Key Learning(s) - East Pennsboro Area School District
... mathematical product of the Force acting on the rotating object and the distance away from the axis of rotation that the force is acting ...
... mathematical product of the Force acting on the rotating object and the distance away from the axis of rotation that the force is acting ...
Ch6 - Force and Motion-II
... What if the string breaks? • If the string breaks, no net force acts on the ball, so it obeys Newton’s first law and moves in a straight line. ...
... What if the string breaks? • If the string breaks, no net force acts on the ball, so it obeys Newton’s first law and moves in a straight line. ...
Cable Noise Analysis and Suppression in DAS
... period. In each seismic trace, wavelet extraction includes the following: finding the wavelet in each period, calculating these wavelets to normalize wavelets, and then stacking all wavelets to an average wavelet. The Cable noise attenuation law is dependent on optical fiber materials and length. Ac ...
... period. In each seismic trace, wavelet extraction includes the following: finding the wavelet in each period, calculating these wavelets to normalize wavelets, and then stacking all wavelets to an average wavelet. The Cable noise attenuation law is dependent on optical fiber materials and length. Ac ...
C04 The Laws of Motion (Concept)
... C) The string pulling downward on the ceiling with an 8.0 N force. D) The toy pulling upward on the Earth with an 8.0 N force. ...
... C) The string pulling downward on the ceiling with an 8.0 N force. D) The toy pulling upward on the Earth with an 8.0 N force. ...
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Shahrood University of
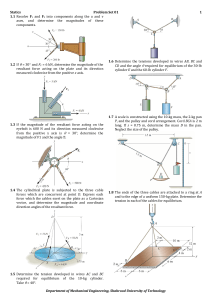
... 2.3 A vertical force of F = 60 N is applied to the handle of the pipe wrench. Determine the moment that this force exerts along the axis AB (x axis) of the pipe assembly. Both the wrench and pipe assembly ABC lie in the plane. Suggestion: Use a scalar analysis. 2.7 Handle forces F1 and F2 are applie ...
... 2.3 A vertical force of F = 60 N is applied to the handle of the pipe wrench. Determine the moment that this force exerts along the axis AB (x axis) of the pipe assembly. Both the wrench and pipe assembly ABC lie in the plane. Suggestion: Use a scalar analysis. 2.7 Handle forces F1 and F2 are applie ...
Systems of Particles - University of Central Florida
... Two blocks of masses M and 3M are placed on a horizontal, frictionless surface. A light spring is attached to one of them, and the blocks are pushed together with the spring between them. A cord initially holding the blocks together is burned; after this, the block of mass 3M moves to the right wit ...
... Two blocks of masses M and 3M are placed on a horizontal, frictionless surface. A light spring is attached to one of them, and the blocks are pushed together with the spring between them. A cord initially holding the blocks together is burned; after this, the block of mass 3M moves to the right wit ...
AP free response for last week
... that the electric potential is zero at x = infinity, with the origin 0 of the x-axis at the center of the ring. a. What is the electric potential at a point P on the x-axis? b. Where along the x-axis is the electric potential the greatest? Justify your answer. c. What is the magnitude and direction ...
... that the electric potential is zero at x = infinity, with the origin 0 of the x-axis at the center of the ring. a. What is the electric potential at a point P on the x-axis? b. Where along the x-axis is the electric potential the greatest? Justify your answer. c. What is the magnitude and direction ...
SECOND MIDTERM -- REVIEW PROBLEMS
... Given 2 = 20.0°, :K = 0.50, :S = 0.55. The block is launched down the plane with an initial velocity of 2.75 m/s, and its mass is 1.25 kg. Calculate how far the block slides from its starting point before stopping. The plane (if needed) is infinitely long. ...
... Given 2 = 20.0°, :K = 0.50, :S = 0.55. The block is launched down the plane with an initial velocity of 2.75 m/s, and its mass is 1.25 kg. Calculate how far the block slides from its starting point before stopping. The plane (if needed) is infinitely long. ...
shear-wave splitting, new geophysics, and earthquake stress
... spaced that they verge on fracturing and hence are criticalsystems (also known as complex-systems). Critical-systems impose fundamentally new properties on conventional subcritical geophysics and hence are a New Geophysics. Earthquake stress-forecasting: Shear-wave splitting above swarms of small ea ...
... spaced that they verge on fracturing and hence are criticalsystems (also known as complex-systems). Critical-systems impose fundamentally new properties on conventional subcritical geophysics and hence are a New Geophysics. Earthquake stress-forecasting: Shear-wave splitting above swarms of small ea ...
Chapter 2: Seismology (part B)
... Figure 2.46 shows that rays which sample the inner core in the equatorial plane of the Earth (ie sources and receivers near the equator) travel with "normal" travel times but rays which travel parallel to the rotation axis (e.g. South Sandwich Islands to a station at College, Alaska) have a DF phase ...
... Figure 2.46 shows that rays which sample the inner core in the equatorial plane of the Earth (ie sources and receivers near the equator) travel with "normal" travel times but rays which travel parallel to the rotation axis (e.g. South Sandwich Islands to a station at College, Alaska) have a DF phase ...
Static Friction
... Static and Kinetic Friction If you try to slide a heavy box resting on the floor, you may find it difficult to get the box moving. Static friction is the force that is acting against the box. If you apply a light horizontal push that does not move the box, the static friction force is also small and ...
... Static and Kinetic Friction If you try to slide a heavy box resting on the floor, you may find it difficult to get the box moving. Static friction is the force that is acting against the box. If you apply a light horizontal push that does not move the box, the static friction force is also small and ...
Physics I - Rose
... Assess: A small frequency change from the additional mass is reasonable because frequency is inversely proportional to the square root of the mass. ...
... Assess: A small frequency change from the additional mass is reasonable because frequency is inversely proportional to the square root of the mass. ...
Using the Law of Universal Gravitation
... “zero-g” or ”weightlessness.” The shuttle orbits about 400 km above Earth’s surface. At that distance, g = 8.7 m/s2, only slightly less than on Earth’s surface. Thus, Earth’s gravitational force is certainly not zero in the ...
... “zero-g” or ”weightlessness.” The shuttle orbits about 400 km above Earth’s surface. At that distance, g = 8.7 m/s2, only slightly less than on Earth’s surface. Thus, Earth’s gravitational force is certainly not zero in the ...
Physics 106P: Lecture 15 Notes
... Fy T sin 30 0 mg Mg Torques Hint: Choose axis of rotation at support because Fx & Fy are not known ...
... Fy T sin 30 0 mg Mg Torques Hint: Choose axis of rotation at support because Fx & Fy are not known ...
File
... • The force of friction is always parallel to the surface of contact. • The force of kinetic friction is always opposite the direction of the motion. • To determine the direction of the force of static friction, use the principle of equilibrium. For an object in equilibrium, the frictional force mus ...
... • The force of friction is always parallel to the surface of contact. • The force of kinetic friction is always opposite the direction of the motion. • To determine the direction of the force of static friction, use the principle of equilibrium. For an object in equilibrium, the frictional force mus ...