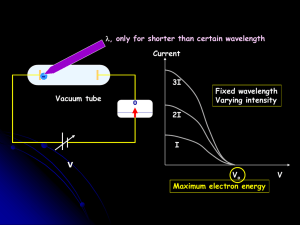
Document
... from Niels Bohr who explained experimentally observed discrete nature of atomic spectrum of Hydrogen. In spite of its immediate success in providing theoretical account of the spectrum and other nature of Hydrogen atom, a complete understanding of Bohr’s atom came only after de Broglie’s conjecture ...
... from Niels Bohr who explained experimentally observed discrete nature of atomic spectrum of Hydrogen. In spite of its immediate success in providing theoretical account of the spectrum and other nature of Hydrogen atom, a complete understanding of Bohr’s atom came only after de Broglie’s conjecture ...
QUANTUM MECHANICAL MODEL OF THE ATOM
... • Quantum mechanics is a theoretical science that deals with the study of the motions of the microscopic objects that have both observable wave like and particle like properties. • Quantum mechanics is based on a fundamental equation which is called Schrodinger equation. • Schrodinger’s equation: Fo ...
... • Quantum mechanics is a theoretical science that deals with the study of the motions of the microscopic objects that have both observable wave like and particle like properties. • Quantum mechanics is based on a fundamental equation which is called Schrodinger equation. • Schrodinger’s equation: Fo ...
Chemistry - Isotopes
... Planck’s ____________ theory attributed to light a ______________ nature, in addition to its wave nature. Louis de Broglie then turned this around and suggested that particles also exhibit some of the characteristics of ____________. These two ideas together are referred to as the _________-________ ...
... Planck’s ____________ theory attributed to light a ______________ nature, in addition to its wave nature. Louis de Broglie then turned this around and suggested that particles also exhibit some of the characteristics of ____________. These two ideas together are referred to as the _________-________ ...
Nuclear and Particle Physics
... α deflected less than β ⇒ α must have larger mass γ not deflected ⇒ uncharged ...
... α deflected less than β ⇒ α must have larger mass γ not deflected ⇒ uncharged ...
Quantum Numbers - Evan`s Chemistry Corner
... o ℓ =0 is called s o ℓ =1 is called p o ℓ =2 is called d o ℓ =3 is called f o For ℓ >3, the sublevels are named alphabetically, (g, h, and i), but there are no atoms with electrons in these locations. ...
... o ℓ =0 is called s o ℓ =1 is called p o ℓ =2 is called d o ℓ =3 is called f o For ℓ >3, the sublevels are named alphabetically, (g, h, and i), but there are no atoms with electrons in these locations. ...
Optical Response in Infinite Dimensions
... • Small non-zero t¿ U broadens the atomic levels into Hubbard sub-bands • Further increasing t, decreases the band gap and continuously closes the gap (Second order MIT) ...
... • Small non-zero t¿ U broadens the atomic levels into Hubbard sub-bands • Further increasing t, decreases the band gap and continuously closes the gap (Second order MIT) ...
Bohr model and electron configuration
... Energy is quantized. It comes in chunks. A quantum is the amount of energy needed to move from one energy level to another. Since the energy of an atom is never “in between” there must be a quantum leap in energy. Schrödinger derived an equation that described the energy and position of the elec ...
... Energy is quantized. It comes in chunks. A quantum is the amount of energy needed to move from one energy level to another. Since the energy of an atom is never “in between” there must be a quantum leap in energy. Schrödinger derived an equation that described the energy and position of the elec ...
AtomLightEmissQuantum
... waves The number of photons in a beam controls the brightness. The frequency of the light controls the energy of individual photons ...
... waves The number of photons in a beam controls the brightness. The frequency of the light controls the energy of individual photons ...