is about 0.14 kg. The softball has less velocity after it leaves your hand than th ...
... Mass and Acceleration If you throw a softball and a baseball as hard as you can, why don’t they have the same speed? The difference is due to their masses. A softball has a mass of about 0.20 kg, but a baseball’s mass is about 0.14 kg. The softball has less velocity after it leaves your hand than th ...
L 5: F
... Mount the detector so it does not see much of the table or apparatus on the table. Think about where to mount it. The motion detector switch should be on broad beam. 2. Open the experiment file called L05.A2-1 Falling Ball. This experiment file will also set the data collection to a faster rate than ...
... Mount the detector so it does not see much of the table or apparatus on the table. Think about where to mount it. The motion detector switch should be on broad beam. 2. Open the experiment file called L05.A2-1 Falling Ball. This experiment file will also set the data collection to a faster rate than ...
ODU-Mechanics-Questions
... (i) Draw a diagram showing all the forces acting on the rocket just after take-off. (ii) Calculate the initial acceleration of the rocket. (b) As the rocket rises the thrust remains constant but the acceleration of the rocket increases. Give three reasons for this increase in acceleration. (c) Expla ...
... (i) Draw a diagram showing all the forces acting on the rocket just after take-off. (ii) Calculate the initial acceleration of the rocket. (b) As the rocket rises the thrust remains constant but the acceleration of the rocket increases. Give three reasons for this increase in acceleration. (c) Expla ...
Uniform Circular Motion PP
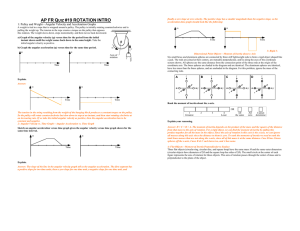
... Vertical Circular Motion – Top of Circle • You can see from the equation that the normal force is now the centripetal force minus your weight. If the centripetal force were equal to your weight, you would feel as though you were weightless. Note that this is also the point where the normal force is ...
... Vertical Circular Motion – Top of Circle • You can see from the equation that the normal force is now the centripetal force minus your weight. If the centripetal force were equal to your weight, you would feel as though you were weightless. Note that this is also the point where the normal force is ...
Chapter 24 Physical Pendulum
... expression for the period is no longer valid. We shall calculate the first-order (or higherorder) correction to the period of the pendulum. Let’s first consider the mechanical energy, a conserved quantity in this system. Choose an initial state when the pendulum is released from rest at an angle θ i ...
... expression for the period is no longer valid. We shall calculate the first-order (or higherorder) correction to the period of the pendulum. Let’s first consider the mechanical energy, a conserved quantity in this system. Choose an initial state when the pendulum is released from rest at an angle θ i ...
FE7
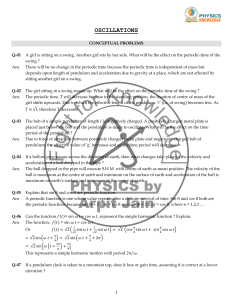
... When non-conservative forces are present, an oscillation can die out unless energy is continually supplied to the system by a driving force. An oscillation which is kept going by a periodic driving force is called a forced oscillation. An example is a car engine. If the driving force is sinusoidal ( ...
... When non-conservative forces are present, an oscillation can die out unless energy is continually supplied to the system by a driving force. An oscillation which is kept going by a periodic driving force is called a forced oscillation. An example is a car engine. If the driving force is sinusoidal ( ...
- Physics Knowledge
... depends upon length of pendulum and acceleration due to gravity at a place, which are not affected by sitting another girl on a swing. The girl sitting in a swing stands up. What will be the effect on the periodic time of the swing ? The periodic time, T will decrease because in the standing positio ...
... depends upon length of pendulum and acceleration due to gravity at a place, which are not affected by sitting another girl on a swing. The girl sitting in a swing stands up. What will be the effect on the periodic time of the swing ? The periodic time, T will decrease because in the standing positio ...
Mechanical Concepts
... than to change speed, but several forces are applied in succession, each succeeding force must be applied at the point when the preceding one has made, its greatest contribution in the imparting of velocity. Applications: a) Once the race car driver has started motion it takes force to maintain spee ...
... than to change speed, but several forces are applied in succession, each succeeding force must be applied at the point when the preceding one has made, its greatest contribution in the imparting of velocity. Applications: a) Once the race car driver has started motion it takes force to maintain spee ...
College Physics, 2e (Knight)
... Newton's First Law, you will move in a straight line until acted on by an outside force - thus, you move in a straight line while the car turns (at least until you run into the door. At this time, the car exerts a force on you, causing your direction of motion to change.). Var: 1 7) Explain, from a ...
... Newton's First Law, you will move in a straight line until acted on by an outside force - thus, you move in a straight line while the car turns (at least until you run into the door. At this time, the car exerts a force on you, causing your direction of motion to change.). Var: 1 7) Explain, from a ...
4. Analysis of Standing Vertical Jumps Using a
... You might wish to enlarge the graph by changing the ranges of the time and force axes. Suggested ranges are 0.00 to 3.00 seconds, and 0 to 2000 N. Select the end value of the time axis (should be 5.00) by clicking with the mouse. Type in the new end value (3.00), then press the Enter key. Repeat for ...
... You might wish to enlarge the graph by changing the ranges of the time and force axes. Suggested ranges are 0.00 to 3.00 seconds, and 0 to 2000 N. Select the end value of the time axis (should be 5.00) by clicking with the mouse. Type in the new end value (3.00), then press the Enter key. Repeat for ...