INTERPLAY BETWEEN STRUCTURAL AND ELECTRONIC PROPERTIES OF CARBON NANOTUBES
... level, indicated that the achiral “armchair” (n, n) nanotubes 9 should be metallic, whereas all (n, m) tubes, with n − m a nonzero multiple of three, should be small gap semiconductors or semimetals 7 . Nanotubes not fitting in either category should be semiconducting, with a band gap roughly proport ...
... level, indicated that the achiral “armchair” (n, n) nanotubes 9 should be metallic, whereas all (n, m) tubes, with n − m a nonzero multiple of three, should be small gap semiconductors or semimetals 7 . Nanotubes not fitting in either category should be semiconducting, with a band gap roughly proport ...
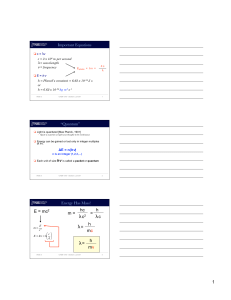
dual-valent
... the individual effect of the just mentioned ruling parameters may reveal more insight into the ordering phenomena. ...
... the individual effect of the just mentioned ruling parameters may reveal more insight into the ordering phenomena. ...
Lecture 1: Crystal structure
... – Translational symmetry, i.e. The crystal appears identical at several equivalent regions defined by a basic periodicity ...
... – Translational symmetry, i.e. The crystal appears identical at several equivalent regions defined by a basic periodicity ...
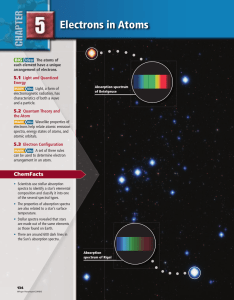
Ionization due to the interaction between two Rydberg atoms
... Since there are only four particles, we do not need to use an asymptotic or multipole expansion to compute the forces between the particles. Only the hydrogen atom has a pure Coulomb interaction. For quantum calculations, there is a well-defined prescription for including the core electrons in the c ...
... Since there are only four particles, we do not need to use an asymptotic or multipole expansion to compute the forces between the particles. Only the hydrogen atom has a pure Coulomb interaction. For quantum calculations, there is a well-defined prescription for including the core electrons in the c ...
Scheme for a coherently controlled pulsed electron gun F. Robicheaux
... Recent work has focused on the study of the timedependent electron emission of highly excited alkali atoms in a strong electric field using experimental1–3 and theoretical4,5 tools. The measurements on these Rydberg atoms were performed by monitoring the time-dependent flux of electrons that are nat ...
... Recent work has focused on the study of the timedependent electron emission of highly excited alkali atoms in a strong electric field using experimental1–3 and theoretical4,5 tools. The measurements on these Rydberg atoms were performed by monitoring the time-dependent flux of electrons that are nat ...
Relativistic theory of one– and two electron systems: valley of
... done just after 1913. But, these relativistic corrections have been done only in the year 1916 by Sommerfeld (in the framework of the elliptical orbits model) and after in the year 1926 by use of the relativistic wave equation established by Dirac after the discovery of the spin electron (1925) by U ...
... done just after 1913. But, these relativistic corrections have been done only in the year 1916 by Sommerfeld (in the framework of the elliptical orbits model) and after in the year 1926 by use of the relativistic wave equation established by Dirac after the discovery of the spin electron (1925) by U ...
abstract.
... gedanken experiment illustrated in Fig.2. A hydrogen atom possesses an electron whose wave function at t=0 is supposed to be a linear combination of 1s and 2p x. The whole atom is placed at the centre of an electric ring situated within the plane xy. The ring is electrically charged, the total charg ...
... gedanken experiment illustrated in Fig.2. A hydrogen atom possesses an electron whose wave function at t=0 is supposed to be a linear combination of 1s and 2p x. The whole atom is placed at the centre of an electric ring situated within the plane xy. The ring is electrically charged, the total charg ...
Modern Methods in Drug Discovery
... As a simplification the wave function of all electrons in a molecule is assumed to be the product of one-electron functions which themselves describe a single electron. ...
... As a simplification the wave function of all electrons in a molecule is assumed to be the product of one-electron functions which themselves describe a single electron. ...
Lecture Notes: Condensed Matter Theory I (TKM1)
... Condensed matter physics is concerned with the behavior of large aggregates of atoms or molecules in liquid or solid form. It is one of the largest branches of physics, with a wide variety of di¤erent systems, approaches, challenges and concepts. Often, it is subdivided in soft condensed matter phys ...
... Condensed matter physics is concerned with the behavior of large aggregates of atoms or molecules in liquid or solid form. It is one of the largest branches of physics, with a wide variety of di¤erent systems, approaches, challenges and concepts. Often, it is subdivided in soft condensed matter phys ...
Section 1.5 - 1 1.5 The Vector Model of the Atom Classical Physics: If
... Meaning: A single electron in an orbital can have slightly different energies depending on its particular l & s combination. The orbital angular momentum and the spin angular momentum vectors can either “reinforce” or “oppose” each other. ...
... Meaning: A single electron in an orbital can have slightly different energies depending on its particular l & s combination. The orbital angular momentum and the spin angular momentum vectors can either “reinforce” or “oppose” each other. ...