Automatically Building Special Purpose Search Engines with
... – Multiple dependent modalities (words, formatting, layout) – Past & future ...
... – Multiple dependent modalities (words, formatting, layout) – Past & future ...
What is Probability? Patrick Maher August 27, 2010
... Statements of inductive probability are commonly expressed as a conditional. For example, someone may say: “If it rains tomorrow then I will probably stay home.” A more accurate statement of what is meant here would be: the probability that I will stay home tomorrow, given that it rains (and other t ...
... Statements of inductive probability are commonly expressed as a conditional. For example, someone may say: “If it rains tomorrow then I will probably stay home.” A more accurate statement of what is meant here would be: the probability that I will stay home tomorrow, given that it rains (and other t ...
Preprint.
... where {W (t), 0 ≤ t ≤ 1} is a standard Brownian motion. To the best of our knowledge, there is no functional CLT for this general class of heteroscedastic time series. However, for the convenience of the reader we shall recall some existing results for the GARCH(p, q) models below. The typical appro ...
... where {W (t), 0 ≤ t ≤ 1} is a standard Brownian motion. To the best of our knowledge, there is no functional CLT for this general class of heteroscedastic time series. However, for the convenience of the reader we shall recall some existing results for the GARCH(p, q) models below. The typical appro ...
A Bayesian Method for the Induction of Probabilistic Networks from
... system, and that x2 and x3, represent two findings. Given the database, what are the qualitative dependency relationships among the variables? For example, do x1 and x3 influence each other directly, or do they do so only through x2? What is the probability that x3 will be present if x1 is present? ...
... system, and that x2 and x3, represent two findings. Given the database, what are the qualitative dependency relationships among the variables? For example, do x1 and x3 influence each other directly, or do they do so only through x2? What is the probability that x3 will be present if x1 is present? ...
COSC343: Artificial Intelligence
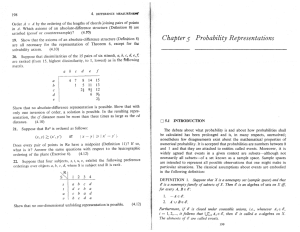
... Basic concepts: sample space, sample points, full joint probability distribution, event, random variable Estimating probabilities from relative frequencies Conditional probability: definition in terms of prior probabilities. The chain rule: rewriting P(a ∧ b . . . ∧ n) as a product involving a prior ...
... Basic concepts: sample space, sample points, full joint probability distribution, event, random variable Estimating probabilities from relative frequencies Conditional probability: definition in terms of prior probabilities. The chain rule: rewriting P(a ∧ b . . . ∧ n) as a product involving a prior ...