QUANTUM CHEMISTRY AND GROUP THEORY(2) M.Sc. DEGREE
... be expressed as Ψ (x, y, z, t) for a particle in 3D box. The probability of finding a particle in the volume element dτ is Ψ *(x, y, z, t) Ψ (x, y, z, t) dτ at time t. The wave function must satisfy certain mathematical conditions because of this probabilistic interpretation. For the case of a singl ...
... be expressed as Ψ (x, y, z, t) for a particle in 3D box. The probability of finding a particle in the volume element dτ is Ψ *(x, y, z, t) Ψ (x, y, z, t) dτ at time t. The wave function must satisfy certain mathematical conditions because of this probabilistic interpretation. For the case of a singl ...
The variational principle and simple properties of the ground
... particular, it is shown that the ground-state wave function can be taken to be real and non-negative, and that it cannot be degenerate. Other consequences for the angular momentum and the parity of the ground state are also presented. There is a vast literature on the properties of the groundstate w ...
... particular, it is shown that the ground-state wave function can be taken to be real and non-negative, and that it cannot be degenerate. Other consequences for the angular momentum and the parity of the ground state are also presented. There is a vast literature on the properties of the groundstate w ...
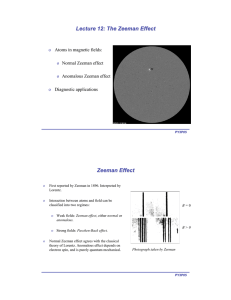
o Atoms in magnetic fields: Normal Zeeman effect Anomalous Zeeman effect
... In the case of precessing atomic magnetic in figure on last slide, neither Sz nor Lz are constant. ...
... In the case of precessing atomic magnetic in figure on last slide, neither Sz nor Lz are constant. ...
QUANTUM NUMBERS
... these diagrams indicate which orbital energy levels are occupied by electrons for an atom or ion In fig.2 on p. 187, as atoms become larger & the main energy levels come closer, some sublevels may overlap Generally the sublevels for a particular value of n, increase in energy in the order of s ...
... these diagrams indicate which orbital energy levels are occupied by electrons for an atom or ion In fig.2 on p. 187, as atoms become larger & the main energy levels come closer, some sublevels may overlap Generally the sublevels for a particular value of n, increase in energy in the order of s ...
what is wave function?
... the atom because it does not have sufficient energy If the electron is treated as a wave and applying Schrodinger equation, its wave function ...
... the atom because it does not have sufficient energy If the electron is treated as a wave and applying Schrodinger equation, its wave function ...
Slide 1
... concluded that electrons have specific energy levels. • Erwin Schrödinger (1887–1961): Proposed quantum mechanical model of atom, which focuses on wavelike properties of electrons. ...
... concluded that electrons have specific energy levels. • Erwin Schrödinger (1887–1961): Proposed quantum mechanical model of atom, which focuses on wavelike properties of electrons. ...
Electron Notes
... • quanta - amount of energy needed to move from one energy level to another. • Since energy of an atom is never “in between” there must be a quantum leap in energy. ...
... • quanta - amount of energy needed to move from one energy level to another. • Since energy of an atom is never “in between” there must be a quantum leap in energy. ...
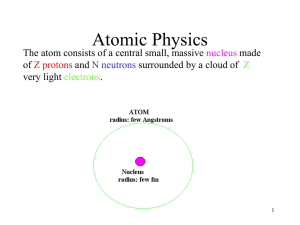
Atomic Physics
... protons and neutrons with electrons in orbits about the nucleus. The neutron has no charge and the number of protons and electrons are the same so that the atom has no net charge. The diameter of the nucleus is much smaller than the diameter of the atom, but the nucleus contains most of the mass of ...
... protons and neutrons with electrons in orbits about the nucleus. The neutron has no charge and the number of protons and electrons are the same so that the atom has no net charge. The diameter of the nucleus is much smaller than the diameter of the atom, but the nucleus contains most of the mass of ...
COMPCHEM1_2011
... • The maximum energy configuration along the reaction path is called the transition state – energy curves downwards in one direction only – There is one imaginary vibrational frequency, all other vibrational frequencies are real ...
... • The maximum energy configuration along the reaction path is called the transition state – energy curves downwards in one direction only – There is one imaginary vibrational frequency, all other vibrational frequencies are real ...
Electrons as waves
... Electrons as waves • Scientists accepted the fact that light has a dual wave- particle nature. • De Broglie pointed out that in many ways the behavior of the Bohr’s quantized electron orbits was similar to the known behavior of waves. • Electrons should be thought of as having a dual wave-particle n ...
... Electrons as waves • Scientists accepted the fact that light has a dual wave- particle nature. • De Broglie pointed out that in many ways the behavior of the Bohr’s quantized electron orbits was similar to the known behavior of waves. • Electrons should be thought of as having a dual wave-particle n ...
Chapter 5 Mendeleev`s Periodic Table
... hydrogen had a discrete line spectrum rather than a continuous spectrum. • Bohr's basic theory: electrons in atoms can only be at certain energy levels, and they can give off or absorb radiation only when they jump from one level to another. • In his model that an atom consists of an extremely dense ...
... hydrogen had a discrete line spectrum rather than a continuous spectrum. • Bohr's basic theory: electrons in atoms can only be at certain energy levels, and they can give off or absorb radiation only when they jump from one level to another. • In his model that an atom consists of an extremely dense ...
Lecture 1.6 PowerPoint
... • 1.6 – I can characterize an electron based on its 4 quantum numbers (n, l, ml, and ms). I can explain what each of these numbers indicate and discuss the importance of these numbers. • 1.7 – I can describe the shape, number, and energy level of the s, p, d, and f orbitals. Furthermore, I can draw ...
... • 1.6 – I can characterize an electron based on its 4 quantum numbers (n, l, ml, and ms). I can explain what each of these numbers indicate and discuss the importance of these numbers. • 1.7 – I can describe the shape, number, and energy level of the s, p, d, and f orbitals. Furthermore, I can draw ...
PowerPoint - OrgSites.com
... Assigning the Numbers The three quantum numbers (n, l, and m) are integers. The principal quantum number (n) cannot be zero. n must be 1, 2, 3, etc. The angular momentum quantum number (l) can be any integer between 0 and n - 1. For n = 3, l can be either 0, 1, or 2. The magnetic quantu ...
... Assigning the Numbers The three quantum numbers (n, l, and m) are integers. The principal quantum number (n) cannot be zero. n must be 1, 2, 3, etc. The angular momentum quantum number (l) can be any integer between 0 and n - 1. For n = 3, l can be either 0, 1, or 2. The magnetic quantu ...
Chapter 5: Electrons in Atoms
... Calculations show previous models didn’t always correctly describe electron motion ...
... Calculations show previous models didn’t always correctly describe electron motion ...