2. Semiconductor Physics 2.1 Basic Band Theory
... We have the number of energy states for a given energy interval and want to know how many (charge)carriers we will find in the same energy interval in thermal equilibrium. Since we want to look at particles other than electrons too, but only at charged particles, we use the term "carrier" here. In o ...
... We have the number of energy states for a given energy interval and want to know how many (charge)carriers we will find in the same energy interval in thermal equilibrium. Since we want to look at particles other than electrons too, but only at charged particles, we use the term "carrier" here. In o ...
Chemical Physics High-spin-low-spin transitions in Fe(II) complexes
... field itself changes when an electron is removed from the system or added to it. The difference between the negative orbital energy which must be the ionization potential according to Koopmans' theorem and the real ionization potential is called the orbital relaxation energy. Usually for organic mol ...
... field itself changes when an electron is removed from the system or added to it. The difference between the negative orbital energy which must be the ionization potential according to Koopmans' theorem and the real ionization potential is called the orbital relaxation energy. Usually for organic mol ...
Chemistry Lesson Plans #12
... There are 3 kinds of p orbitals, which have different orientations in space (x, y &z) o d orbitals are more like two sets of dumbbells at right angles to each other o f orbitals are too complex to visualize The p and d orbitals taper as they approach the nucleus, indicating areas where electrons hav ...
... There are 3 kinds of p orbitals, which have different orientations in space (x, y &z) o d orbitals are more like two sets of dumbbells at right angles to each other o f orbitals are too complex to visualize The p and d orbitals taper as they approach the nucleus, indicating areas where electrons hav ...
May 2004
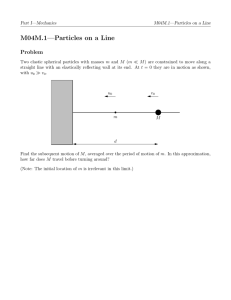
... A beam of particles of mass m and energy E propagates along the z axis of a coordinate system, and scatters from the cubic potential ...
... A beam of particles of mass m and energy E propagates along the z axis of a coordinate system, and scatters from the cubic potential ...
Atomic Theory Notes Packet
... ________________ a. Which color of light contains the greatest amount of energy? ________________ b. The least amount of energy? ________________ c. To which energy level did all the excited electrons return to? ________________ d. An electron absorbs a specific amount of energy, called a ___, when ...
... ________________ a. Which color of light contains the greatest amount of energy? ________________ b. The least amount of energy? ________________ c. To which energy level did all the excited electrons return to? ________________ d. An electron absorbs a specific amount of energy, called a ___, when ...
20040929114512301
... – Decoherence is an interesting problem: heating rates of seconds gives loads of time for gates. – Quantum memories are harder to realize: few qubit applications? ...
... – Decoherence is an interesting problem: heating rates of seconds gives loads of time for gates. – Quantum memories are harder to realize: few qubit applications? ...
File
... electrons of helium occupy the first energy level of the atom. The letter "s" stands for the angular momentum quantum number "l". It tells us that the two electrons of the helium electron occupy an "s" or spherical orbital. The exponent "2" refers to the total number of electrons in that orbital ...
... electrons of helium occupy the first energy level of the atom. The letter "s" stands for the angular momentum quantum number "l". It tells us that the two electrons of the helium electron occupy an "s" or spherical orbital. The exponent "2" refers to the total number of electrons in that orbital ...
Atomic Structure and Atomic Spectra
... The solution of Schrodinger's equation for the problem of the H-atom is far too involved to reproduce here (see references). Indeed Bohr's relation for the electronic energy levels in the hydrogen atom is a result of that solution. However, such a full quantum mechanical treatment also results in tw ...
... The solution of Schrodinger's equation for the problem of the H-atom is far too involved to reproduce here (see references). Indeed Bohr's relation for the electronic energy levels in the hydrogen atom is a result of that solution. However, such a full quantum mechanical treatment also results in tw ...
Review II
... A. Two bonded nonmetals share electrons such that both get an octet (duet) B. Both species get "credit" for all electrons in bond C. Two species can share two, four, or six electrons 1. Two electrons shared is a single bond 2. Four electrons shared is a double bond 3. Six electrons shared is a tripl ...
... A. Two bonded nonmetals share electrons such that both get an octet (duet) B. Both species get "credit" for all electrons in bond C. Two species can share two, four, or six electrons 1. Two electrons shared is a single bond 2. Four electrons shared is a double bond 3. Six electrons shared is a tripl ...
Chem700 MO
... also known as the self consistent field (SCF) equations, since each orbital depends on all the other orbitals, and they are adjusted until they are all converged calculating all two electron integrals is a major bottleneck, because they are difficult (6 dimensional integrals) and very numerous (form ...
... also known as the self consistent field (SCF) equations, since each orbital depends on all the other orbitals, and they are adjusted until they are all converged calculating all two electron integrals is a major bottleneck, because they are difficult (6 dimensional integrals) and very numerous (form ...
The energy
... • Only the size of the orbit was important, which was described by the n quantum number. ...
... • Only the size of the orbit was important, which was described by the n quantum number. ...
An implementation of atomic form factors - IGFAE
... is known as the first Born approximation [1–3]. The response of the hydrogen-like atom to a definite momentum of the exchanged photon is given by the Fourier transform of its charge density, known as the atomic form factor. The hydrogen-like form factors have been studied in the framework of hydroge ...
... is known as the first Born approximation [1–3]. The response of the hydrogen-like atom to a definite momentum of the exchanged photon is given by the Fourier transform of its charge density, known as the atomic form factor. The hydrogen-like form factors have been studied in the framework of hydroge ...
Chapter 7. Atomic Physics
... The structure of atoms and that of the periodic table can be explained with this principle and the further assumption that atomic electrons tend to occupy the lowest available energy states. To see how this works, let us consider the next simplest atom after hydrogen, i.e., helium. The helium atom ...
... The structure of atoms and that of the periodic table can be explained with this principle and the further assumption that atomic electrons tend to occupy the lowest available energy states. To see how this works, let us consider the next simplest atom after hydrogen, i.e., helium. The helium atom ...
Atomic Physics
... The structure of atoms and that of the periodic table can be explained with this principle and the further assumption that atomic electrons tend to occupy the lowest available energy states. To see how this works, let us consider the next simplest atom after hydrogen, i.e., helium. The helium atom ...
... The structure of atoms and that of the periodic table can be explained with this principle and the further assumption that atomic electrons tend to occupy the lowest available energy states. To see how this works, let us consider the next simplest atom after hydrogen, i.e., helium. The helium atom ...
Chp.23 Outline - Redlands High School
... How many Joules are in an electron volt? 2) What is a blackbody? As the temperature of a blackbody increases what does classical mechanics predict for the intensity of different wavelengths of EM radiation that are emitted from a blackbody? Draw the actual intensitywavelength curve of a blackbody. H ...
... How many Joules are in an electron volt? 2) What is a blackbody? As the temperature of a blackbody increases what does classical mechanics predict for the intensity of different wavelengths of EM radiation that are emitted from a blackbody? Draw the actual intensitywavelength curve of a blackbody. H ...
Problem set 6
... of each Fourier component of a matter wave ψ(x, t) was given by ei(kx−ω(k)t) corresponding to a right moving wave if k, ω(k) were of the same sign. We could equally well have considered the time evolution ei(kx+ω(k)t) . We do this here. Write down an expression for φ(x, t) for this ‘left moving’ wav ...
... of each Fourier component of a matter wave ψ(x, t) was given by ei(kx−ω(k)t) corresponding to a right moving wave if k, ω(k) were of the same sign. We could equally well have considered the time evolution ei(kx+ω(k)t) . We do this here. Write down an expression for φ(x, t) for this ‘left moving’ wav ...