Carsten Held, PPT
... and thus incomplete without some version of the projection postulate: • A5 If S is found to have value ak of A as a result of an A measurement, then S’s state is Pak immediately after this measurement. This objection is irrelevant. The below arguments explicitly refer to A4 only and will go through ...
... and thus incomplete without some version of the projection postulate: • A5 If S is found to have value ak of A as a result of an A measurement, then S’s state is Pak immediately after this measurement. This objection is irrelevant. The below arguments explicitly refer to A4 only and will go through ...
CHAPTER 1 PROBABILITY Probability:
... convictions and experience concerning the likelihood of occurrence of a random event. It is a way to quantify an individual‟s beliefs, assessment and judgement about a random phenomenon. Probability assigned for the occurrence of an event may be based on just guess or on having some idea about the r ...
... convictions and experience concerning the likelihood of occurrence of a random event. It is a way to quantify an individual‟s beliefs, assessment and judgement about a random phenomenon. Probability assigned for the occurrence of an event may be based on just guess or on having some idea about the r ...
Chapter 6
... 11, 2006) included results from a survey of adults aged 18 to 50. The accompanying data are consistent with summary values given in the article. ...
... 11, 2006) included results from a survey of adults aged 18 to 50. The accompanying data are consistent with summary values given in the article. ...
251y0244
... g. Use the same method to find the complete conditional probability of x for long term residents, show that this is a valid distribution and compute the conditional mean for long-term residents. (5.5) h. If you are ready for some real thinking, find the conditional mean for short-term residents and ...
... g. Use the same method to find the complete conditional probability of x for long term residents, show that this is a valid distribution and compute the conditional mean for long-term residents. (5.5) h. If you are ready for some real thinking, find the conditional mean for short-term residents and ...
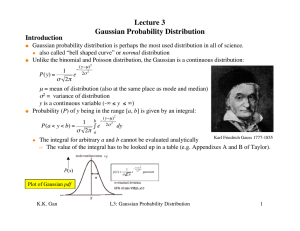
Lecture 3 Gaussian Probability Distribution Introduction
... n sm is sometimes called “the error in the mean” (more on that later). l For CLT to be valid: u m and s of pdf must be finite. †u No one term in sum should dominate the sum. l A random variable is not the same as a random number. u Devore: Probability and Statistics for Engineering and the Sciences: ...
... n sm is sometimes called “the error in the mean” (more on that later). l For CLT to be valid: u m and s of pdf must be finite. †u No one term in sum should dominate the sum. l A random variable is not the same as a random number. u Devore: Probability and Statistics for Engineering and the Sciences: ...