Math109 Week 03
... exactly on the basis of the information given. On the other hand, consider the problem faced by the produce manager of the supermarket, who must order enough apples to have on hand each day without knowing exactly how many pounds customer will buy during the day. The customer’s demand is an exam ...
... exactly on the basis of the information given. On the other hand, consider the problem faced by the produce manager of the supermarket, who must order enough apples to have on hand each day without knowing exactly how many pounds customer will buy during the day. The customer’s demand is an exam ...
21-110: Problem Solving in Recreational Mathematics
... Problem 5. (From The Colossal Book of Short Puzzles and Problems by Martin Gardner.) Bill, a student in mathematics, and his friend John, an English major, usually spun a coin on the bar to see who would pay for each round of beer. One evening Bill said: “Since I’ve won the last three spins, let me ...
... Problem 5. (From The Colossal Book of Short Puzzles and Problems by Martin Gardner.) Bill, a student in mathematics, and his friend John, an English major, usually spun a coin on the bar to see who would pay for each round of beer. One evening Bill said: “Since I’ve won the last three spins, let me ...
Document
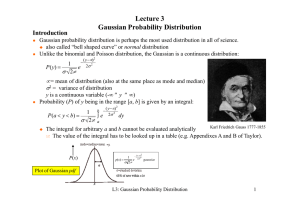
... We call this a "good" fit since the probability is close to 100%. If however the c2 was large (e.g. 15), the probability would be small (≈ 0.2% for 3 dof). We would say this was a “bad” fit. RULE OF THUMB A “good” fit has c2 /dof ≤ 1 ...
... We call this a "good" fit since the probability is close to 100%. If however the c2 was large (e.g. 15), the probability would be small (≈ 0.2% for 3 dof). We would say this was a “bad” fit. RULE OF THUMB A “good” fit has c2 /dof ≤ 1 ...
2.10. Strong law of large numbers If Xn are i.i.d with finite mean, then
... Let A = {ω : G ω has an infinite connected component}. If there is an infinite component, changing X e for finitely many e cannot destroy it. Conversely, if there was no infinite cluster to start with, changing X e for finitely many e cannot create one. In other words, A is a tail event for the coll ...
... Let A = {ω : G ω has an infinite connected component}. If there is an infinite component, changing X e for finitely many e cannot destroy it. Conversely, if there was no infinite cluster to start with, changing X e for finitely many e cannot create one. In other words, A is a tail event for the coll ...
A and B
... First a definition . . . When thinking about what happens with combinations of outcomes, things are simplified if the individual trials are independent. Roughly speaking, this means that the outcome of one trial doesn’t influence or change the outcome of another. For example, coin flips are in ...
... First a definition . . . When thinking about what happens with combinations of outcomes, things are simplified if the individual trials are independent. Roughly speaking, this means that the outcome of one trial doesn’t influence or change the outcome of another. For example, coin flips are in ...
Chapters 12 and 13 - class notes
... boys. For example, GGB means the first two children are girls and the third child is a boy. All 8 arrangements are (approximately) equally likely. (a) Write down all 8 arrangements of the sexes of three children. What is the probability of any one of these arrangements? (b) Let X be the number of gi ...
... boys. For example, GGB means the first two children are girls and the third child is a boy. All 8 arrangements are (approximately) equally likely. (a) Write down all 8 arrangements of the sexes of three children. What is the probability of any one of these arrangements? (b) Let X be the number of gi ...
Chapter 8
... Discrete probability distribution. The variable can take on only certain values (usually whole numbers). Continuous probability distribution. The variable can take on an infinite number of values (dependent on the precision of the measuring tool). ...
... Discrete probability distribution. The variable can take on only certain values (usually whole numbers). Continuous probability distribution. The variable can take on an infinite number of values (dependent on the precision of the measuring tool). ...